Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
Linagliptin
As low as
55
CHF
CHF 55.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3618-M01010 mgCHF 55.00
AG-CR1-3618-M05050 mgCHF 120.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
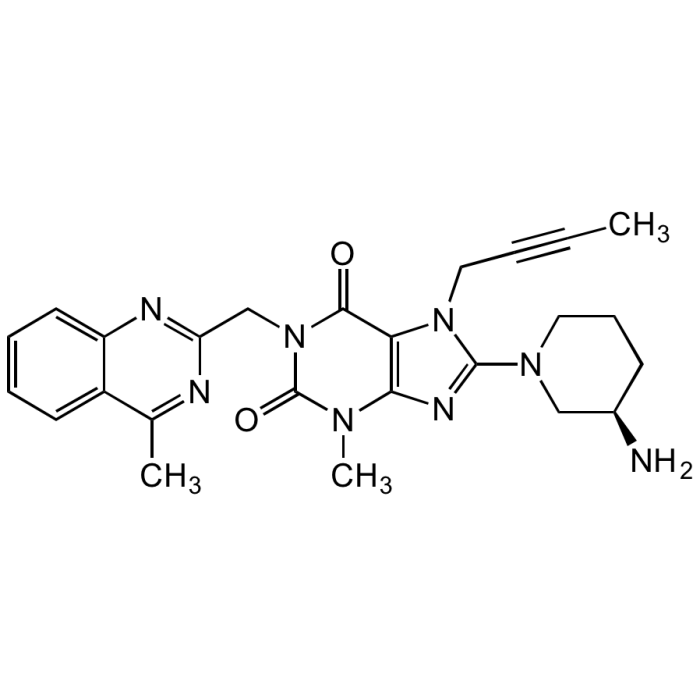
| Synonyms | 8-(3-(R)-Aminopiperidin-1-yl)-7-but-2-ynyl-3-methyl-1-(4-methyl-quinazolin-2-ylmethyl)-3,7-dihydropurine-2,6-dione; BI-1356 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C25H28N8O2 |
| MW | 472.5 |
| CAS | 668270-12-0 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (5mg/ml), ethanol or methanol. Slightly soluble in water (~1mg/ml). |
| InChi Key | LTXREWYXXSTFRX-QGZVFWFLSA-N |
| Smiles | CC#CCN1C(=NC2=C1C(=O)N(CC1=NC3=CC=CC=C3C(C)=N1)C(=O)N2C)N1CCC[C@@H](N)C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Antidiabetic agent.
- Highly potent and selective competitive inhibitor of dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (DPP4; DPP IV; CD26), an enzyme that degrades, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Prevents the inactivation of endogenous GLP-1 and GIP.
- Shown to restore β cell function and survival in human isolated islets through GLP-1 stabilization.
- Improves insulin sensitivity.
- Anti-inflammatory compound.
- DPP4 is a cell surface aminopeptidase that exerts diverse biological activities, such as protease activity, association with adenosine deaminase, interaction with the extracellular matrix, regulation of intracellular signal transduction coupled with the control of cell migration and proliferation, and in addition cell surface co-receptor activity mediating viral entry. DPP4 is a viral receptor of human coronaviruses and therefore is investigated as a potential target for SARS-CoV-2 infections.
Product References
- 8-(3-(R)-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-7-but-2-ynyl-3-methyl-1-(4-methyl-quinazolin-2-ylmethyl)-3,7-dihydropurine-2,6-dione (BI 1356), a highly potent, selective, long-acting, and orally bioavailable DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: M. Eckhardt, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 50, 6450 (2007)
- Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of single oral doses of BI 1356, an inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase 4, in healthy male volunteers: S. Hüttner, et al.; J. Clin. Pharmacol. 48, 1171 (2008)
- (R)-8-(3-amino-piperidin-1-yl)-7-but-2-ynyl-3-methyl-1-(4-methyl-quinazolin-2-ylmethyl)-3,7-dihydro-purine-2,6-dione (BI 1356), a novel xanthine-based dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor, has a superior potency and longer duration of action compared with other dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: L. Thomas, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 325, 175 (2008)
- Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and tolerability of multiple oral doses of linagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor in male type 2 diabetes patients: T. Heise, et al.; Diabetes Obes. Metab. 11, 786 (2009)
- The DPP4 inhibitor linagliptin delays the onset of diabetes and preserves β-cell mass in non-obese diabetic mice: J. Jelsing, et al.; J. Endocrinol. 214, 381 (2012)
- The dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor linagliptin attenuates inflammation and accelerates epithelialization in wounds of diabetic ob/ob mice: C. Schurmann, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 342, 71 (2012)
- Linagliptin improves insulin sensitivity and hepatic steatosis in diet-induced obesity: M. Kern, et al.; PLoS One 7, e38744 (2012)
- Emerging DPP-4 inhibitors: focus on linagliptin for type 2 diabetes: B. Gallwitz; Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 6, 1 (2013) (Review)
- The DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin restores β-cell function and survival in human isolated islets through GLP-1 stabilization: P. Shah, et al.; J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 98, E1163 (2013)
- Linagliptin: from bench to bedside: J. Doupis; Drug. Des. Devel. Ther. 8, 431 (2014) (Review)
- Single cell RNA sequencing of 13 human tissues identify cell types and receptors of human coronaviruses: F. Qi, et al.; BBRC (Epub ahead of print) (2020)
- DPP-4 Inhibitors Attenuate Fibrosis After Glaucoma Filtering Surgery by Suppressing the TGF-β/Smad Signaling Pathway: M. Yoshida, et al.; Invest. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci 64, (2023)