Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
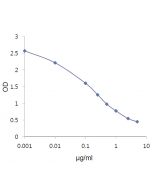
RBP4 (human) ELISA Kit (Quantitative)

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Retinol Binding Protein 4 |
| Product Type | Kit |
| Properties | |
| Application Set | Quantitative ELISA |
| Specificity | Detects human RBP4. Does not cross-react with mouse RBP4, rat RBP4, human adiponectin, human resistin, human vaspin, human leptin or human Nampt. |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Quantity | 1 x 96 wells |
| Sensitivity | 380pg/ml |
| Range | 0.39 to 25ng/ml |
| Sample Type |
Cell Culture Supernatant Plasma Serum Urine |
| Assay Type | Sandwich |
| Detection Type | Colorimetric |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
After standard reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Plate and reagents should reach room temperature before use. |
| Use/Stability | 12 months after the day of manufacturing. See expiry date on ELISA Kit box. |
| Documents | |
| Manual |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4; RBP) is a 21kDa secreted protein, a member of the lipocalin family and is known as the primary transporter of retinol (vitamin A) to tissues. A recent report revealed RBP4 as an adipokine linking glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) suppression in adipose tissue to insulin. Elevated human and mouse serum RBP4 levels are associated with insulin resistance and its severity, obesity and certain components of metabolic syndrome. Furthermore, human serum RBP4 levels are closely related to renal function and recent studies have shown an association between serum RBP4 levels and urinary albumin excretion. The urinary RBP4 concentration may be a valuable marker for both, insulin resistance and microalbuminuria in insulin-resistant subjects.
- Two patterns of adipokine and other biomarker dynamics in a long-term weight loss intervention: M. Blueher, et al.; Diabetes Care 35, 342 (2012)
- The normoglycemic first-degree relatives of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus have low circulating omentin-1 and adiponectin levels: S. Akbarzadeh, et al.; Cytokine 58, 295 (2012)
- Increased plasma levels of retinol-binding protein 4 with visceral obesity is associated with cardiovascular risk factors: J.C. Won, et al.; J. Diabet. Invest. 3, 457 (2012)
- The association of carotid intima media thickness with retinol binding protein-4 and total and high molecular weight adiponectin in type 2 diabetic patients: M. Mansouri, et al.; J. Diabet. Metab. Dis. 11, 2 (2012)
- Effects of a Combined Aerobic and Resistance Exercise Program on C1q/TNF-Related Protein-3 (CTRP-3) and CTRP-5 Levels: H.Y. Choi, et al.; Diabetes Care 36, 3321 (2013)
- Associations between tissue visfatin/nicotinamide, phosphoribosyltransferase (Nampt), retinol binding protein-4, and vaspin concentrations and insulin resistance in morbidly obese subjects: Z. Goktas, et al.; Mediators Inflamm. 2013, 861496 (2013)
- Lack of relationship between cord serum angiopoietin-like protein 4 (ANGPTL4) and lipolytic activity in human neonates born by spontaneous delivery: H. Ortega-Senovilla, et al.; PLoS One 8, e81201 (2013)
- Associations of retinol-binding protein 4 with oxidative stress, inflammatory markers, and metabolic syndrome in a middle-aged and elderly Chinese population: Y. Liu, et al.; Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 6, 25 (2014)
- Identification of adipokine clusters related to parameters of fat mass, insulin sensitivity and inflammation: G. Flehmig, et al.; PLoS One 9, e99785 (2014)
- Amyloid deposition in a mouse model humanized at the transthyretin and retinol-binding protein 4 loci: X. Li, et al.; Lab. Investig. 98, 512 (2018)
- Development of a mouse IgA monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent sandwich assay for the analyses of RBP4: N.S. Lee, et al.; Sci. Rep. 8, 2578 (2018)
- Serum Carotenoids Are Inversely Associated with RBP4 and Other Inflammatory Markers in Middle-Aged and Elderly Adults: L. Jing, et al.; Nutrients 10, 260 (2018)
- Higher serum carotenoids associated with improvement of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adults: a prospective study: ML Xiao, et al.; Eur. J. Nutr. 58, 721 (2019)
- Circulating retinol-binding protein 4 is associated with the development and regression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: X. Wang, et al.; Diabetes Metab. 46, 119 (2020)
- Retinol-binding protein-4 was associated with sensitization to inhalant allergens in the elderly population: B.K. Kim, et al.; Korean J.Intern. Med. 36, 447 (2021)
- RBP4-based Multimarker Score: A Prognostic Tool for Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients: B. Ye, et al.; J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. ahead of print (2023)