Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
Adiponectin (mouse) ELISA Kit

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | ACRP30; AdipoQ; apM1; GBP28; Adipocyte Complement Related Protein of 30kDa |
| Product Type | Kit |
| Properties | |
| Application Set | Quantitative ELISA |
| Specificity | Detects mouse adiponectin. Does not cross-react with human adiponectin, rat adiponectin, mouse resistin, mouse RELM-β or mouse leptin. |
| Crossreactivity | Mouse |
| Quantity |
1 x 96 wells 2 x 96 wells (Twin Plex) |
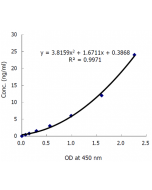
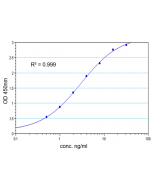
| Sensitivity | 50pg/ml |
| Range | 0.125 to 8ng/ml |
| Sample Type |
Cell Culture Supernatant Plasma Serum |
| Assay Type | Sandwich |
| Detection Type | Colorimetric |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
After standard reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Plate and reagents should reach room temperature before use. |
| Use/Stability | 12 months after the day of manufacturing. See expiry date on ELISA Kit box. |
| Documents | |
| Manual |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Adiponectin [ACRP30; AdipoQ] is a promising biomarker of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) but also as a potential target for management of the metabolic syndrome. It is a very robust marker that is not prone to degradation or acute inflammatory challenges, is present in relatively high concentrations in the peripheral circulation, and can be collected by a variety of methods. The benefits of using adiponectin assays in clinical settings include, (a) prediction of risk of diabetes and metabolic status and (b) providing a tool to monitor metabolic improvements. Adiponectin exerts anti-atherogenic and anti-inflammatory properties and may be important as a biomarker for obesity-related cardiovascular disease (CVD). New findings showed urinary adiponectin excretion as an independent new biomarker of microvascular and macrovascular damage in T2DM and suggested it as a very promising tool for early cardiovascular disease risk assessment. Adiponectin serum level was also described as a good biomarker of colorectal adenoma, this being related to the positive correlation between obesity and increased risk of cancer at various sites (colorectal, breast, prostate and endometrium).
- Chop-deficient mice showed increased adiposity but no glucose intolerance: Y. Ariyama, et al.; Obesity 15, 1647 (2007)
- Overexpression of human adiponectin in transgenic mice results in suppression of fat accumulation and prevention of premature death by highcalorie diet: S. Otabe, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 293, E210 (2007)
- Resveratrol inhibits TNF-α-induced changes of adipokines in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: J. Ahn, et al.; BBRC 364, 972 (2007)
- Transgenic mice expressing nuclear sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c in adipose tissue exhibit liver histology similar to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: H. Nakayama, et al.; Metabolism 56, 470 (2007)
- Anti-diabetic Effects of Compound K versus Metformin versus Compound K-Metformin Combination Therapy in Diabetic db/db Mice: S.H. Yoon, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 30, 2196 (2007)
- Compound K Enhances Insulin Secretion with Beneficial Metabolic Effects in db/db Mice: G.C. Han, et al.; J. Agric. Food Chem. 55, 10641 (2007)
- Expression of Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase substrate-1 in pancreatic beta-Cells and its role in promotion of insulin secretion and protection against diabetes: M. Kobayashi, et al.; Endocrinology 149, 5662 (2008)
- A Vinegar-processed Ginseng Radix (Ginsam) Ameliorates Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia in C57BL/KsJ db/db Mice: E.J. Han, et al.; Food Sci. Biotechnol. 17, 1228 (2008)
- Effects of adiponectin transgenic expression in liver of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis model mice: H. Nakayama, et al.; Metabolism 58, 901 (2009)
- Construction of adiponectin-encoding plasmid DNA and gene therapy of non-obese type 2 diabetes mellitus: M.H. Nan, et al.; J. Drug Target. 18, 67 (2010)
- ER stress in adipocytes inhibits insulin signaling, represses lipolysis, and alters the secretion of adipokines without inhibiting glucose transport: L. Xu, et al.; Horm. Metab. Res. 42, 643 (2010)
- Feeding silk protein hydrolysates to C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice improves blood glucose and lipid profiles: E.Y. Jung, et al.; Nutr. Res. 30, 783 (2010)
- Hyperadiponectinemia enhances bone formation in mice: Y. Mitsui, et al.; BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 12, 18 (2011)
- A promising culture model for analyzing the interaction between adipose tissue and cardiomyocytes: M. Anan, et al.; Endocrinology 152, 1599 (2011)
- Hyperadiponectinemia protects against premature death in metabolic syndrome model mice by inhibiting AKT signaling and chronic inflammation: S. Otabe, et al.; J. Endocrinol. 213, 67 (2012)
- Effects of Combining Linagliptin Treatment with BI-38335, A Novel SGLT2 Inhibitor, on Pancreatic Islet Function and Inflammation in db/db Mice: L. Chen, et al.; Curr. Mol. Med. 12, 995 (2012)
- Chitooligosaccharide ameliorates diet-induced obesity in mice and affects adipose gene expression involved in adipogenesis and inflammation: E.H. Choi, et al.; Nutr. Res. 32, 218 (2012)
- Anti-Hyperglycemic Effect of Fermented Ginseng in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mouse Model: W.J. Jeon, et al.; Phytother. Res. 27, 166 (2013)
- Anthocyanin increases adiponectin secretion and protects against diabetes-related endothelial dysfunction: Y. Liu, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 306, E975 (2014)
- Relation of circulating adiponectin level with epicardial adipose tissue thickness among overweight and obese indian patients: A cross sectional study: A.M. Chakraborty, et al.; Acta Sci. Med. Sci. 4, (2020)
- Myeloid Cell–Specific IL-4 Receptor Knockout Partially Protects from Adipose Tissue Inflammation: J. Ackermann, et al.; J. Immunol. 207, 3081 (2021)