Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
PMA - Standard Reagent for THP1 Cell Differentiation
Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), also known as 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate or TPA, is a naturally occurring phorbol ester found in plants like croton oil.
PMA is commonly used to activate protein kinase C (PKC), a family of enzymes involved in various cellular processes such as cell growth, differentiation, proliferation and apoptosis (programmed cell death). PMA can activate all isoforms of PKC, but it has a particularly strong affinity for PKCα, PKCε and PKCδ. PMA-activated PKC can phosphorylate a variety of target proteins, including transcription factors, signaling molecules and cytoskeletal proteins. PKC is a critical component of many signaling pathways and its activation can lead to a cascade of intracellular events.
- Cell growth and differentiation: PMA can promote cell growth and differentiation by activating PKC. This effect is thought to be mediated by the activation of genes that promote cell growth and differentiation.
- Apoptosis: PMA can also induce apoptosis or programmed cell death. This effect is thought to be mediated by the activation of genes that promote apoptosis.
- Cancer: PMA is a known tumor promoter. This means that it can increase the risk of cancer by promoting cell growth and differentiation.
- Inflammation: PMA can induce inflammation. This effect is thought to be mediated by the activation of genes that promote inflammation.
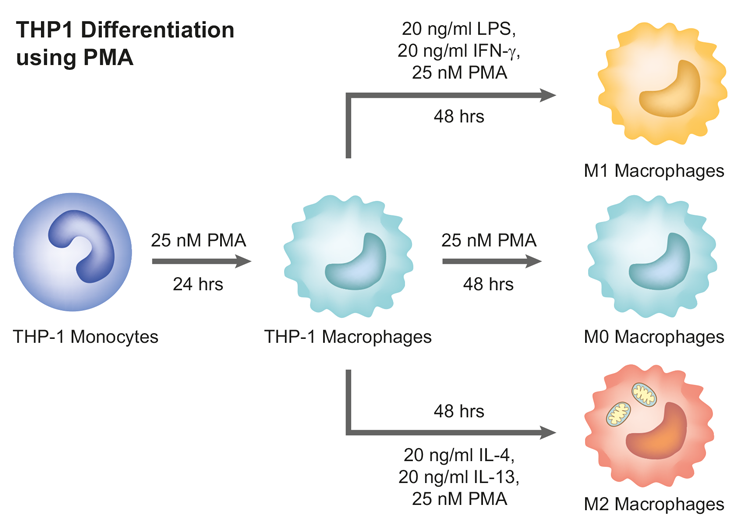
Figure: THP1 cell differentiation into macrophages using PMA.
Differentiation of THP-1 Cells
The human monocytic cell line, THP-1, is the most widely used cell line for in vitro studies investigating primary human macrophage function. The reason is that following the differentiation of THP-1 cells using PMA, they acquire a macrophage-like phenotype, which mimics in many respects, primary human macrophages (M0 macrophages). PMA is a potent activator of protein kinase C (PKC), which is a key regulator of macrophage differentiation. When PMA is added to THP-1 cells, it causes them to express the surface markers CD14, CD16 and CD68, which are characteristic of M0 macrophages. PMA also induces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines by M0 macrophages. Further treatment with PMA can activate M0 macrophages and differentiate them into M1 or M2 macrophages.
Activation of M0 Macrophages
M0 macrophages are a type of macrophages that are not yet fully activated. They are characterized by their expression of a variety of surface markers, including CD14, CD16 and CD68. M0 macrophages are also able to produce a variety of cytokines, including IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α.
Addition of PMA M0 macrophages activates them through PKC activation. Consequently, activated M0 macrophages undergo a number of changes, including, the increased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, increased production of reactive oxygen species, increased phagocytic activity and increased migration.
- PMA can induce the differentiation of M0 macrophages into M1 macrophages, which are pro-inflammatory cells that play a role in fighting infection.
- PMA can also induce the differentiation of M0 macrophages into M2 macrophages, which are anti-inflammatory cells that play a role in tissue repair.
- PMA can increase the production of reactive oxygen species by M0 macrophages, which can help to kill bacteria and other pathogens.
- PMA can increase the phagocytic activity of M0 macrophages, which allows them to engulf and destroy foreign particles.
- PMA can increase the migration of M0 macrophages, which allows them to travel to the site of infection or injury.
The differentiation of THP-1 cells into M0 macrophages is a complex process, important for the immune response to infection and injury.
Figure: THP-1 cells differentiation into M0 macrophages.
Literature References:
-
In vitro studies on the mode of action of the phorbol esters, potent tumor promoters: part 1: P.M. Blumberg; Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 8, 153 (1980)
-
In vitro studies on the mode of action of the phorbol esters, potent tumor promoters: part 2: P.M. Blumberg; Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 8, 199 (1981)
-
The choice of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate differentiation protocol influences the response of THP-1 macrophages to a pro-inflammatory stimulus: M.E. Lund, et al.; J. Immunol. Methods 430, 64 (2016)
-
Standardized protocols for differentiation of THP-1 cells to macrophages with distinct M(IFNγ+LPS), M(IL-4) and M(IL-10) phenotypes: E.W. Baxter, et al.; J. Immunol. Methods 478, 112721 (2020)
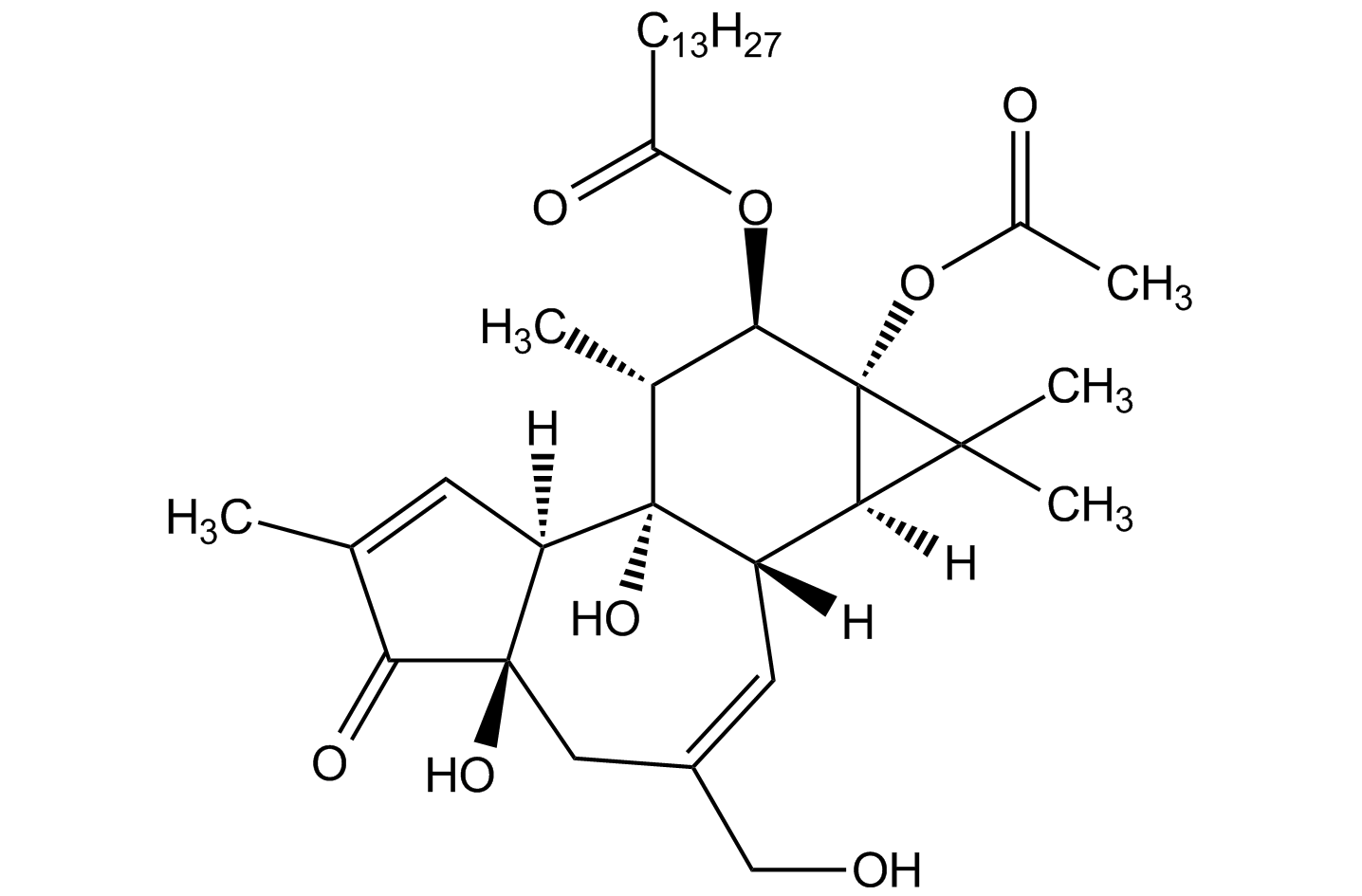
Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)
Other names: TPA; 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate
PMA is the most common phorbol. It is a potent tumor promoter and highly inflammatory in nature. It is a potent activator of protein kinase C (PKC), a family of enzymes that play a role in many cellular processes, including cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis. It is a standard reagent for THP1 cell differentiation.
AG-CN2-0010 (1 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 25 mg, BULK)
AdipoGen Life Sciences is an original Manufacturer of high-purity PMA. BULK quantities are available from Stock!
|
Product Specifications: CAS: 16561-29-8Source: Semisynthetic Purity: >98% HPLC Identity: Determined by 1H-NMR Contact us at info@adipogen.com and inquire about BULK Pricing! |
 |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| Ingenol-3-angelate (I3A) | AG-CN2-0012 | Specific PKC activator. |
| Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) | AG-CN2-0010 | Potent PKC activator. |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| Staurosporine | AG-CN2-0022 | Potent, cell permeable, reversible, ATP-competitive broad spectrum PKC antagonist. |
| Bisindolylmaleimide I | AG-CR1-0009 | Cell permeable, selective PKC inhibitor (Ki = 10 nM). |
| Bisindolylmaleimide I . hydrochloride | AG-CR1-0110 | Cell permeable, selective PKC inhibitor (Ki = 10 nM), water soluble. |
| Bisindolylmaleimide II | AG-CR1-0010 | PKC antagonist. |
| Bisindolylmaleimide III | AG-CR1-0112 | Potent and selective PKC inhibitor. |
| Bisindolylmaleimide IV | AG-CR1-0152 | Cell permeable PKC inhibitor. |
| Bisindolylmaleimide VIII . acetate | AG-CR1-0114 | Selective PKC inhibitor. |
| Bisindolylmaleimide IX . methanesulfonate | AG-CR1-0111 | Selective, cell permeable PKC inhibitor. |
| Bisindolylmaleimide X . hydrochloride | AG-CR1-0113 | Selective PKC inhibitor. |
| Bisindolylmaleimide XI . hydrochloride | AG-CR1-0109 | Selective cell permeable PKC inhibitor. |
| Calphostin C | AG-CN2-0430 | Potent, highly specific, cell permeable, light-dependent PKC antagonist. |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| Bisindolylmaleimide V | AG-CR1-0023 | Negative control for PKC inhibitors. |
| 4α-Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate | AG-CN2-0082 | Negative control for phorbol ester activation of PKC and studies with PMA. |
