Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
COVID-19
Latest Insights & Products for SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 Research

Go to:
>> Coronaviruses (CoVs) - SARS-CoV & SARS-CoV-2 [2019-nCoV]
>> ACE2 & Functional Receptor for SARS Coronaviruses
>> Biological Therapeutic Strategies against SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19
>> Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants and Mutations
>> COVID-19 Diagnostics (ELISA and Screening Assays, Available for Variants!)
>> Overview on the AdipoGen Life Sciences Panel of Products (Proteins)
>> Overview on the AdipoGen Life Sciences Panel of Products (Antibodies)
>> Overview on the AdipoGen Life Sciences Panel of Products (Small Molecules)
>> Cytokine Storm and Severity of COVID-19
Coronaviruses (CoVs) - SARS-CoV & SARS-CoV-2 [2019-nCoV]
Coronaviruses (CoVs) are enveloped non-segmented positive-sense RNA viruses infecting human and vertebrates. They are classified into four types (genus), α-CoV, β-CoV, γ-CoV and δ-CoV. They can infect the respiratory, gastrointestinal, hepatic and central nervous system of human and many wild animals. The family of Coronaviridae constantly circulates within the human population and mainly causes mild respiratory diseases. Recently, a new severe acute respiratory syndrome β-coronavirus called SARS-CoV-2 (or 2019-nCoV) has emerged, which causes an epidemic of acute respiratory syndrome called coronavirus human disease 2019 or COVID-19. Typical clinical symptoms of these patients are dry cough, fever, breathing difficulties, headache and pneumonia. Disease onset may result in progressive respiratory failure, heart tissue damage and even death.
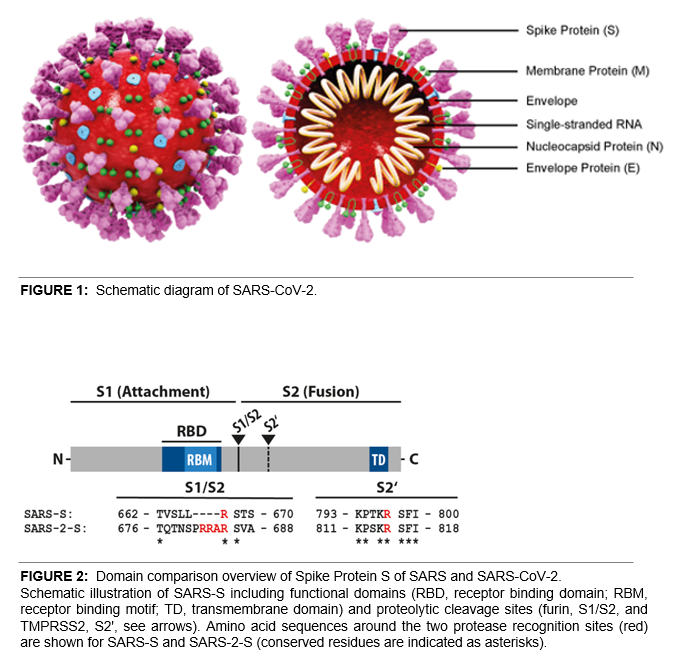 SARS-CoV-2 shares 79.5% sequence identity with SARS-CoV and is 96.2% identical at the genome level to the bat coronavirus BatCoV RaTG133, suggesting it had originated in bats. The coronaviral genome encodes four major structural proteins: the Spike (S) protein, Nucleocapsid (N) protein, Membrane/Matrix (M) protein and the Envelope (E) protein (see Figure 1). The SARS Envelope (E) protein plays a role in viral budding and virion envelope morphogenesis. The SARS Membrane/Matrix (M) protein is one of the major structural viral proteins. It is an integral membrane protein involved in the budding of the viral particles and interacts with SARS Spike (S) protein and the Nucleocapsid (N) protein. The N protein contains two domains, both of them bind the virus RNA genome via different mechanisms.
SARS-CoV-2 shares 79.5% sequence identity with SARS-CoV and is 96.2% identical at the genome level to the bat coronavirus BatCoV RaTG133, suggesting it had originated in bats. The coronaviral genome encodes four major structural proteins: the Spike (S) protein, Nucleocapsid (N) protein, Membrane/Matrix (M) protein and the Envelope (E) protein (see Figure 1). The SARS Envelope (E) protein plays a role in viral budding and virion envelope morphogenesis. The SARS Membrane/Matrix (M) protein is one of the major structural viral proteins. It is an integral membrane protein involved in the budding of the viral particles and interacts with SARS Spike (S) protein and the Nucleocapsid (N) protein. The N protein contains two domains, both of them bind the virus RNA genome via different mechanisms.
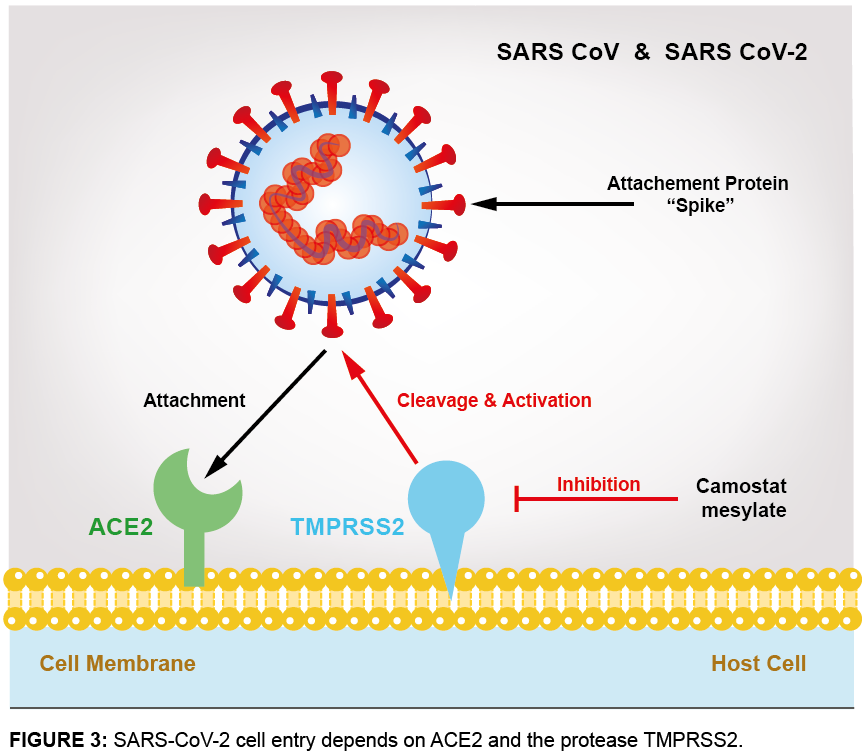
The CoV Spike (S) protein assembles as trimer and plays the most important role in viral attachment, fusion and entry. It is composed of a short intracellular tail, a transmembrane anchor, and a large ectodomain that consists of a receptor binding S1 subunit and a membrane-fusing S2 subunit (see Figure 2, adapted from Cell, Hofmann, et al. (2020)). The S1 subunit contains a receptor binding domain (RBD), which binds to the cell surface receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) present at the surface of epithelial cells.
LITERATURE REFERENCES:
- The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak - an update on the status: Y.R. Guo, et al.; Mil. Med. Res. 7, 11 (2020) (Review)
- SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor: M. Hoffmann, et al.; Cell 181, 731 (2020)
- Characterization of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of 2019 novel coronavirus: implication for development of RBD protein as a viral attachment inhibitor and vaccine: W. Tai, et al.; Cell Mol. Immunol. 17, 613 (2020)
- Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2: R. Yan, et al.; Science 367, 1444 (2020)
- Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein: A.C. Walls, et al.; Cell 181, 281 (2020) (Review)
ACE2 & Functional Receptor for SARS Coronaviruses
 Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a type I transmembrane metallocarboxypeptidase within the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), which plays a key role in blood pressure regulation, fluid and electrolyte balance, thirst, cardiac/renal function and growth. ACE2 is expressed on the cell surface of type 2 alveolar epithelial cells in the lungs as well as on cells in many other tissues. ACE2 shares approximately 60% homology with ACE, the other key enzyme of the RAS system.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a type I transmembrane metallocarboxypeptidase within the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), which plays a key role in blood pressure regulation, fluid and electrolyte balance, thirst, cardiac/renal function and growth. ACE2 is expressed on the cell surface of type 2 alveolar epithelial cells in the lungs as well as on cells in many other tissues. ACE2 shares approximately 60% homology with ACE, the other key enzyme of the RAS system.
ACE2 converts angiotensin II (Ang II) into Ang(1–7), which acts on the Mas receptor and plays a role in cardiovascular disease to lower blood pressure through vasodilation and by promoting kidney sodium and water excretion, but also to lower inflammation. The effects of ACE2 directly oppose those induced by ACE–Ang II signaling, whereby ACE converts Ang I into Ang II, which increases blood pressure by inducing vasoconstriction, increasing kidney reabsorption of sodium and water and promoting inflammation.
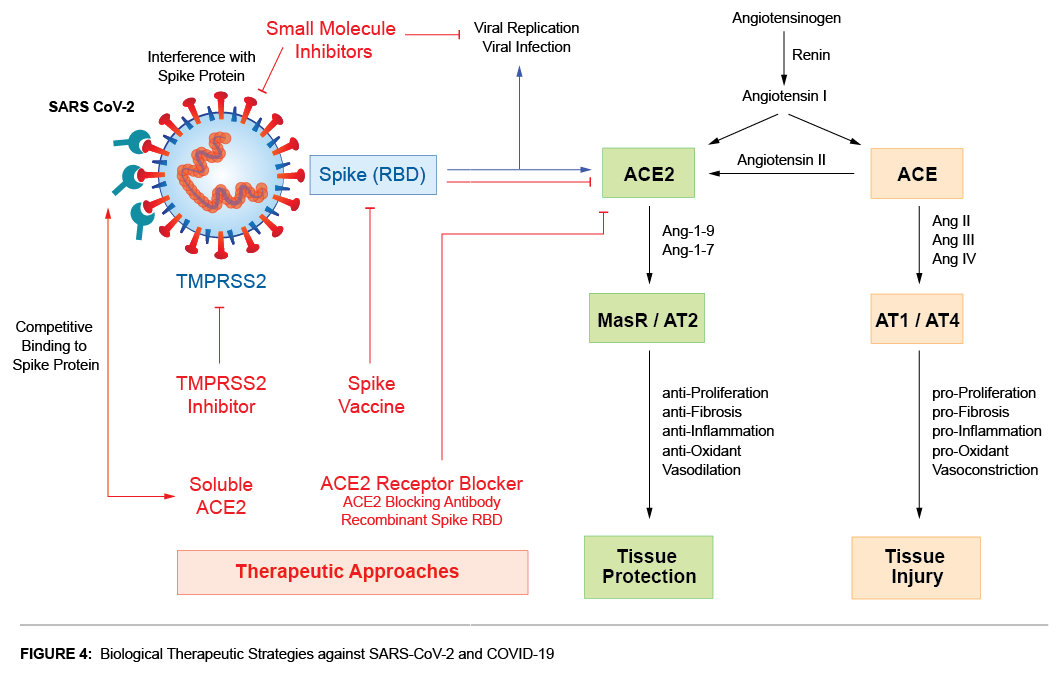
ACE2 has been identified as a key receptor on target cells for SARS-CoV infections in 2002. ACE2 functions as the entry receptor of the new SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus that emerged in China in 2019 and is the cause of the new disease COVID-19. Stronger binding of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 to ACE2, along with proteolytic cleavage of Spike by furin (specific to SARS-CoV-2,not found in other beta-coronavirus) and transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2) facilitates entry of the virus into cells, viral replication and cell-to-cell transmission. The spike protein priming by both the co-receptor serine proteases furin and TMPRSS2 is crucial for SARS-CoV-2 infection of target cells and could explain the enhanced spreading of SARS-CoV-2 (see Figure 3).
LITERATURE REFERENCES:
- Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 Receptor and Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System: M. Gheblawi, et al.; Circ. Res. 126, 1546 (2020)
- SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor: M. Hoffmann, et al.; Cell 181, 731 (2020)
Biological Therapeutic Strategies against SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19
18 years ago the SARS-CoV lead to respiratory diseases in infected people. To date there are no effective vaccines against any type of the coronavirus, which can cause pneumonia and possibly bronchitis. Nevertheless, there are several strategies that are being pursued.
Soluble Human ACE2:
The novel coronavirus uses membrane-bound ACE2 as the receptor. The soluble form of ACE2 lacks the membrane anchor and circulates in small amounts in the blood. This soluble form may act as a competitive interceptor of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses by preventing binding of the viral particle to the surface-bound, full-length ACE2.
ACE2 fused to the Fc portion of immunoglobulin has been reported to neutralize SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Soluble recombinant human ACE2 protein could actually be beneficial as a novel biological therapeutic to combat or limit infection progression caused by coronaviruses that utilize ACE2 as a receptor.
Human ACE2 Blocking Antibodies:
Treatment with blocking anti-ACE2 antibodies disrupts the interaction between virus and receptor, neutralizing the spread of SARS-CoV-2.
Spike S (RBD) Protein:
The CoV spike (S) protein plays the most important role in viral attachment, fusion and entry and serves as a target for development of antibodies, entry inhibitors and vaccines. The soluble recombinant RBD (receptor binding domain) of coronavirus (including SARS-CoV-2) Spike proteins exhibit significantly high binding affinity to ACE2 receptor and could block the binding by competing with the virus. Attachment of recombinant SARS-CoV-2 RBD to ACE2-expressing cells could inhibit the infection to host cells.
SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies:
SARS-CoV2 specific antibodies could cross-react with SARS-CoV-2 proteins, mainly the Spike, but also the envelope, membrane and nucleocapsid proteins, and SARS-CoV-2 induced antisera could cross-neutralize SARS-CoV-2, suggesting the potential to develop SARS-CoV-2 proteins-based vaccines for prevention of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV infections. Spike (RBD) seems to be a strong immunogenic domain of coronaviruses with a large part of the antibody immune response that is directed against this region.
LITERATURE REFERENCES:
- Angiotensin‑converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a SARS‑CoV‑2 receptor: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic target: H. Zhang, et al.; Intensive Care Med. 46, 586 (2020) (Review)
- Therapeutic options for the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV): G. Li & E. De Clercq; Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 19, 149 (2020) (Review)
- SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor: M. Hoffmann, et al.; Cell 181, 271 (2020)
- Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infections in engineered human tissues using clinical-grade soluble human ACE2: J.M. Penninger, et al.; Cell 181, 905 (2020)
- Soluble angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: a potential approach for coronavirus infection therapy? D. Batlle, et al.; Clin. Sci. 134, 543 (2020)
Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants and Mutations
A range of SARS-CoV-2 variants has emerged across the world since the COVID-19 pandemic began. Most attention has been on fast-spreading variants recently identified in the UK (B.1.1.7, Alpha), South Africa (B.1.351, Beta), Brazil (P.1, Gamma) and India (B.1.617, Delta and Kappa). Scientists suspect that the variants’ particular patterns of mutations have the potential to affect their transmissibility, virulence and/or ability to evade parts of the immune system. The latter could make people with vaccine-induced or natural immunity to SARS-CoV-2 vulnerable to becoming reinfected with novel variants and these possible effects remain under investigation.

Reagents for SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 Research
COVID-19 Diagnostics
As the world is struggling to contain the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak, healthcare infrastructure and testing capacity have emerged as major issues. There is an urgent need for access to accurate and standardized diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2 (the causative agent of COVID-19). Laboratory testing for COVID-19 and the associated SARS-CoV-2 virus includes methods that detect the presence of the virus (PCR technology) and those that detect antibodies produced in response to infection. Detection of antibodies (serology) can be used both for clinical purposes and population surveillance. AdipoGen Life Sciences has an ongoing pipeline for detection of soluble ACE2, antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and a HTS detection kit for the determination of SARS-CoV-2 blocking reagents.
LITERATURE REFERENCES:
- Detection of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19: Z. Du, et al.; J. Med. Virol. 92, 1735 (2020)
Highly Specific SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies Detection Kit
 AdipoGen Life Sciences has developed a sensitive, specific and fast SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies Detection Kit (Prod. No. AG-48B-0002) that can be used to detect the presence of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in serum/plasma in about 2 hours independently of species and isotypes!
AdipoGen Life Sciences has developed a sensitive, specific and fast SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies Detection Kit (Prod. No. AG-48B-0002) that can be used to detect the presence of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in serum/plasma in about 2 hours independently of species and isotypes!
This Detection Kit is based on a colorimetric reaction, which measures the binding of the RBD of the Spike S protein from SARS-CoV-2 to its human receptor ACE2. The presence of neutralizing/blocking antibodies in the samples are detected by reduction of signal indicating the inhibition of the Spike-ACE2 binding.
The SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies Detection Kit contains key reagents required to test the presence of functional neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 present in the serum or plasma. It is an easy, fast and scalable (automation) alternative to the classical neutralization assays using Vero E6 cells, such as virus neutralization test (VNT) and pseudo-virus neutralization test (pVNT) and does not need biosafety requirements.
High Specificity has been confirmed and published:
- Comparison of two commercial surrogate ELISAs to detect a neutralizing antibody response to SARS-CoV-2: K. Mueller, et al.; J. Virol. Methods 292, 114122 (2021), DOWNLOAD PDF.
- Evaluation of Two Rapid Lateral Flow Tests and Two Surrogate ELISAs for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Specific Neutralizing Antibodies: P. Girl, et al.; SSRN 3963559 (2021), DOWNLOAD PDF
This kit is administrable in vaccine and therapeutic development as it is suitable for all antibody isotypes and can be used to determine neutralizing antibodies in animal models. The kit will also be useful in current COVID-19 investigations of sero-prevalence, assessment of immune response, herd immunity, longevity of protective immunity, efficacy of different vaccine candidates as well as tracking infections in animals.
Neutralizing Antibody Detection Kits for SARS-CoV-2 Variants
| Product Name | PID | Application/Activity |
| SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies Detection Kit (B.1.617.2 Variant, Delta) | AG-48B-0007 | To measure the presence of neutralizing/blocking antibodies in human serum/plasma that inhibit the binding of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike (RBD) (B.1.617.2 Variant, Delta) protein to its human receptor ACE2. |
|
The STANDARD for Initial SARS-CoV-2 Strain |
AG-48B-0002 | To measure the presence of neutralizing/blocking antibodies in human serum/plasma that inhibit the binding of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike (RBD) (initial strain) protein to its human receptor ACE2. |
SARS-CoV-2 (Spike RBD) IgG Serological ELISA Kit
AdipoGen Life Sciences has developed a sensitive and specific SARS-CoV-2 (Spike RBD) IgG Serological ELISA Kit (Prod. No. AG-45B-0020) that can be used for the qualitative measurement of human Immunoglobulin G (IgG) against SARS-CoV-2 Spike (Receptor Binding Domain) protein in serum and plasma samples.
During an infection, IgM antibodies appear first, followed by IgA on mucosal surfaces or IgG in the serum. The spike (S) proteins (mainly the RBD domain) and the nucleocapsid (N) proteins are the main immunogens of coronaviruses leading to an antibody answer. This assay is an indirect ELISA assay (based on a coated Spike (RBD) protein).
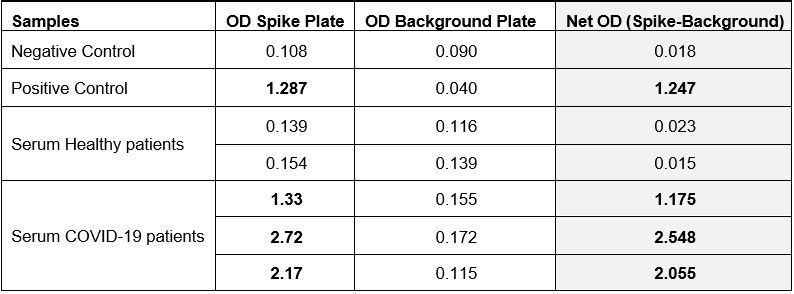
Included in this assay and unique in the market for SARS-CoV-2 IgG assays, is a second plate (antigen non-coated Background Plate or False Positive Control Plate) to determine the sample specific background and to measure the amount of IgG antibodies non-specifically bound to the well. To measure presence of anti-SARS-CoV-2 human IgG antibodies in serum or plasma, net sample optical densities (Net OD) are calculated by subtracting each sample Background Plate OD from the Spike (SARS-CoV-2) antigen plate (Spike Plate) OD.
The Assay Kit can also be used with Dry Blood Samples, which is an inexpensive and easy alternative collecting blood!
Note:
• In the first week of the onset of the infection with the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) patients results may be negative for IgG.
• Patients with low immunity or other diseases that affect immune function, failure of important systemic organs, and use of drugs that suppress immune function can also lead to negative results of new coronavirus IgG.
• Previous infection of SARS or other coronavirus strains may cause a light IgG positive in view of similarities in the nucleocapsid protein, but not in the Spike RBD protein. This means that nucleocapsid-based SARS-CoV-2 IgG assays have a higher chance of cross-reactivites with other coronavirus IgG antibodies than Spike RBD-based SARS-CoV-2 IgG assays, such as this newly developed assay from AdipoGen Life Sciences.
|
Figure: Typical results/values taken by the new SARS-CoV-2 (Spike RBD) IgG Serological ELISA Kit (Prod. No. AG-45B-0020).
|
 |
ACE2 (human) ELISA Kit
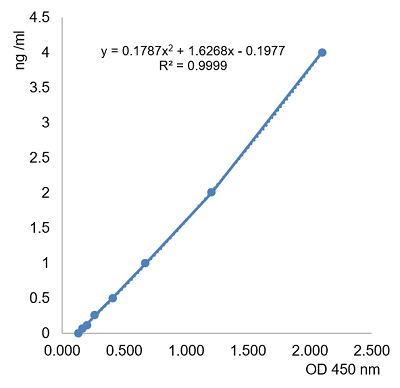
AdipoGen Life Sciences has developed a sensitive and specific colorimetric sandwich ACE2 (human) ELISA Kit (Prod. No. AG-45B-0023) that can to be used for the in vitro quantitative determination of soluble human ACE2 in cell culture supernatants, serum, plasma and urine.
ACE2 has been identified as a key receptor on target cells for SARS-CoV infections in 2002. ACE2 functions as the entry receptor of the new SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus that emerged in China in 2019 and is the cause of the new disease COVID-19. Strong binding of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 to ACE2, along with proteolytic cleavage of ACE2 by transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2), facilitates entry of the virus into cells, viral replication and cell-to-cell transmission. ACE2 can undergo an ADAM17 (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17)-mediated “shedding” from endothelial cells, resulting in the release of the ectodomain into the circulation. This soluble form may act as a competitive interceptor of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses by preventing binding of the viral particle to the surface-bound, full-length ACE2. A reliable ELISA Kit to determine soluble ACE2 in the circulation can be useful in therapeutic developmental studies.
Soluble ACE2 might also be used as biomarker of hypertension and cardiovascular diseases.
|
Figure: Typical Standard Curve
|
 |
Active & Stable Trimeric SARS-CoV-2 Protein
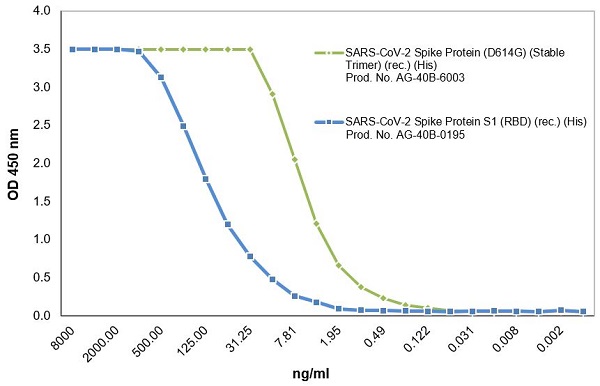
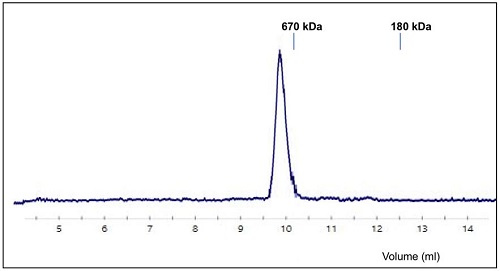
AdipoGen Life Sciences' SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (D614G) (Stable Trimer) (rec.) (His) (Prod. No. AG-40B-6003) is a full-length soluble SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein (aa 16-1213) including a foldon trimerization motif, mutated Furin recognition site (R682S, R685S) and two stabilizing mutations (K986P and V987P). This protein has a His-tag fused to its C-terminus. This protein binds to the human SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 and it binds to anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike antibodies in serum or plasma. It is useful for structural biology research, vaccine development, serological diagnostic kit development and neutralizing antibody screening.
|
Figure: Full-length trimeric SARS-CoV-2 Spike (Prod. No. AG-40B-6003) binds to its receptor ACE2 (human) (rec.) (Prod. No. AG-40B-0192) with high affinity.
|
 |
|
|
|
||
|
Figure: SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (D614G) (Stable Trimer) (rec.) (His) (Prod. No. AG-40B-6003) migrates by Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) as a single peak.
|
 |
Validated Recombinant Proteins for ACE2 & COVID-19 Research
| Product Name | PID | Source | Purity | Application/Activity |
| ACE2 (human) (rec.) | AG-40B-0192 | HEK293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | Soluble human ACE2 competitively inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection. |
| ACE2 (human) (rec.) (Biotin) | AG-40B-0192B | HEK293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | Soluble human ACE2 competitively inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection. |
| ACE2 (human) (rec.) (His) | CHI-B232008 | HEK293 cells | ≥90% (SDS-PAGE) | Soluble human ACE2 competitively inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection. |
| ACE2 (human):Fc (human) (rec.) | CHI-B232006 | HEK293 cells | ≥90% (SDS-PAGE) | Soluble human ACE2 competitively inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection. |
| ACE2 (mouse) (rec.) | AG-40B-0193 | HEK293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | Soluble mouse ACE2 negative control. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (D614G) (Stable Trimer) (rec.) (His) | AG-40B-6003 | HEK 293 cells | ≥90% (SDS-PAGE) | Binds to anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike (RBD) antibodies in serum or plasma. For structural biology research, drug and antibody screening applications and vaccine development. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD) (rec.) (His) | AG-40B-0195 | HEK 293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | Binds to anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike (RBD) antibodies in serum or plasma. For drug and antibody screening applications and immunization. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD) (rec.) (His) (Biotin) | AG-40B-0195B | HEK 293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | This protein forms a tetramer in the presence of streptavidin and this tetramer can be used to activate B cell memory to SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD) (rec.) (His) | CHI-B232004 | HEK 293 cells | ≥90% (SDS-PAGE) | Soluble Protein S (RBD) competitively inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection. For drug and antibody screening applications and immunization. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD) (rec.) (His) (B.1.1.7 Variant, Alpha) | AG-40B-0205 | HEK 293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | Binds to anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike (RBD) antibodies in serum or plasma. For drug and antibody screening applications and immunization. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD) (rec.) (His) (B.1.351 Variant, Beta) | AG-40B-0206 | HEK 293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | Binds to anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike (RBD) antibodies in serum or plasma. For drug and antibody screening applications and immunization. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD) (rec.) (His) (P.1 Variant, Gamma) | AG-40B-0207 | HEK 293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | Binds to anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike (RBD) antibodies in serum or plasma. For drug and antibody screening applications and immunization. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD) (rec.) (His) (B.1.617.1 Variant, Kappa) | AG-40B-0208 | HEK 293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | Binds to anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike (RBD) antibodies in serum or plasma. For drug and antibody screening applications and immunization. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD) (rec.) (GST-His) | CHI-B249001 | HEK 293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | Soluble Protein S (RBD) competitively inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection. For drug and antibody screening applications and immunization. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD):Fc (human) (rec.) | CHI-B232003 | HEK 293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | Soluble Protein S (RBD) competitively inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection. For drug and antibody screening applications and immunization. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD):Fc (human) (rec.) | AG-40B-0194 | HEK 293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | Soluble Protein S (RBD) competitively inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection. For drug and antibody screening applications and immunization. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD):Fc (human) (rec.) (B.1.1.7 Variant, Alpha) | AG-40B-0202 | HEK 293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | More transmissible variant of SARS-CoV-2, called B.1.1.7 that carries a mutation in the RBD at the position 501 (N501Y).For drug and antibody screening applications and immunization. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD):Fc (human) (rec.) (B.1.351 Variant, Beta) | AG-40B-0203 | HEK 293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | New variant of SARS-CoV-2, called B.1.351, that carries three mutations in the RBD at the positions 417, 484 and 501 (K417N, E484K, N501Y) and is associated with a higher viral load with potential for increased transmissibility. For drug and antibody screening applications and immunization. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD):Fc (human) (rec.) (P.1 Variant, Gamma) | AG-40B-0204 | HEK 293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | New variant of SARS-CoV-2, called P.1 that carries three mutations in the RBD at the positions 417, 484 and 501 (K417T, E484K, N501Y). For drug and antibody screening applications and immunization. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD):Fc (human) (rec.) (B.1.617.1 Variant, Kappa) | AG-40B-0209 | HEK 293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | New variant of SARS-CoV-2, called B.1.617.1 that carries two mutations in the RBD at the positions 452 and 484 (L452R, E484Q). For drug and antibody screening applications and immunization. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD):Fc (human) (rec.) (B.1.617.2 Variant, Delta) | AG-40B-0211 | HEK 293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | New variant of SARS-CoV-2, called B.1.617.2 that carries two mutations in the RBD at the positions 452 and 478 (L452R, T478K). For drug and antibody screening applications and immunization. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD):Fc (human) (rec.) (B.1.617.2.1 Variant, Delta Plus) | AG-40B-0212 | HEK 293 cells | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | New variant of SARS-CoV-2, called B.1.617.2.1 that carries three mutations in the RBD at the positions 417, 452 and 478 (K417N, L452R, T478K). For drug and antibody screening applications and immunization. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein (rec.) (His) | CHI-B233501 | E. coli | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | For drug screening applications. |
| PLpro (SARS Coronavirus) (rec.) (His) | SBB-DE0024 | E. coli | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | Involved in the processing of the viral polyprotein. |
| ISG15 (human) (rec.) (Rhodamine 110) | SBB-PS0002 | E. coli | ≥97% (LCMS) | PLPro substrate. Inhibits viral budding and acts as IFNγ-inducing cytokine. |
UNIQUE Human ACE2 Monoclonal Blocking Antibody
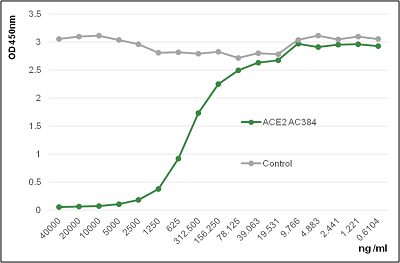
AdipoGen Life Sciences' anti-ACE2 (human), mAb (blocking) (AC384) (preservative free) (Prod. No. AG-20A-0037PF) is a monoclonal antibody that recognizes human ACE2 and works specifically in ELISA, Western Blot and Functional Application. The antibody blocks the binding of human ACE2 to the Spike protein of SARS-Cov-2.
|
Figure: Binding of ACE2 (human) to the Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 is inhibited by the antibody anti-ACE2 (human), mAb (blocking) (AC384) (AG-20A-0037PF).
|
 |
Flow Cytometry-Competent Human ACE2 Monoclonal Antibodies
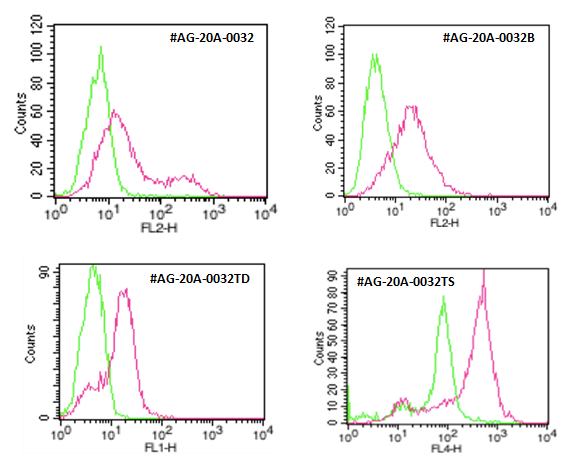
AdipoGen Life Sciences' anti-ACE2 (human), mAb (AC18F) (Prod. No. AG-20A-0032) is a monoclonal antibody clone that recognizes human ACE2 and works specifically in Flow Cytometry (FACS). The antibody is available in different formats, unlabeled (#AG-20A-0032) and Biotin-labeled (#AG-20A-0032B), as well as labeled with the dyes ATTO488 (#AG-20A-0032TD) and ATTO647N (#AG-20A-0032TS). All variants are FACS-competent using the appropriate secondary reagents.
|
Figure: Detection of endogenous human ACE2 by different formats of anti-ACE2 (human), mAb (AC18F) (AG-20B-0032).
Download: Cell Detachment Protocol for FACS. |
 |
All Human ACE2 Antibodies
| Product Name | PID | Isotype | Applications | Species |
| anti-ACE2 (human), mAb (AC18F) | AG-20A-0032 | Mouse IgG1κ | ELISA, FACS, WB | Human |
| anti-ACE2 (human), mAb (AC18F) (Biotin) | AG-20A-0032B | Mouse IgG1κ | ELISA, FACS, WB | Human |
| anti-ACE2 (human), mAb (AC18F) (ATTO 488) | AG-20A-0032TD | Mouse IgG1κ | FACS | Human |
| anti-ACE2 (human), mAb (AC18F) (ATTO 647N) | AG-20A-0032TS | Mouse IgG1κ | FACS | Human |
| anti-ACE2 (human), mAb (AC384) | AG-20A-0037 | Mouse IgG1κ | ELISA, WB | Human |
| anti-ACE2 (human), mAb (AC384) (Biotin) | AG-20A-0037B | Mouse IgG1κ | ELISA, WB | Human |
| anti-ACE2 (human), mAb (blocking) (AC384) (preservative free) | AG-20A-0037PF | Mouse IgG1κ | FUNC (Blocking), ELISA, WB | Human |
| anti-ACE2 (human), pAb | AG-25A-0042 | Rabbit | ELISA, WB | Human |
New SARS-CoV-2 Recombinant Antibodies
| Product Name | PID | Isotype | Applications | Species |
| anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD), mAb (rec.) (Covi-1) (preservative-free) | AG-27B-6005PF | Human IgG1 | ELISA, WB, FUNC (Blocking) | SARS-CoV-2 RBD |
| anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD), mAb (rec.) (Covi-2) (preservative-free) | AG-27B-6006PF | Human IgG1 | ELISA, WB, FUNC (Blocking) | SARS-CoV-2 RBD |
| anti-SARS-CoV-2 N Protein, mAb (rec.) (Capsi-1) (preservative free) | AG-27B-6007PF | Human IgG1 | ELISA, Colloidal Gold Immuno-chromatogr. Test | SARS-CoV-2 N Protein |
| anti-SARS-CoV-2 N Protein, mAb (rec.) (AB75-C03) | AG-27B-6304 | Mouse IgG2a | ELISA, ICC, WB | SARS-CoV-2 N Protein |
| anti-SARS-CoV-2 N Protein, mAb (rec.) (AB79-E11) (Fc Mouse) | AG-27B-6305 | Mouse IgG2a | ELISA, ICC, WB | SARS-CoV-2 N Protein |
| anti-SARS-CoV-2 N Protein, mAb (rec.) (AB83-C12) | AG-27B-6306 | Mouse IgG2a | ELISA, ICC, WB | SARS-CoV-2 N Protein |
| anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (NTD), mAb (rec.) (AB72-1-G09) | AG-27B-6307 | Mouse IgG2a | ELISA | SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1 N-Terminal Domain Protein |
| anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (NTD), mAb (rec.) (AB72-1-H10) | AG-27B-6308 | Mouse IgG2a | ELISA | SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1 N-Terminal Domain Protein |
| anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD), mAb (rec.) (AB65-3-G12) | AG-27B-6309 | Mouse IgG2a | ELISA | SARS-CoV-2 RBD |
| anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD), mAb (rec.) (AB68-A09) (Fc Human) | AG-27B-6310 | Human IgG1 | ELISA, ICC, WB | SARS-CoV-2 RBD |
| anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD), mAb (rec.) (AB68-A09) (Fc Mouse) | AG-27B-6311 | Mouse IgG2a | ELISA, ICC, WB | SARS-CoV-2 RBD |
| anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (SD2), mAb (rec.) (AB66-6-C10) | AG-27B-6312 | Mouse IgG2a | ELISA, ICC, WB | SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1 Subdomain 2 Protein |
Antiviral Compounds - Potential Small Molecule Therapeutics Against COVID-19
There are no approved drugs to treat the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Existing drugs, that have a known favorable safety profile, are being examined for strategies to treat the disease and fast-track a treatment plan. Several influenza and HIV drugs are currently undergoing clinical trial in coronavirus patients. The rational selection of drugs already on the market is being made based on their ability to inhibit any proteins essential for virus-receptor interaction and/or viral life cycle.
LITERATURE REFERENCES:
- Recent discovery and development of inhibitors targeting coronaviruses: T. Pillaiyar, et al.; Drug Discov. Today 25, 668 (2020)
- Rapid Identification of Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease by Deep Docking of 1.3 Billion Compounds: A.T. Ton, et al.; Mol. Inform. 39, 2000028 (2020)
- Potential inhibitors against 2019-nCoV coronavirus M protease from clinically approved medicines: X. Liu & X.J. Wang; J. Genet. Genomics 47, 119 (2020)
- Identification of FDA Approved Drugs Targeting COVID-19 Virus by Structure-Based Drug Repositioning: P. Wang, et al.; ChemRxiv (Preprint) (2020)
- Structure of Mpro from COVID-19 virus and discovery of its inhibitors: Z. Jin, et al.; Nature 582, 289 (2020)
AdipoGen Life Sciences offers a Selection of Antiviral Small Molecules as Potential Tools for in vitro Studies of COVID-19 (not for human use).
All Small Molecules are available in BULK Quantities at preferable BULK Pricing!
| Product Name | PID | CAS Number | Target | Antiviral Activity |
| Aloxistatin [E-64d] | AG-CR1-3737 | 88321-09-9 | Viral entry Cathepsin L |
Viral Replication |
| Amastatin . hydrochloride | AG-CP3-7003 | 100938-10-1 | Viral entry ANPEP (Aminopeptidase N) |
Viral Replication |
| Artesunate | AG-CN2-0469 | 88495-63-0 | NF-κB suppression | Viral Replication Cytokine Storm |
| Baricitinib | AG-CR1-3734 | 1187594-09-7 | JAK1/JAK2 / Immunomodulation AP-2 associated protein kinase 1 / Endocytosis |
Viral Replication |
| Boceprevir | AG-CR1-3735 | 394730-60-0 | Main Protease (Mpro) | Viral Transcription/Replication |
| Budesonide | AG-CR1-3753 | 51333-22-3 | Glucocorticod Receptors Inflammatory Factors |
Viral Replication Cytokine Storm |
| Camostat mesylate | AG-CR1-3716 | 59721-29-8 | Viral entry TMPRSS2 |
Viral Replication |
| Chloroquine . diphosphate | AG-CR1-3721 | 50-63-5 | Lysosome function Zinc ionophore Immunomodulation |
Viral Replication |
| Hydroxychloroquine . sulfate | AG-CR1-3720 | 747-36-4 | Lysosome function Zinc ionophore Immunomodulation |
Viral Replication |
| Clevudine | AG-CR1-3736 | 163252-36-6 | RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRps) | Viral Transcription/Replication |
| Darunavir | AG-CR1-3712 | 206361-99-1 | Papain-like viral protease (PLVP) | Viral Maturation/Replication |
| Darunavir . ethanolate | AG-CR1-3724 | 635728-49-3 | Papain-like viral protease (PLVP) | Viral Maturation/Replication |
| 2-Deoxy-D-glucose | AG-CR1-3681 | 154-17-6 | Glycolysis/Cell Metabolism | Viral Replication/Cytokine Storm |
| Dexamethasone | AG-CR1-3742 | 50-02-2 | Inflammatory Factors | Cytokine Storm |
| Dexamethasone phosphate . 2Na | AG-CR1-3744 | 2392-39-4 | Inflammatory Factors | Cytokine Storm |
| Dihydroartemisinin | AG-CN2-0468 | 71939-50-9 | NF-κB suppression | Viral Replication Cytokine Storm |
| Ebselen | AG-CR1-0031 | 60940-34-3 | Main Protease (Mpro)/3C-like Protease | Viral Transcription/Replication |
| EIDD-2801 (Molnupiravir) | AG-CR1-3733 | 2349386-89-4 | RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRps) | Viral Transcription/Replication |
| Elbasvir | AG-CR1-3729 | 1370468-36-2 | RdRP, Papain-like Proteinase and Helicase | Viral Replication |
| Euphol | AG-CN2-0541 | 514-47-6 | Main Protease (Mpro) | Viral Transcription/Replication |
| Famotidine | AG-CR1-3730 | 76824-35-6 | SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease (PLpro) | Viral Replication |
| Favipiravir | AG-CR1-3717 | 259793-96-9 | RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRps) | Viral Transcription/Replication |
| Ibudilast | AG-CR1-3738 | 50847-11-5 | Macrophage Inhibitory Factor (MIF) Immunomodulation |
Viral Replication Cytokine Storm |
| Imatinib mesylate | AG-CR1-3725 | 220127-57-1 | Virion fusion with endosomal membrane | Viral Replication |
| Leupeptin . hemisulfate | AG-CP3-7000 | 103476-89-7 | Viral entry TMPRSS2 |
Viral Replication |
| Lopinavir | AG-CR1-3715 | 192725-17-0 | Coronavirus endopeptidase C30 (CEP_C30) | Viral Maturation/Replication |
| Merafloxacin | AG-CR1-3756 | 91188-00-0 | Programmed -1 Ribosomal Frameshifting | Viral Replication |
| Mycophenolic acid | AG-CN2-0419 | 24280-93-1 | SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease (PLpro) | Viral Replication |
| Nafamostat mesylate | AG-CR1-3731 | 82956-11-4 | Viral entry TMPRSS2 |
Viral Replication |
| Nelfinavir . mesylate | AG-CR1-3726 | 159989-65-8 | Post-entry inhibitor | Viral Replication |
| Niclosamide | AG-CR1-3643 | 50-65-7 | Endosome acidification | Viral Replication |
| Niclosamide . ethanolamine | AG-CR1-3644 | 1420-04-8 | Endosome acidification | Viral Replication |
| Nitazoxanide | AG-CR1-3723 | 55981-09-4 | Viral hemagglutinin Viral IE2 |
Viral Maturation/ |
| Opaganib | AG-CR1-3749 | 915385-81-8 | Sphingosine Kinase 2 Inflammatory Factors |
Cytokine Storm |
| Oseltamivir . phosphate | AG-CR1-3714 | 204255-11-8 | Viral neuraminidase Release of viral particles |
Viral Replication |
| PX-12 | AG-CR1-3739 | 141400-58-0 | Main Protease (Mpro)/3C-like Protease | Viral Transcription/Replication |
| Remdesivir | AG-CR1-3713 | 1809249-37-3 | RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRps) | Viral Transcription/Replication |
| AG-CR1-3722 | 1191237-69-0 | RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRps) | Viral Transcription/Replication | |
| Ribavirin | AG-CR1-3719 | 36791-04-5 | RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRps) RNA capping activity Viral mutation rates Immunomodulation |
Viral Transcription/Replication |
| Ritonavir | AG-CR1-3683 | 155213-67-5 | Coronavirus endopeptidase C30 (CEP_C30) | Viral Maturation/Replication |
| Rosuvastatin . calcium salt | AG-CR1-3728 | 147098-20-2 | Main Protease Mpro | Viral Replication |
| Ruxolitinib . phosphate salt | AG-CR1-3645 | 1092939-17-7 | JAK1/JAK2 Immunomodulation |
Viral Replication |
| Ruxolitinib (free base) | AG-CR1-3624 | 941678-49-5 | JAK1/JAK2 Immunomodulation |
Viral Replication |
| Saquinavir . mesylate | AG-CR1-3727 | 149845-06-7 | Main Protease Mpro | Viral Replication |
| Shikonin | AG-CN2-0487 | 517-89-5 | Main Protease (Mpro)/3C-like Protease | Viral Transcription/Replication |
| Suramin . hexasodium salt | AG-CR1-3575 | 129-46-4 | Viral Entry/Fusion RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRps) |
Viral Transcription/Replication |
| TDZD-8 | AG-CR1-3740 | 327036-89-5 | Main Protease (Mpro)/3C-like Protease | Viral Transcription/Replication |
| Telaprevir | AG-CR1-3741 | 402957-28-2 | 3C-like Protease | Viral Replication |
| Tofacitinib | AG-CR1-3625 | 477600-75-2 | JAK1/JAK3 Immunomodulation |
Viral Replication |
| Tofacitinib citrate | AG-CR1-3732 | 540737-29-9 | JAK1/JAK3 Immunomodulation |
Viral Replication |
| Tofacitinib citrate | CDX-T0461 | 540737-29-9 | JAK1/JAK3 Immunomodulation |
Viral Replication |
| Umifenovir . HCl [Arbidol] | AG-CR1-3718 | 131707-23-8 | Viral entry Fusion into host cells |
Viral Replication |
| VIP (human, mouse, rat) . AcOH [RLF-100] | AG-CP3-0041 | 1444827-29-5 | Viral Replication Immunomodulation |
Viral Replication |
NOT FOR HUMAN USE
Cytokine Storm and Severity of COVID-19
The most critically ill COVID-19 patients are known to undergo a cytokine storm leading to poor prognosis and need of urgent anti-inflammatory treatment/hospitalization. There are many variations on this phenomenon and they go by many names: systemic inflammatory response syndrome, macrophage activation syndrome or cytokine release syndrome (CRS).
A cytokine storm is an overproduction of immune cells and their activating compounds, the cytokines. When SARS-CoV-2 enters the lungs, it triggers an immune response, attracting immune cells to the region to attack the virus, resulting in localized inflammation. But in some patients, excessive or uncontrolled levels of cytokines are released which then activate more immune cells, resulting in hyperinflammation. The resulting lung inflammation and fluid buildup can lead to respiratory distress and can be contaminated by a secondary bacterial pneumonia. This increases the risk of mortality in patients. Cytokine storms might explain why some people have a severe reaction to coronaviruses while others only experience mild symptoms. They could also be the reason why younger people are less affected, as their immune systems are less developed and so produce lower levels of inflammation-driving cytokines. Cytokine storms are a common complication not only of COVID-19 and flu but of other respiratory diseases caused by coronaviruses such as SARS and MERS. They are also associated with non-infectious diseases such as multiple sclerosis and pancreatitis.
Therefore the diagnostic detection and treatment of cytokine storms has become an important part of rescuing severe patients. Targets like IL-1, IL-6, IL-7, IL-10, IL-18, IL-33, IFN-γ, TNF-α or many others might play an important role in cytokine release syndrome (CRS). Detection of their levels and blockage of their signaling pathways with immunomodulatory agents (biologicals, small molecules) is expected to become a new method for the treatment of severe patients.
AdipoGen Life Sciences offers a broad range of Cytokine Immunoassays as well as recombinant cytokines and blocking antibodies, which are already being successfully used to research the various cytokine storm factors involved and to characterize the immune response.
LITERATURE REFERENCES:
- COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression: P. Mehta, et al. ; The Lancet 395, p1033 (2020)
- The cytokine release syndrome (CRS) of severe COVID-19 and Interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) antagonist Tocilizumab may be the key to reduce the mortality: C. Zhang, et al. ; Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 55, 105954 (2020)
Selected Biologicals for Cytokine Storm Research
More Information
|
Product Flyer
|
|
|
Reagents for SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 Research - Overview Flyer
|
 Download |
|
|
|
||
|
Reagents for SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 Research >>This Flyer includes direct URL-links to the product landing pages. |
Download PDF with Weblinks |
