Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
RANKL, Soluble (human) (rec.)
As low as
205
CHF
CHF 205.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-40B-0008-C01010 µgCHF 205.00
AG-40B-0008-30103 x 10 µgCHF 410.00

Figure 1: ELISA binding assay between human RANKL (Prod. No. AG-40B-0008) and mouse RANK:Fc (Prod. No. AG-40B-0092). The EC50 =15ng/ml on the mouse RANK receptor. Not shown, the EC50=1ng/ml on the human RNK receptor.
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | TRANCE; ODF; OPGL; TNFSF11; CD254 |
| Product Type | Protein |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | HEK 293 cells |
| Sequence | Human RANKL (aa 152-317) is fused at the N-terminus to a FLAG®-tag. |
| Crossreactivity |
Human Mouse |
| Specificity | Binds to human and mouse RANK. |
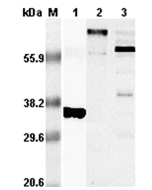
| MW | ~28kDa (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Endotoxin Content | <0.01EU/μg purified protein (LAL test; Lonza). |
| Concentration | 0.1mg/ml after reconstitution. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute with 100μl sterile water. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Contains PBS. |
| Other Product Data | UniProt link O14788: RANKL (human) |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Centrifuge lyophilized vial before opening and reconstitution. PBS containing at least 0.1% BSA should be used for further dilutions. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. Working aliquots are stable for up to 3 months when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
RANKL is an osteoclast differentiation and activation factor. Augments the ability of dendritic cells to stimulate naive T cell proliferation. Important regulator of interactions between T cells and dendritic cells and may play a role in the regulation of the T cell-dependent immune response. RANKL plays an important role in the progression of breast cancer.
Product References
- Receptor activator of NF-κB and osteoprotegerin expression by human microvascular endothelial cells, regulation by inflammatory cytokines, and role in human osteoclastogenesis: P. Collin-Osdoby, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 276, 20659 (2001)
- Functional expression of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB in Hodgkin disease cell lines: P. Fiumara, et al.; Blood 98, 2784 (2001)
- Suppression of IL-12 Production by Soluble CD40 Ligand: Evidence for Involvement of the p44/42 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway: M. Wittmann, et al.; J. Immunol. 168, 3793 (2002)
- Induction of Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by the Proteasome Inhibitor PS-341 in Hodgkin Disease Cell Lines Is Independent of Inhibitor of Nuclear Factor-kappaB Mutations or Activation of the CD30, CD40, and RANK Receptors: B. Zheng, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 10, 3207 (2004)
- Osteoprotegerin production by human intestinal epithelial cells: a potential regulator of mucosal immune responses: K. Vidal, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 287, G836 (2004)
- A novel in vivo role for osteoprotegerin ligand in activation of monocyte effector function and inflammatory response: D. Seshasayee, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 279, 30202 (2004)
- Mechanisms of spontaneous osteoclastogenesis in cancer with bone involvement: I. Roato, et al.; FASEB J. 19, 228 (2005)
- Icariin inhibits the osteoclast formation induced by RANKL and macrophage-colony stimulating factor in mouse bone marrow culture: K.M. Chen, et al.; Pharmazie 62, 388 (2007)
- Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa B Ligand (RANKL) Modulates the Expression of Genes Involved in Apoptosis and Cell Cycle in Human Osteoclasts: E. Rimondi, et al.; Anatom. Rec. 290, 838 (2007)
- Evaluating the Bone Tissue Regeneration Capability of the Chinese Herbal Decoction Danggui Buxue Tang from a Molecular Biology Perspective: W.-L. Wang, et al.; Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 853234 (2014
- Tumor necrosis factor receptor family costimulation increases regulatory T-cell activation and function via NF-κB: M. Lubrano di Ricco, et al.; Eur. J. Immunol. 50, 972 (2020)