Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Microtubules, Post-translational Modifications of Tubulins and Neurodegeneration
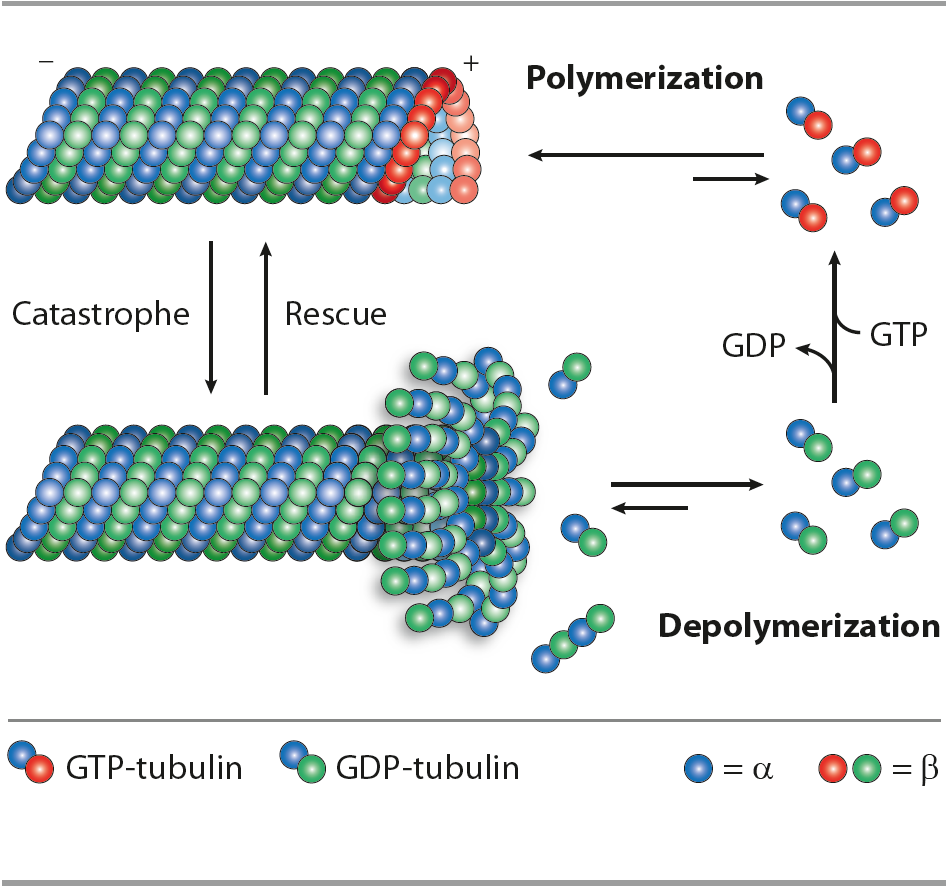
The internal organization, shape, motility and life cycle of eukaryotic cells are all controlled by a complex network of polymeric filaments called the cytoskeleton, which includes actin filaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules. These polymers have important roles in arranging and maintaining the integrity of intracellular compartments. Microtubules are the largest cytoskeletal components involved in intracellular transport (cell signaling), cell migration/trafficking, cell division and proliferation. Microtubules control differentiative processes involving intracellular rearrangements and changes in morphology. Complex microtubule structures form the core components of centrosomes and the centrioles important for mitosis, and the core structures of cilia and flagella, which are called axonemes. Despite their functional diversity, all microtubules are assembled from heterodimers of α‑tubulin and β‑tubulin. Soluble α‑tubulin-β‑tubulin dimers polymerize into polar microtubules in the presence of GTP. Understanding of the cell structure and function is essential for gaining deeper knowledge of normal pathways such as morphogenesis, wound healing, neurogenesis and immune response, as well as abnormal processes such as metastasis and tumor-related angiogenesis.
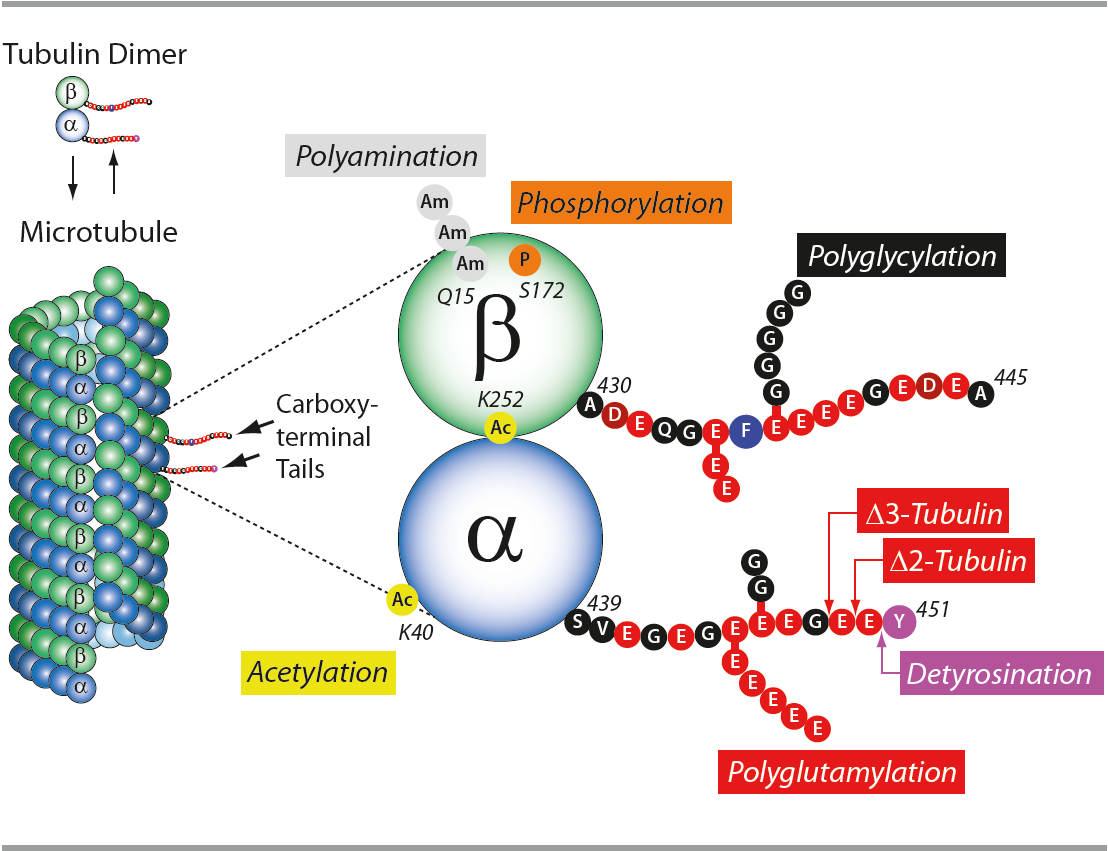
In neurons, microtubules, actin filaments and neurofilaments compose the cytoskeleton, maintaining cell polarity, architecture and morphology. Microtubules (MTs) are highly dynamic polymers formed of tubulin α and β heterodimers. Regulation of MTs polymerization is controlled by microtubule associated proteins, post-translational modifications of tubulin α and β, microtubules and signaling molecules. Deregulation of the neuronal cytoskeleton/MT function constitutes a key insult during the pathogenesis of nervous system diseases, leading to neurodegenerative diseases, including Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, Alzheimer’s diseases (AD), Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia, Parkinson’s disease (PD) and others. Posttranslational modifications (PTMs) are highly dynamic and often reversible processes where protein functional properties are altered by addition of a chemical group or another protein to its amino acid residues. Tubulins and microtubules (MTs) are major substrates for PTMs. They include tyrosination/detyrosination, D2-tubulin formation, acetylation, phosphorylation, polyamination, ubiquitination, polyglutamylation and glycylation. PTMs are involved in fine-tuning of interactions between microtubules and different MT-interacting proteins.
Literature References:
-
Microtubule +TIPs at a glance: A. Akhmanova & M.O. Steinmetz; J. Cell Sci. 123, 3415 (2010)
-
Post-translational regulation of the microtubule cytoskeleton: mechanisms and functions: C. Janke & J.C. Bulinski; Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 12, 773 (2011)
-
Rab GTPases and microtubule motors: C.P. Horgan & M.W. McCaffrey; Biochem. Soc. Trans. 39, 1202 (2011)
-
Rab6 is a Modulator of the Unfolded Protein Response: Implications for Alzheimer’s Disease. H.L. Elfrink, et al. ; J. Alzh. Disease 28, 1 (2011)
-
The tubulin code: molecular components, readout mechanisms, and functions: C. Janke; J. Cell. Biol. 206, 461 (2014)
-
Microtubules in health and degenerative disease of the nervous system: A.J. Matamoros & P.W. Baas; Brain. Res. Bull. 126, 217 (2016)
-
The emerging role of the tubulin code: From the tubulin molecule to neuronal function and disease: S.Chakraborti, et al.; Cytoskeleton 73, 521 (2016)
Most Comprehensive & Unique Reagents for Microtubule Research
UNIQUE - Validated Post-translational Modification-specific Antibodies
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| anti-Polyglutamylation Modification, mAb (GT335) | AG-20B-0020 |
Recognizes the posttranslational modification (poly)glutamylation on proteins. Recognizes most forms of polyglutamylated tubulin (α- and β-tubulin), independent of the length of the glutamate side chains. No specificity to particular tubulin isoforms nor to tubulin from particular species are observed. Detects also other (poly)glutamylated proteins. Since no consensus modification site is known for protein (poly)glutamylation, the detection is not sequence-specific. However, an acidic environment of the modification site is required. Works in Immunocytochemistry, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation and Western blot. |
| anti-Polyglutamylation Modification, mAb (GT335) (Biotin) | AG-20B-0020B |
Recognizes the posttranslational modification (poly)glutamylation on proteins. Recognizes most forms of polyglutamylated tubulin (α- and β-tubulin), independent of the length of the glutamate side chains. No specificity to particular tubulin isoforms nor to tubulin from particular species are observed. Detects also other (poly)glutamylated proteins. Since no consensus modification site is known for protein (poly)glutamylation, the detection is not sequence-specific. However, an acidic environment of the modification site is required. Works in Immunocytochemistry, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation and Western blot. |
| anti-Polyglutamate chain (polyE), pAb (IN105) | AG-25B-0030 |
Recognizes C-terminally located linear α-glutamate chains of 4 and more glutamate residues. Works in Immunocytochemistry, Immunohistochemistry and Western blot. |
| anti-α-Tubulin (acetylated), mAb (TEU318) | AG-20B-0068 |
Detects K40 acetylation of α-tubulin; signal specifically increased by modification with tubulin acetyltransferase α-TAT1. Works in Immunocytochemistry and Western blot. |
| anti-Acetyl-alpha-Tubulin (Lys40), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM318) | REV-31-1204-00 |
This antibody reacts to α-tubulin acetylated at Lysine 40. No cross-reactivity to non-acetylated α-tubulin at Lysine 40. This antibody may also react to mouse or rat Acetyl- α-tubulin at Lysine 40, as predicted by immunogen homology. Works in Immunocytochemistry and Western blot. |
| anti-β-Tubulin (β-monoE), pAb (IN115) | AG-25B-0039 |
The β-monoE antibody selectively labels glutamylation of β-tubulin due to its specificity to a sequence motif (GE(*-E)F) that only exists in β-tubulin isotypes. It allows to specifically detect β-tubulin glutamylation in brain tubulin, where other antibodies predominantly detect α-tubulin glutamylation. Works in Immunocytochemistry, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation and Western blot. |
| anti-Tubulin (glycylated), pAb (Gly-pep1) | AG-25B-0034 |
This antibody recognizes mono or bi-glycylated tubulins. The activity of glycylating enzymes (TTLL3 and TTLL8) in cultured cells leads mainly to the modification of α- and β-tubulin, but also of other, yet unidentified protein substrates also detected by the antibody Gly-pep1. In immunofluorescence labeling, the antibody strongly labels glycylated microtubules. As glycylation of microtubules is particularly found in cilia and flagella, Gly-pep1 labels motile cilia as well as some (mostly very long) primary cilia. Works in Immunocytochemistry, Immunoprecipitation and Western blot. |
| anti-Delta2-Tubulin, pAb (IN120) | AG-25B-0044 |
This antibody recognizes the posttranslationally modified form of α-tubulin known as ∆2-tubulin. This modification is generated after enzymatic removal of two C-terminal amino acids, Y and E in a process of detyrosination (removal of Y by detyrosinating enzymes from the VASH and the MATCAP/TMCP families), followed by the removal of the penultimate E residue by enzymes from the cytosolic carboxy peptidase (CCP) family. Works in Immunocytochemistry, Immunofluorescence and Western blot. |
| anti-Delta2 alpha-Tubulin (dC2-alpha-Tubulin), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM447) | REV-31-1339-00 |
This antibody reacts to Δ2 α-tubulin (dC2-alpha-tubulin), a C-terminally trimmed version of α-tubulin that lacks a carboxy-terminal glutamyl-tyrosine group. Works in Immunocytochemistry, Immunofluorescence and Western blot. |
| anti-Detyrosinated α-Tubulin (human), Rabbit mAb (RM444) | REV-31-1335-00 |
This antibody detyrosinated human α-tubulin. It has no cross-reactivity to non-detyrosinated α-tubulin. Detyrosination is a form of posttranslational modification that occurs on α-tubulin. It consists of the removal of the C-terminal tyrosine to expose a glutamate at the newly formed C-terminus. Tubulin polymers, called microtubules, that contain detyrosinated alpha-tubulin are usually referred to as Glu-microtubules while unmodified polymers are called Tyr-microtubules. Works in Immunocytochemistry, Immunofluorescence and Western blot. |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
|
AG-27B-0009 |
Recognizes human, mouse, rat and drosophila tubulin-GTP in Immunocytochemistry. | |
|
AG-27B-0005 |
Recognizes human, mouse and bovine α-tubulin in Immunocytochemistry and Western blot. | |
| anti-α-Tubulin, mAb (rec.) (F2C) (ATTO 488) | AG-27B-0005TD | Recognizes human, mouse and bovine α-tubulin in Immunocytochemistry. |
| anti-α-Tubulin, Rabbit Monoclonal (RM113) | REV-31-1016-00 | This antibody reacts to α-tubulin, including tubulin α-1A chain and tubulin α-1B chain. Works in Western Blot, IP, Chromatin IP (ChIP), Immunocytochemistry and Immunohistochemistry. Also Biotin-labeled available! |
| anti-β-Tubulin, mAb (AXO45) | AG-20B-0085 |
Recognizes almost all isotypes of β-tubulin specifically in cells and tissues of human, mouse and ciliates in Immunocytochemistry, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation and Western blot. |
| anti-β-Tubulin, mAb (rec.) (S11B) | AG-27B-0008 |
Recognizes human, mouse, rat, pig, drosophila and monkey β-tubulin in Immunocytochemistry and Western blot. |
Rab proteins, members of the small GTPase superfamily, are important regulators of vesicle transport via interactions with effector proteins and motor proteins. Rab1 and 6 are implicated in anterograde and retrograde trafficking in the secretory pathway. Rab1 has been shown to be involved in autophagy by helping the formation of the pre-autophagosomal isolation membrane (phagophore). Rab6 also functions as modulator of the unfolded protein response (UPR), helping the recovery from an ER stress insult. Rab6 is upregulated in Alzheimer’s disease brain.
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
|
AG-27B-0006 |
Recognizes human, mouse, rat and dog Rab1a-GTP and Rab1b-GTP in Immunocytochemistry and Immunoprecipitation. | |
|
AG-27B-0004 |
Recognizes human, mouse and Drosophila GTP-bound Rab6a and Rab6b and mutant Rab6Q72L. Does not detect Rab6•GDP. Works in Immunocytochemistry. | |
| anti-Rab6-GTP, mAb (rec.) (AA2) (ATTO488) | AG-27B-0004TD | Recognizes human, mouse and Drosophila GTP-bound Rab6a and Rab6b and mutant Rab6Q72L. Does not detect Rab6•GDP. Works in Immunocytochemistry. |
|
More Information
|
Downloadable Flyer
|
|
|
The Tubulin Code - Post-translational Modification Antibodies! AdipoGen offers a selection of unique antibodies specific for post-translational modifications of tubulin. Updated - March 2025 |
Download |