Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Dual-Specificity, Tyrosine Phosphorylation-Regulated Kinases (DYRKs)
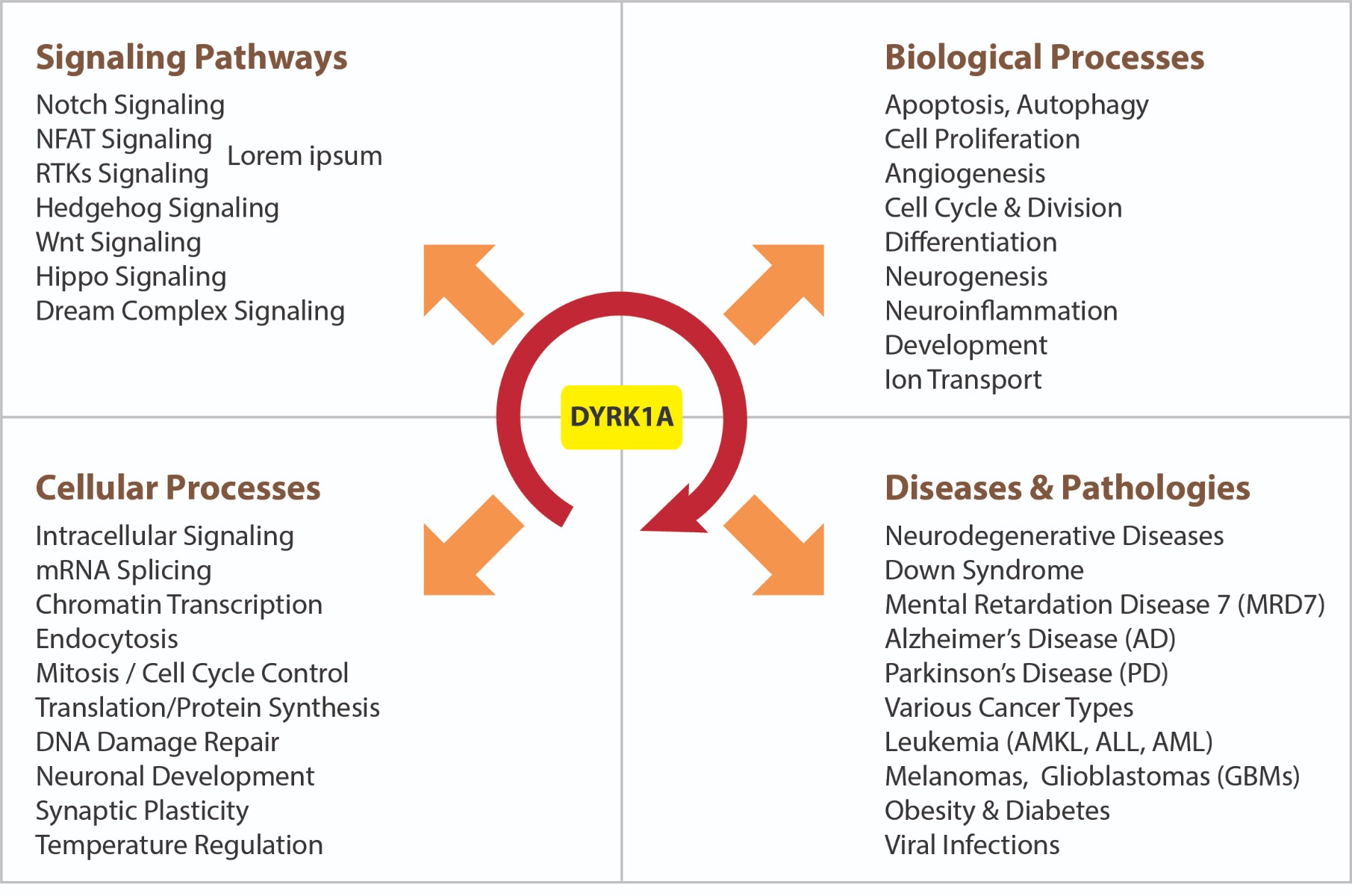
Dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinases (DYRK1A, 1B, 2-4) and cdc2-like kinases (CLK1-4) belong to the CMGC group of serine/threonine kinases. These protein kinases are involved in multiple cellular functions, including intracellular signaling, mRNA splicing, chromatin transcription, DNA damage repair, cell survival, cell cycle control, differentiation, homocysteine/methionine/folate regulation, body temperature regulation, endocytosis, neuronal development, synaptic plasticity, etc.
Abnormal expression and/or activity of some of these kinases, DYRK1A in particular, is seen in many human nervous system diseases, such as cognitive deficits associated with Down syndrome, Alzheimer’s disease, tauopathies, Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. DYRKs and CLKs are also involved in diabetes, abnormal folate/methionine metabolism, osteoarthritis, several solid cancers and leukemias, viral infections, as well as infections caused by unicellular parasites.
Figure: DYRK1A - Regulator of a myriad of processes and signaling pathways.
DYRK (dual-specificity tyrosine-regulated kinase) family members constitute an evolutionarily conserved family of protein kinases. Seven mammalian DYRK-related kinases have been identified: DYRK1A, DYRK1B, DYRK1C, DYRK2, DYRK3, DYRK4A and DYRK4B. The DYRK proteins are dual-specificity protein kinases that autophosphorylate a conserved tyrosine (Y) residue in their own activation loop but phosphorylate their substrates at serine (S) or threonine (T) residues. The Y autophosphorylation occurs during translation and induces kinase activation; however, once the protein is fully translated, kinase activity becomes restricted to S and T residues and no longer depends on Y phosphorylation. An increasing number of substrates involved in signal transduction pathways is being reported for DYRKs. One characteristic feature of several DYRK kinases is their function as priming kinases, meaning that the phosphorylation of a given residue by a DYRK is a prerequisite for the subsequent phosphorylation of a different residue by another protein kinase (GSK3 or PLK).
Phosphorylation by protein kinases is the most universally used mechanism by cells to control their structural proteins and enzymes. All major physiological phenomena are regulated by phosphorylation and many diseases are associated with abnormal phosphorylation. DYRK1A targets a multitude of exogenous protein substrates, including transcription factors (CREB, NFAT, STAT3, FOXO1, GLI1, RNApol2), splicing factors (Cyclin L2, SF2, SF3), translation factor (eIF2Be) or cytoskeletal targets (TAU and MAP1B) and synaptic proteins (dynamin I, amphiphysin I, synaptojanin I). DYRK1A phosphorylates the intracellular domain of the Notch receptor, attenuating the transcriptional effect and regulating Notch-dependent biological processes such as angiogenesis, differentiation or transcription. By phosphorylating APP, Tau, presenilin 1, Asf and septin-4; all proteins involved in either neurofibrillary degeneration or β-Amyloidosis, DYRK1A consequently is an important factor in neuronal cell death and reduced cognitive functioning. Therefore, the search for pharmacological DYRK inhibitors has become a major area of research for the discovery and development of new therapies.
Selected Reviews:
-
Dual-Specificity, Tyrosine Phosphorylation-Regulated Kinases (DYRKs) and cdc2-Like Kinases (CLKs) in Human Disease, an Overview: M.F. Lindberg & L. Meijer; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 6047 (2021)
-
Human Beta Cell Regenerative Drug Therapy for Diabetes: Past Achievements and Future Challenges: P. Wang, et al.; Front. Endocrinol. 12, 671946 (2021)
-
The Omnipresence of DYRK1A in Human Diseases: E. Deboever, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 9355 (2022)
-
Function and inhibition of DYRK1A: Emerging roles of treating multiple human diseases: Y. Yang, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 212, 115521 (2023)
-
Functions of SRPK, CLK and DYRK kinases in stem cells, development, and human developmental disorders: E.K.J. Hogg & G.M. Findlay; FEBS Lett. 597, 2375 (2023)
Leucettinibs
Leucettinibs, are a class of DYRK/CLK Kinase inhibitors inspired by the marine sponge natural product Leucettamine B. Leucettinibs, but not iso-Leucettinibs, inhibit the phosphorylation of DYRK1A substrates in cells. Leucettinibs constitute interesting biological tools, and iso-Leucettinibs, as kinase inactive isomers, are quite appropriate control reagents. They both can help to understand the involvement of DYRKs and CLKs in biological processes, complemented by the use of other chemically different inhibitors and specific molecular biology gene-inactivating tools (siRNA, shRNA). Leucettinibs provide new research tools and potential leads for further optimization toward therapeutic drug candidates.
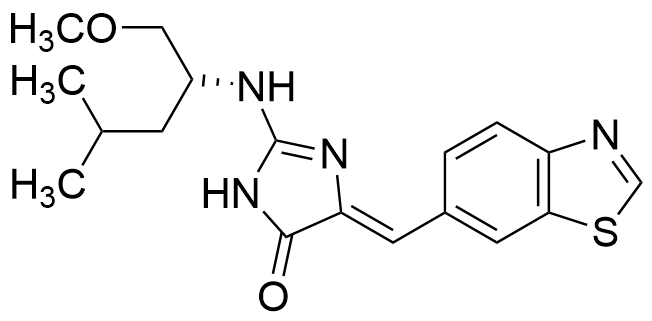
Leucettinib-21
Leucettinib-21 is a potent inhibitor of DYRK1A (IC50=2.4nM), DYRK1B (IC50=6.7nM), CLK1 (IC50=11.8nM) and CLK4 (IC50=5nM) kinases. It inhibits the phosphorylation of Tau at Thr212 and cyclin D1 at Thr286, native DYRK1A in HT-22 cells and triggers cell apoptotic cell death. It corrects cognitive deficits in a Ts65Dn model of Down syndrome and other models.
AG-MR-C0047 (1 mg, 5 mg, 25 mg and BULK)
AdipoGen Life Sciences is an original Manufacturer of Leucettinib-21.
|
Product Specifications: CAS: 2732859-75-3Purity: >99% NMR Identity: Determined by 1H-NMR Contact us at info@adipogen.com and inquire about BULK Pricing! |
 |
| Product Name | PID | CAS | DYRK Activity | Other Kinase Activity |
| Leucettinib-21 | AG-MR-C0047 | 2732859-75-3 | DYRK1A (IC50=2.4nM), DYRK1B (IC50=6.7nM) | CLK1 (IC50=11.8nM), CLK4 (IC50=5nM) |
| iso-Leucettinib-21 | AG-MR-C0048 | 3032977-73-1 | Inactive Control Substance | Inactive Control Substance |
| Leucettinib-92 | AG-MR-C0049 | 2732859-57-1 | DYRK1A (IC50=1.2nM), DYRK1B (IC50=1.8nM), DYRK3 (IC50=19.3nM) | CLK2 (IC50=0.6nM) |
| iso-Leucettinib-92 | AG-MR-C0050 | 2649456-57-3 | Inactive Control Substance | Inactive Control Substance |
| Leucettine L41 | AG-MR-C0023 | 1112978-84-3 | DYRK1A (IC50=40nM), DYRK2 (IC50=35nM) | CLK1, CLK3, GSK-3α/β, CK2, PIM1 |
| Product Name | PID | CAS | DYRK Activity | Other Kinase Activity |
| A-443654 | AG-CR1-3663 | 552325-16-3 | DYRK1A (IC50=10nM), DYRK3 (low nM range) | PKBα, PKBβ, PKBγ, PRK2, MSK1 |
| CX-4945 . HCl | AG-CR1-3629 | 1009820-21-6 | DYRK1A (IC50=6.8nM), DYRK1B (IC50=6.4nM), DYRK3 (IC50=18nM) | CK2, CLKs |
| Product Name | PID | CAS | DYRK Activity | Other Kinase Activity |
| Harmine | AG-CN2-0510 | 442-51-3 | DYRK1A, DYRK2, DYRK3 (IC50=0.08 | 0.9 | 0.8μM) | CLK2, PIM3, CK1, MAO-A |
| DYRK1A/B Inhibitor AnnH31 | AG-CR1-3650 | 241809-12-1 | DYRK1A (IC50=81nM), DYRK1B | CLK1, DYRK2, HIPK2, MAO-A (minimal) |
| DYRK1A/B Inhibitor AnnH75 | AG-CR1-3651 | 2772915-74-7 | DYRK1A (IC50=181nM), DYRK1B | CLK1, CLK4, Haspin/GSG2 |
| DYRK1 Inhibitor Negative Control AnnH79 | AG-CR1-3652 | Not Available | Inactive Control Substance | Inactive Control Substance |
| Product Name | PID | CAS | DYRK Activity | Other Kinase Activity |
| FINDY | AG-CR1-3662 | 1507367-37-4 | Suppressor of DYKR1A intramolecular Ser97-autophosphorylation. | GSK3β, MARK4, PIM1, PIM3, PLK3 |
| INDY | AG-CR1-3665 | 1169755-45-6 | DYRK1A (IC50=240nM), DYRK1B (IC50=230nM), DYRK2, DYRK3 | CLK1, CLK4, CSNK1D, PIM1 |
| TG003 | AG-CR1-3656 | AG-CR1-3656 | DYRK1A | DYRK1B | CLK1, CLK2, CLK4 |
| TG007 | AG-CR1-3666 | AG-CR1-3666 | DYRK1A | DYRK1B | n.a. |
| Product Name | PID | CAS | DYRK Activity | Other Kinase Activity |
| 7BIO | AG-MR-C0020 | 916440-85-2 | DYRK1A (IC50=1.9 μM), DYRK2 (IC50=1.3 μM) | Aurora B Kinase, Aurora C Kinase, Flt3 |
| (S)-CR8 | AG-MR-C0004 | 1084893-56-0 | DYRK1A (IC50=0.9 μM) | CDK1, CDK2, CDK5, CDK9, CK1δ/ε |
| (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate | AG-CN2-0063 | 989-51-5 | DYRK1A (IC50=330nM) | PRAK |
| ID-8 | AG-CR1-3655 | 147591-46-6 | DYRK2, DYRK4 | n.a. |
| NU6102 | AG-CR1-0020 | 444722-95-6 | DYRK1A (IC50=0.9 μM) | CDK1, CDK2, CDK4, PDK1, ROCK-II |
| (S)-Perharidine 1 | AG-MR-C0012 | 1133437-81-6 | DYRK1A (IC50=2.8 μM) | CDK1, CDK2, CDK5, CDK9, CK1δ/ε |
| Purvalanol A | AG-CR1-2903 | 212844-53-6 | DYRK1A (IC50=300nM) | CDK1, CDK2/cyclin A, Cdc2/cyclin B, CDK2/cyclin E, CDK4/cyclin D1, CDK5/p35 |
| SB216763 | AG-CR1-3659 | 280744-09-4 | DYRK1A (IC50=0.8μM) | GSK3α, GSK3β |
| SB415286 | AG-CR1-3658 | 264218-23-7 | DYRK1A (IC50=0.9μM) | GSK3α, GSK3β |
| SMI-16a | CDX-P0110 | 587852-28-6 | DYRK1A | Pim-1, Pim-2 |
| Staurosporine | AG-CN2-0022 | 62996-74-1 | DYRK1A (IC50=20nM) |
PKA, CaMK, MLCK, PKC, PKG, CDK1/cyclin B, CDK2/cyclin A, CDK4/cyclin D, CDK5/p25, GSK-3β, Pim-1 |
