Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Manumycin A - Exosome Biogenesis Inhibitor
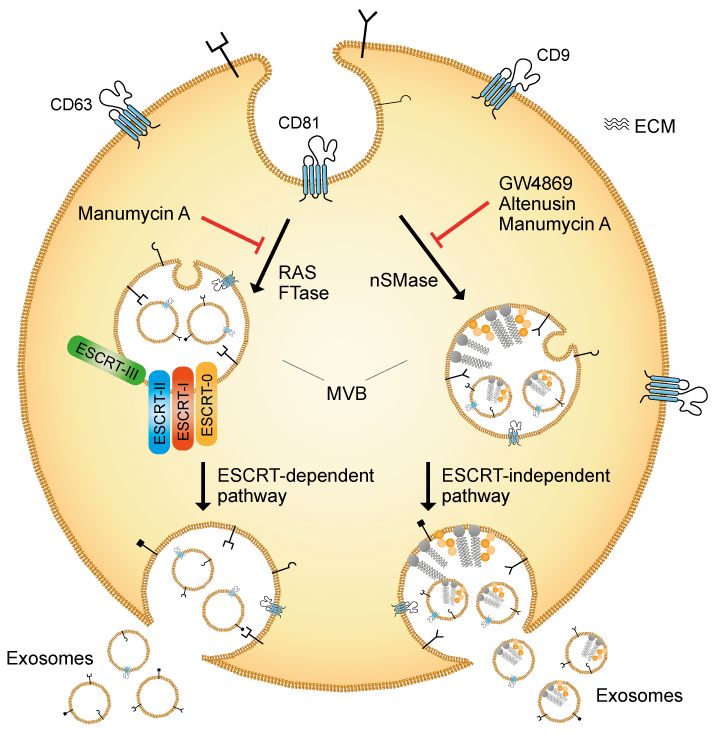
Exosomes are small vesicles that are released by cells into the extracellular space. They are formed by the invagination of the cell membrane and are then pinched off and released into the surrounding environment. Exosomes are typically about 30-100 nanometers in diameter and are composed of a lipid bilayer that encloses a variety of biomolecules, including proteins, RNA and lipids.
Exosomes play an important role in intercellular communication and are involved in a wide range of physiological and pathological processes. They can act as a means of transporting molecules between cells, help to modulate the immune system and regulate cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. Some recent studies have found exosomes to be a potential diagnostic marker for cancer and other diseases, while others have investigated the use of exosomes as a way to deliver therapeutic molecules to specific cells or tissues.
RAS signaling directly regulates the sorting of a variety of cargos into exosomes. RAS proteins are small GTPases that play a critical role in cell signaling pathways. Farnesyltransferase (FTase) is responsible for the addition of a farnesyl group to RAS proteins, which is an essential step in their proper function and localization within the cell.
Manumycin A, a natural antibiotic, was identified as an inhibitor of exosome biogenesis and secretion. Manumycin A is a selective inhibitor of FTase. By inhibiting the farnesylation of RAS, Manumycin A suppresses RAS/RAF/ERK1/2 signaling and reduces exosome generation. Targeting exosome biogenesis might be crucial for RAS signaling inhibitors to exert their anticancer effects.
Figure: Schematic of exosome biogenesis and inhibition (adapted from M. Catalano & L. O'Discroll; J. Extracell. Vesicles 9, 1703244 (2019).
Literature References:
-
Manumycin A and Its Analogues Are Irreversible Inhibitors of Neutral Sphingomyelinase: C. Arenz, et al.; Chem. Biochem. 2, 141 (2001)
-
Manumycin A suppresses exosome biogenesis and secretion via targeted inhibition of Ras/Raf/ERK1/2 signaling and hnRNP H1 in castration-resistant prostate cancer cells: A. Datta, et al.; Cancer Lett. 408, 73 (2017)
-
Manumycin A Is a Potent Inhibitor of Mammalian Thioredoxin Reductase‑1 (TrxR-1): A. Tuladhar & K.S. Rein; ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 9, 318 (2018)
-
Inhibiting extracellular vesicles formation and release: a review of EV inhibitors: M. Catalano & L. O’Driscoll; J. Extracell. Vesicles 9, 1703244 (2019) (Review)
-
Role of Ceramides and Lysosomes in Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis, Cargo Sorting and Release: R. Horbay, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 15317 (2022) (Review)
-
Exosome biogenesis: machinery, regulation, and therapeutic implications in cancer: Q.-F. Han, et al.; Mol. Cancer 21, 207 (2022) (Review)
-
Analyzing the postulated inhibitory effect of Manumycin A on farnesyltransferase: A. Hagemann, et al.; Front. Chem. 10, 967947 (2022) (Review)
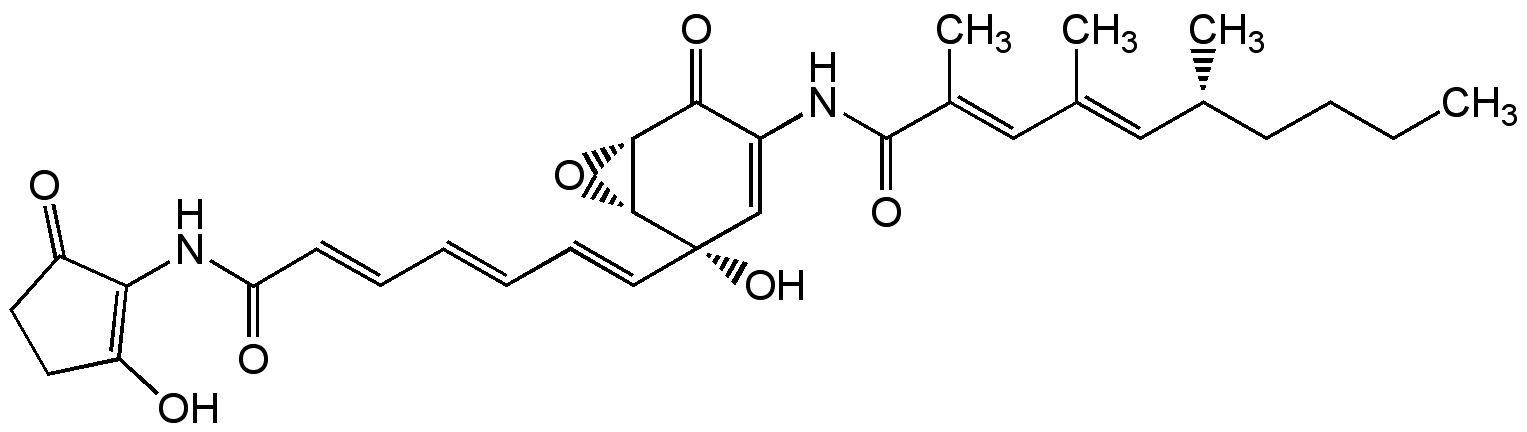
Manumycin A
Manumycin A is a potent, selective and competitive cell permeable RAS-farnesyltransferase inhibitor and an irreversible neutral sphingomyelinase nSMase inhibitor.
AG-CN2-2000 for Catalog and Bulk Items (1 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg)
This compound has been found to have a variety of biological activities, including:
- Antimicrobial activity: Against a wide range of bacteria, including Gram-positive and Gram-negative species. It is particularly effective against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and other antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
- Antitumor activity: Against a variety of cancer cell lines, including breast, ovarian and lung cancer. Works by inducing apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells and inhibiting angiogenesis in tumors.
- Anti-inflammatory activity: By inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory molecules such as TNF-α and IL-6.
- Exosome inhibitory activity: Inhibits the formation and release of exosomes.
- Immunomodulatory activity: Modulates the immune system by upregulating the production of certain immune cells and cytokines.
AdipoGen Life Sciences is an original Manufacturer of Manumycin A. Available from stock in BULK quantities!
|
Product Specifications: CAS: 52665-74-4Source: Isolated from Streptomyces parvulus Purity: >98% HPLC Identity: Determined by 1H-NMR Contact us at info@adipogen.com and inquire about BULK Pricing! |
 |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| Palmarumycin C3 | BVT-0078 | RAS-farnesyltransferase inhibitor. |
| Altenusin | AG-CN2-0143 | Noncompetitive nSMase inhibitor. |
| Arglabin | AG-CN2-0458 | RAS-farnesyltransferase inhibitor. |
| OM173-αA | AG-CN2-0158 | RAS-competitive non-CAAX mimetic type farnesyltransferase (FTase) inhibitor. |
| Andrastin A | AG-CN2-0144 | Protein farnesyltransferase (PFTase) inhibitor. |
| Manumycin B | BVT-0264 | RAS-farnesyltransferase (FTase) inhibitor. |
| Dihydromanumycin A | BVT-0414 | Manumycin A derivative not yet tested for its biological activity. |
| Deoxymanumycin A | BVT-0158 | Manumycin A derivative not yet tested for its biological activity. |
STANDARD Exosomes Markers
Sensitive and specific antibodies are an essential tool for the detection of extracellular vesicles (EVs), including exosomes, which express antigens with 3D conformations and/or post-translational modifications that often differ from the cellular counterpart. The group of tetraspanin proteins CD9, CD63 and CD81 are the most common EV-associated markers reported in the literature and have been used for EV capture in many studies, including ELISA, flow cytometry and lab-on-a-chip assays. Each of these tetraspanins has been demonstrated to play an active role in EV biogenesis or cargo sorting, suggesting their essential role in the EV secretory pathway. Ancell Corporation offers specific and sensitive antibodies for tetraspanin detection and exosome capture and a plethora of additional antigen-specific antibodies which consequently allows to phenotype EV populations based on the antigen profile.
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| anti-CD9 (human), mAb (SN4) | ANC-156- | Recognizes human CD9 [TSPAN-29]. Works in Flow Cytometry. |
| anti-CD37 (human), mAb (IPO-24) | ANC-186- | Recognizes human CD37 [TSPAN26]. Works in Flow Cytometry. |
| anti-CD53 (human), mAb (63.5A3) | ANC-204- | Recognizes human CD53 [TSPAN25]. Works in Flow Cytometry. |
| anti-CD63 (human), mAb (AHN16.1) | ANC-215- | Recognizes human CD63 [TSPAN30]. Works in Flow Cytometry, IHC. |
| anti-CD81 (human), mAb (1.3.3.22) | ANC-302- | Recognizes human CD81 [TSPAN28]. Works in Flow Cytometry and Western blot. |
For a List of human CD Antibodies available through AdipoGen Life Sciences, please download the Ancell Corporation Brochure.
Tim-4 (T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein 4) is a single-pass type I membrane protein that belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and TIM family. Tim-4 contains one Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain. It is expressed on dendritic cells and macrophages. Tim-4 plays an important role in the proliferation of T helper type 2 (Th2) cells. Tim-4 binds to phosphatidylserine (PS) on the surface of apoptotic cells in a calcium-dependent manner and mediates phagocytosis of apoptotic cells.
EV membranes are rich in phosphatidylserine (PS) and Tim-4 binds to PS on the surface of EVs. A new protocol from the group of Prof. Rikinari Hanayama describes an affinity-based method for isolating EVs using streptavidin magnetic beads conjugated with Tim-4-biotin to capture EVs in a calcium-dependent manner. This new protocol could replace ultracentrifugation, which is the most commonly used method for purifying EVs. This new Tim-4-dependent method gives a good yield and high purity and allows isolation of all populations of EVs compared to other approaches (ultracentrifugation, PEG precipitation, or selected antibodies immunoprecipitation). Various studies are currently being conducted to develop therapeutic and diagnostic methods targeting or utilizing EVs. Therefore, developing ideal methods for isolating and quantifying EVs is an active area of research.
Literature References:
1. A novel affinity-based method for the isolation of highly purified extracellular vesicles: W. Nakai, et al.; Sci. Rep. 6, 33935 (2016)
2. High purity isolation and sensitive quantification of extracellular vesicles using affinity to Tim-4: T. Yoshida, et al.; Curr. Prot. Cell Biol. 77, 3.45.1-3.45.18 (2017)
3. Bifurcated Asymmetric Field Flow Fractionation of Nanoparticles in PDMS-Free Microfluidic Devices for Applications in Label-Free Extracellular Vesicle Separation: M. Priedols, et al.; Polymers 15, 789 (2023)
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| Tim-4 (mouse):Fc (human) (rec.) (Biotin) | AG-40B-0180B | Used to isolate extracellular vesicles. Works in human and mouse. |
| Tim-4 (mouse):Fc (human) (rec.) | AG-40B-0180 | Used to isolate extracellular vesicles. Works in human and mouse. |
| Tim-4 (mouse):Fc (mouse) (rec.) | CHI-MF-110T4 | Used to isolate extracellular vesicles. Works in mouse. |
| Tim-4 (human):Fc (mouse) (rec.) | CHI-HF-211T4 | Used to isolate extracellular vesicles. Works in human. |
| Tim-4 (human):Fc (human) (rec.) | CHI-HF-210T4 | Used to isolate extracellular vesicles. Works in human. |
|
More Information |
Downloadable Flyer |
|
|
Manumycin A - Exosome Biogenesis Inhibitor AdipoGen Life Sciences offers a broad range of exosome biogenesis modulators (e.g. Manumycin A), standard exosome markers (e.g. CD9, CD63, CD81) and exosomal capturing/sorting biomarkers (Tim-4). |
Download |
