Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
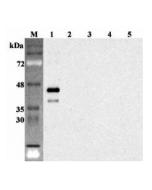
anti-Sirtuin 6 (human), mAb (S6R82-2)

1: Human sirtuin 6 (His-tagged).
2: Human sirtuin 1 (His-tagged).
3: Human sirtuin 2 (His-tagged).
4: Human sirtuin 5 (His-tagged).
5: Unrelated protein (His-tagged) (negative control).
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | SIRT6; NAD-dependent Deacetylase Sirtuin-6; Mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase Sirtuin 6; SIR2-like Protein 6; SIR2L6 |
| Product Type | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Clone | S6R82-2 |
| Isotype | Mouse IgG2bκ |
| Immunogen/Antigen | Recombinant human sirtuin 6. |
| Application |
ELISA: (direct and indirect: 1:2’000-1:5’000) Note: Tested on recombinant proteins and/or target-protein transfected cell lines in ELISA, Western Blot and/or FACS. |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Specificity |
Recognizes human sirtuin 6. Detects a band of ~47kDa by Western blot. |
| Purity Detail | Protein G-affinity purified. |
| Concentration | 1mg/ml |
| Formulation | Liquid. 0.2μm-filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Contains no preservatives. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After opening, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) is a NAD-dependent protein deacetylase with activity towards 'Lys-9' and 'Lys-56' of histone H3. It modulates acetylation of histone H3 in telomeric chromatin during the S-phase of the cell cycle. It is required for genomic stability and for normal IGF1 serum levels and normal glucose homeostasis. It also regulates cellular senescence and apoptosis. Unlike most sirtuins, SIRT6 preferentially removes long-chain fatty-acyl, rather than acetyl, protein modifications. This activity regulates secretion of the inflammation-associated protein TNF-α.