Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
RevMab
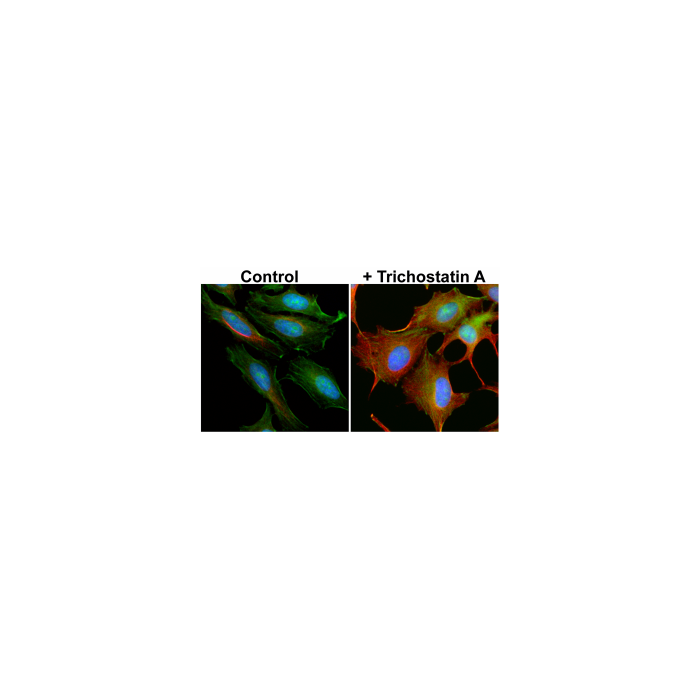
anti-Acetyl-alpha-Tubulin (Lys40), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM318)
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | alpha-Tubulin K40ac |
| Product Type | Recombinant Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Clone | RM318 |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Source/Host | Rabbit |
| Immunogen/Antigen | An acetyl-peptide corresponding to Acetyl- alpha-Tubulin (Lys40). |
| Application |
Immunocytochemistry (ICC): 1:1000-1:5000 dilution |
| Crossreactivity | All Vertebrates |
| Specificity |
This antibody reacts to alpha-Tubulin acetylated at Lysine 40. No cross reactivity to non-acetylated alpha-Tubulin at Lysine 40. This antibody may also react to mouse or rat Acetyl- alpha-Tubulin at Lysine 40, as predicted by immunogen homology. |
| Purity | Protein A purified. |
| Purity Detail | Protein A affinity purified from an animal origin-free culture supernatant. |
| Concentration | N/A |
| Formulation | Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| Accession Number | P68363 |
| Declaration | Manufactured by RevMab Biosciences. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Microtubules are key elements of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton that dynamically assemble from heterodimers of α- and β-tubulin. Two different mechanisms can generate microtubule diversity: the expression of different α- and β-tubulin genes, referred to as tubulin isotypes, and the generation of posttranslational modifications (PTMs) on α- and β-tubulin. Tubulin PTMs include the well-known acetylation or phosphorylation, and others that have so far mostly been found on tubulin, detyrosination/tyrosination, polyglutamylation and polyglycylation. These PTMs might have evolved to specifically regulate tubulin and microtubule functions. Tubulin acetylation was discovered on K40 of flagellar α-tubulin in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and is generally enriched on stable microtubules in cells. It is located on the microtubule lumenal surface. As a result of its localization at the inner face of microtubules, K40 acetylation might rather affect the binding of microtubule inner proteins, a poorly characterized family of proteins. Functional experiments in cells have further suggested that K40 acetylation regulates intracellular transport by regulating the traffic of kinesin motors probably by indirect mechanisms. Acetyltransferase α-Tat1 (or Mec-17) specifically acetylate α-tubulin K40. Acetylation of tubulin by α-Tat1 accumulates selectively in stable, long-lived microtubules thus explaining the link between this posttranslational modication and stable microtubules in cells. However, the direct cellular function of K40 acetylation on microtubules is still unclear.





