Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
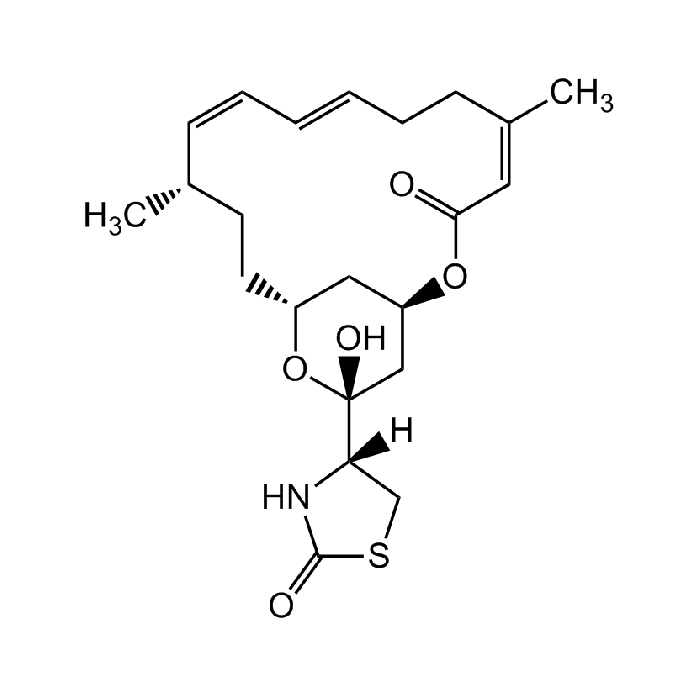
Latrunculin A
As low as
150
CHF
CHF 150.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0027-C100100 µgCHF 150.00
AG-CN2-0027-C500500 µgCHF 560.00
BULK available!
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | LAT-A; NSC 613011 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C22H31NO5S |
| MW | 421.6 |
| Merck Index | 14: 5378 |
| CAS | 76343-93-6 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Latrunculia magnifica. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥97% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Colorless viscous film |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (25mg/ml) or ethanol (25mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | DDVBPZROPPMBLW-IZGXTMSKSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C(SC1)N[C@]1([H])[C@](C2)(O)O[C@@H](C[C@H]2O3)CC[C@H](C)/C=C\C=C\CC/C(C)=C\C3=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. Store solutions at -20°C in the dark. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Cell permeable marine toxin [1].
- Disrupts microfilament-mediated processes [2].
- Actin polymerization inhibitor in vitro and in vivo by the formation of a 1:1 complex with monomeric G-actin [1, 2, 3, 6].
- Depolymerizes actin filaments (F-actin) [3].
- Potent phagocytosis inhibitor [4].
- Anticancer compound [7, 8]. Suppresses hypoxia-induced HIF-1 activation in tumor cells [7]. Inhibits tumor cell invasion [7].
- Acts via a different mechanism than cytochalasins.
Product References
- Latrunculins: novel marine toxins that disrupt microfilament organization in cultured cells: I. Spector, et al.; Science 219, 493 (1983)
- Latrunculin inhibits the microfilament-mediated processes during fertilization, cleavage and early development in sea urchins and mice: G. Schatten, et al.; Exp. Cell Res. 166, 191 (1986)
- Inhibition of actin polymerization by latrunculin: A: M. Coue, et al.; FEBS Lett. 213, 316 (1987)
- Latrunculin A is a potent inhibitor of phagocytosis by macrophages: C.A. de Oliveira & B. Mantovani; Life Sci. 43, 1825 (1988)
- Latrunculins-novel marine macrolides that disrupt microfilament organization and affect cell growth: I. Comparison with cytochalasin D: I. Spector, et al.; Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 13, 127 (1989)
- Actin-latrunculin A structure and function. Differential modulation of actin-binding protein function by latrunculin A: E.G. Yarmola, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 275, 28120 (2000)
- Latrunculin A and its C-17-O-carbamates inhibit prostate tumor cell invasion and HIF-1 activation in breast tumor cells: K.A. Sayed, et al.; J. Nat. Prod. 71, 396 (2008)
- Latrunculin a has a strong anticancer effect in a peritoneal dissemination model of human gastric cancer in mice: H. Konishi, et al.; Anticancer Res. 29, 2091 (2009)
- Nucleolar asymmetry and the importance of septin integrity upon cell cycle arrest: U. Rai, et al.; PLoS ONE 12, e0174306 (2017)
- Trogocytosis of ligand-receptor complex and its intracellular transport in CD30 signaling: M. Nakashima, et al.; Biol Cell. 110, 109 (2018)
- Integrating chemical and mechanical signals through dynamic coupling between cellular protrusions and pulsed ERK activation: J.M. Yang, et al.; Nat. Comm. 9, 4673 (2018)
- Rap1 organizes lymphocyte front-back polarity via RhoA signaling and talin1: Y. Ueda, et al.; iScience 26, 107292 (2023)