Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
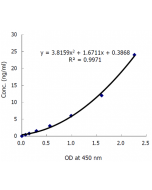
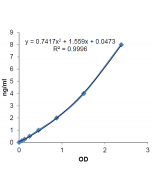
Adiponectin (human) ELISA Kit

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | ACRP30; AdipoQ; apM1; GBP28; Adipocyte complement related protein of 30kDa |
| Product Type | Kit |
| Properties | |
| Application Set | Quantitative ELISA |
| Specificity | Detects human adiponectin. Does not cross-react with mouse adiponectin, rat adiponectin, human resistin, human RELM-β or human leptin. |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Quantity |
1 x 96 wells 2 x 96 wells (Twin Plex) |
| Sensitivity | 100pg/ml |
| Range | 0.5 to 32ng/ml |
| Sample Type |
Cell Culture Supernatant Plasma Serum Urine |
| Assay Type | Sandwich |
| Detection Type | Colorimetric |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
After standard reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Plate and reagents should reach room temperature before use. |
| Use/Stability | 12 months after the day of manufacturing. See expiry date on ELISA Kit box. |
| Documents | |
| Manual |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Adiponectin [ACRP30; AdipoQ] is a promising biomarker of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) but also as a potential target for management of the metabolic syndrome. It is a very robust marker that is not prone to degradation or acute inflammatory challenges, is present in relatively high concentrations in the peripheral circulation, and can be collected by a variety of methods. The benefits of using adiponectin assays in clinical settings include, (a) prediction of risk of diabetes and metabolic status and (b) providing a tool to monitor metabolic improvements. Adiponectin exerts anti-atherogenic and anti-inflammatory properties and may be important as a biomarker for obesity-related cardiovascular disease (CVD). New findings showed urinary adiponectin excretion as an independent new biomarker of microvascular and macrovascular damage in T2DM and suggested it as a very promising tool for early cardiovascular disease risk assessment. Adiponectin serum level was also described as a good biomarker of colorectal adenoma, this being related to the positive correlation between obesity and increased risk of cancer at various sites (colorectal, breast, prostate and endometrium).
- Plasma adiponectin levels in postmenopausal women with or without long-term hormone therapy: J. Ima; Maturitas 54, 65 (2006)
- Association between hypoadiponectinemia and cardiovascular risk factors in nonobese healthy adults. J.A. Im, et al.; Metabolism 55, 1546 (2006)
- Relationship of serum adiponectin and resistin levels with breast cancer risk: J.H. Kang, et al.; J. Korean Med. Sci. 22, 117 (2007)
- Improved insulin sensitivity and adiponectin level after exercise training in obese Korean youth: E.S. Kim, et al.; Obesity 15, 3023 (2007)
- Associations of adiponectin with sex hormone-binding globulin levels in aging male and female populations: T. Yasui, et al.; Clin. Chim. Acta 386, 69 (2007)
- Crosstalk between high-molecular-weight adiponectin and T-cadherin during liver fibrosis development in rats: K. Asada, et al.; Intl. J. Mol. Med. 20, 725 (2007)
- Retinol binding protein 4, low birth weight-related insulin resistance and hormonal contraception: A. Zugaro, et al.; Endocrine 32, 166 (2007)
- Leptin is Associated with Endothelial Dysfunction in Healthy Obese Premenopausal Women: K. Kwon, et al.; Kor. Circ. J. 37, 251 (2007)
- Correlation between estrogens and serum adipocytokines in premenopausal and postmenopausal women: S.C. Hong, et al.; Menopause 14, 835 (2007)
- Transgenic mice expressing nuclear sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c in adipose tissue exhibit liver histology similar to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: H. Nakayama, et al.; Metabolism 56, 470 (2007)
- Insulin-sensitizing effects of exercise on Adiponectin and Retinol Binding Protein-4 concentrations in young and middle-aged women: S. Lim, et al.; J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 2263 (2008)
- Retinol Binding Protein-4 elevation is associated with serum TSH level independently of obesity in elderly subjects with normal glucose tolerance: S. H. Choi, et al.; J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 2313 (2008)
- Fat in liver/muscle correlates more strongly with insulin sensitivity in rats than abdominal fat: S. Lim, et al.; Obesity 17, 188 (2008)
- Obesity-related promotion of aberrant crypt foci in DMH-treated obesis Zucker rats correlates with dyslipidemia rather than hyperinsulinemia: T.C. Koch, et al.; Eur. J. Nutr. 47, 161 (2008)
- Changes of Serum Adiponectin Levels in Murine Experimental Sparganosis: H.J. Yang; Kor. J. Parasitol. 46, 91 (2008)
- Mas Deficiency in FVB/N mice produces marked changes in lipid and glycemic metabolism: S.H. Santos, et al.; Diabetes 57, 340 (2008)
- Weight Loss with a Low-Carbohydrate, Mediterranean, or Low-Fat Diet: I. Shai, et al.; N. Engl. J. Med. 359, 229 (2008)
- Adipose-specific knockout of raptor results in lean mice with enhanced mitochondrial respiration: P. Polak, et al.; Cell Metab. 8, 399 (2008)
- Serum Adipocyte Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Levels Are Associated With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: J.H. Koh, et al.; Diab. Care 32, 147 (2009)
- Elevated serum g-glutamyltransferase levels are independently associated with insulin resistance in non-diabetic subjects: J.Y. Shin, et al.; Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 84, 152 (2009)
- The Lou/C rat: A model of spontaneous food restriction associated with improved insulin sensitivity and decreased lipid storage in adipose tissue: C. Veyrat-Durebex, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 296, E1120 (2009)
- MicroRNA Expression in Human Omental and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue: N. Klöting, et al.; PLoS One 4, e4699 (2009)
- Adipokines and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Relationship with Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: M. Vadacca, et al.; J. Rheumatol. 36, 295 (2009)
- Relationship between serum adipocytokine levels and metabolic syndrome in menopausal women: H.T. Park, et al.; Gynecol. Endocrinol. 25, 27 (2009)
- Circuit resistance exercise improves glycemic control and adipokines in females with type 2 diabetes mellitus: S. Kang, et al.; JSSM 8, 682 (2009)
- Relationship between genotype and serum levels of adipokines and bone mineral density in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: K. Mirzaei, et al.; Iran. J. Diab. Lip. Dis. 8, 77 (2009)
- Combined Impact of Adiponectin and Retinol-binding Protein 4 on Metabolic Syndrome in Elderly People: The Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging: S. Lim, et al.; Obesity 18, 826 (2010)
- Body weight control by a high-carbohydrate/low-fat diet slows the progression of diabetic kidney damage in an obese, hypertensive, type 2 diabetic rat model: S. Ohtomo, et al.; J. Obes. 2010, 136502 (2010)
- Combined effects of body mass index and cardio/respiratory fitness on serum vaspin concentrations in Korean young men: J.K. Chou, et al.; Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 108, 347 (2010)
- Adiponectin, Resistin and Leptin Response to Dietary Intervention in Diabetic Nephropathy: L. Kozlowska, et al.; J. Ren. Nutr. 20, 255 (2010)
- Possible involvement and the mechanisms of excess trans-fatty acid consumption in severe NAFLD in mice: N. Obara, et al.; J. Hepatol. 53, 326 (2010)
- Improved lipid and glucose metabolism in transgenic rats with increased circulating angiotensin-(1-7): S.H. Santos, et al.; Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 30, 953 (2010)
- Dietary sphingolipids ameliorate disorders of lipid metabolism in Zucker fatty rats: K. Yunoki, et al.; J. Agric. Food Chem. 58, 7030 (2010)
- Association of insulin resistance with anti-Mullerian hormone levels in women without polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): H.T. Park, et al.; Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf) 72, 26 (2010)
- Effects of body composition, leptin, and adiponectin on bone mineral density in prepubertal girls: Y.J. Rhie, et al.; J. Korean Med. Sci. 25, 1187 (2010)
- Adiponectin is produced by lymphocytes and is a negative regulator of granulopoiesis: L.J. Crawford, et al.; J. Leukoc. Biol. 88, 807 (2010)
- A nonthiazolidinedione peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor / dual agonist CG301360 alleviates insulin resistance and lipid dysregulation in db/db mice: H.W. Jeong, et al.; Mol. Pharmacol. 78, 877 (2010)
- Adipokine pattern in subjects with impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance in comparison to normal glucose tolerance and diabetes: A. Tonjes, et al.; PLoS One 5, e13911 (2010)
- Body weight control by a high-carbohydrate/low-fat diet slows the progression of diabetic kidney damage in an obese, hypertensive, type 2 diabetic rat model: S. Ohtomo, et al.; J. Obes. 2010, 136502 (2010)
- Serum levels of CK18 M30 and leptin are useful predictors of steatohepatitis and fibrosis in paediatric NAFLD: E. Fitzpatrick, et al.; J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 51, 500 (2010)
- Resistin, adiponectin and visfatin; can adipocytokines predict gestational diabetes mellitus and early post partum metabolic syndrome?: A. Hossein-nezhad, et al.; Iran. J. Diab. Lip. Dis. 9, 6 (2010)
- Combined effects of body mass index and cardio/respiratory fitness on serum vaspin concentrations in Korean young men: J.K. Cho, et al.; Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 108, 347 (2010)
- A nonthiazolidinedione peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α/γ dual agonist CG301360 alleviates insulin resistance and lipid dysregulation in db/db mice: H.W. Jeong, et al.; Mol. Pharmacol. 78, 877 (2010)
- Organotypic culture of human bone marrow adipose tissue: K. Uchihashi, et al.; Pathol. Int. 60, 259 (2010)
- ADIPOQ SNP45 associated with lean body mass in physically active normal weight adolescent girls: C.L. Passariello, et al.; Am. J. Hum. Biol. 22, 813 (2010)
- Adiponectin, resistin and leptin response to dietary intervention in diabetic nephropathy: L. Kozłowska, et al.; J. Ren. Nutr. 20, 255 (2010)
- Body weight control by a high-carbohydrate/low-fat diet slows the progression of diabetic kidney damage in an obese, hypertensive, type 2 diabetic rat model: S. Ohtomo, et al.; J. Obes. 2010, 136502 (2010)
- Adipocytokines and bone mineral density in adolescent female athletes: R. Gruodyte, et al.; Acta Paediatr. 99, 1879 (2010)
- Effect of green tea extract on bone turnover markers in type 2 diabetic patients; A double- blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial study: K. Mirzaei, et al.; DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 17 (Suppl 1), 38 (2010)
- Phenotypic and genetic variation in leptin as determinants of weight regain: G. Erez, et al.; Int. J. Obes. (Lond) 35, 785 (2011)
- Apolipoprotein B/A1 ratio is associated with free androgen index and visceral adiposity and may be an indicator of metabolic syndrome in male children and adolescents: Y.H. Lee, et al.; Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf) 74, 579 (2011)
- Circulating Nampt and RBP4 levels in patients with carotid stenosis undergoing carotid endarterectomy (CEA): G. Aust, et al.; Clin. Chim. Acta 412, 1195 (2011)
- Serum visfatin is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus independent of insulin resistance and obesity: A. Esteghamati, et al.; Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 91, 154 (2011)
- Role of AMP-activated Protein Kinase and Adiponectin during Development of Hepatic Steatosis in High-fat Diet-induced Obesity in Rats: S.K. Ha, et al.; J. Comp. Pathol. 145, 88 (2011)
- Adipokines, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and breast cancer recurrence: a cohort study: S.W. Oh, et al.; Breast Cancer Res. 13, R34 (2011)
- Plasma visfatin and adiponectin concentrations in physically active adolescent girls: relationships with insulin sensitivity and body composition variables: J. Jurimae, et al.; JPEM 24, 419 (2011)
- Relationship between inflammation biomarkers, antioxidant vitamins, and bone mineral density in patients with metabolic syndrome: Y. Lee, et al.; Nutr. Res. Pract. 5, 150 (2011)
- Clinically silent adrenal adenomas - their relation to the metabolic syndrome and to GNB3 C825T gene polymorphism: I. Lazurova, et al.; Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 123, 618 (2011)
- Optimal cut points of waist circumference (WC) and visceral fat area (VFA) predicting for metabolic syndrome (MetS) in elderly population in the Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging (KLoSHA): S. Lim, et al.; Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 54, e29(2012)
- Effects of aerobic exercise training on C1q tumor necrosis factor α-related protein isoform 5 (myonectin): association with insulin resistance and mitochondrial DNA density in women: S. Lim, et al.; J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 97, E88 (2012)
- Genetic effects of adiponectin single nucleotide polymorphisms on the clustering of metabolic risk factors in young Korean adults: J.Y. Lee, et al.; Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 112, 623 (2012)
- The effects of detraining on blood adipokines and antioxidant enzyme in Korean overweight children: J. Woo, et al.; Eur. J. Pediatr. 171, 235 (2012)
- Plasma adiponectin elevation in elderly individuals with subsyndromal depression: H.G. Jeong, et al.; Psychoneuroendocrinol. 37, 948 (2012)
- Leptin, adiponectin and vascular stiffness parameters in women with systemic lupus erythematosus: M. Vadacca, et al.; Intern. Emerg. Med. 8, 705 (2013)
- Change of coronary flow velocity during the cold pressor test is related to endothelial markers in subjects with chest pain and a normal coronary angiogram: H.J. Hwang, et al.; Clin. Cardiol. 35, 119 (2012)
- Efficacy and safety of ginsam, a vinegar extract from Panax ginseng, in type 2 diabetic patients: Results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled study: J.W. Yoon, et al.; J. Diabet. Inv. 3, 309 (2011)
- The normoglycemic first-degree relatives of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus have low circulating omentin-1 and adiponectin levels: S. Akbarzadeh, et al.; Cytokine 58, 295 (2012)
- High-sensitivity C-reactive protein is independently associated with arterial stiffness in women with metabolic syndrome: E.G. Oh, et al.; J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 27, 61 (2012)
- Chitooligosaccharide ameliorates diet-induced obesity in mice and affects adipose gene expression involved in adipogenesis and inflammation: E.H. Choi, et al.; Nutr. Res. 32, 218 (2012)
- AMPK activation with glabridin ameliorates adiposity and lipid dysregulation in obesity: J.W. Lee, et al.; J. Lipid. Res. 53, 1277 (2012)
- The role of leptin and its short-form receptor in inflammation in db/db mice infused with peritoneal dialysis fluid: J.C. Leung, et al.; Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 27, 3119 (2012)
- The Value of Visfatin in the Prediction of Metabolic Syndrome: A Multi-Factorial Analysis: A. Esteghamati, et al.; J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 5, 541 (2012)
- Carotid intima media thickness, brachial flow mediated dilation and previous history of gestational diabetes mellitus: H. Fakhrzadeh, et al.; J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 38, 1057 (2012)
- Progranulin as a Prognostic Biomarker for Breast Cancer Recurrence in Patients Who Had Hormone Receptor-Positive Tumors: A Cohort Study: D.H. Koo, et al.; PLoS One 7, e39880 (2012)
- Mitochondrial DNA copy number in peripheral blood is associated with femoral neck bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: J.H. Kim & D.C. Lee; J. Rheumatol. 39, 1465 (2012)
- Low Serum Adiponectin Levels in Korean Children with a Family History of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Y.J. Oh, et al.; Horm. Res. Paediatr. 77, 382 (2012)
- Comparison of regional body composition and its relation with cardiometabolic risk between BMI-matched young and old subjects: Y. Lee, et al.; Atherosclerosis 224, 258 (2012)
- The framingham risk score, diet, and inflammatory markers in Korean men with metabolic syndrome: C. Sohn, et al.; Nutr. Res. Pract. 6, 246 (2012)
- Association between obesity and asthma in the elderly population: potential roles of abdominal subcutaneous adiposity and sarcopenia: W.J. Song, et al.; Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 109, 243 (2012)
- Omentin-1, visfatin and adiponectin levels in relation to bone mineral density in Iranian postmenopausal women: M. Tohidi, et al.; Bone 51, 876 (2012)
- A 12-week after-school physical activity programme improves endothelial cell function in overweight and obese children: a randomised controlled study: J.H. Park, et al.; BMC Pediatr. 12, 111 (2012)
- Adiponectin, leptin and lipid profiles evaluation in oral contraceptive pill consumers: S. Fallah, et al.; Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 285, 1747 (2012)
- Dietary intervention induces flow of changes within biomarkers of lipids, inflammation, liver enzymes, and glycemic control: R. Golan, et al.; Nutrition 28, 131 (2012)
- Metabolic Syndrome is Associated with Low Adiponectin Level and Increased Insulin Resistance in Apparently Healthy Koreans: K.H. Yoo, et al.; Korean J. Obes. 21, 175 (2012)
- Gastrectomy for Early Gastric Cancer is Associated with Decreased Cardiovascular Mortality in Association with Postsurgical Metabolic Changes:Y.H. Lee, et al.; Ann. Surg. Oncol. 20, 1250 (2012)
- Implication of Progranulin and C1q/TNF-Related Protein-3 (CTRP3) on Inflammation and Atherosclerosis in Subjects with or without Metabolic Syndrome: H.J. Yoo, et al.; PLOS One 8, e55744 (2013)
- Effects of a Combined Aerobic and Resistance Exercise Program on C1q/TNF-Related Protein-3 (CTRP-3) and CTRP-5 Levels: H.Y. Choi, et al.; Diabetes Care 36, 3321 (2013)
- Urinary adiponectin concentration is positively associated with micro- and macro-vascular complications: W.S. Jeon, et al.; Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 12, 137 (2013)
- Effect of weight reduction following bariatric surgery on serum visfatin and adiponectin levels in morbidly obese subjects: M.J. Hosseinzadeh-Attar, et al.; Obes. Facts 6, 193 (2013)
- Implications of C1q/TNF-related protein-3 (CTRP-3) and progranulin in patients with acute coronary syndrome and stable angina pectoris: K.M. Choi, et al.; Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 13, 14 (2014)
- Identification of adipokine clusters related to parameters of fat mass, insulin sensitivity and inflammation: G. Flehmig, et al.; PLos One 9, e99785 (2014)