Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
Tim-4 (mouse):Fc (human) (rec.) (Biotin)
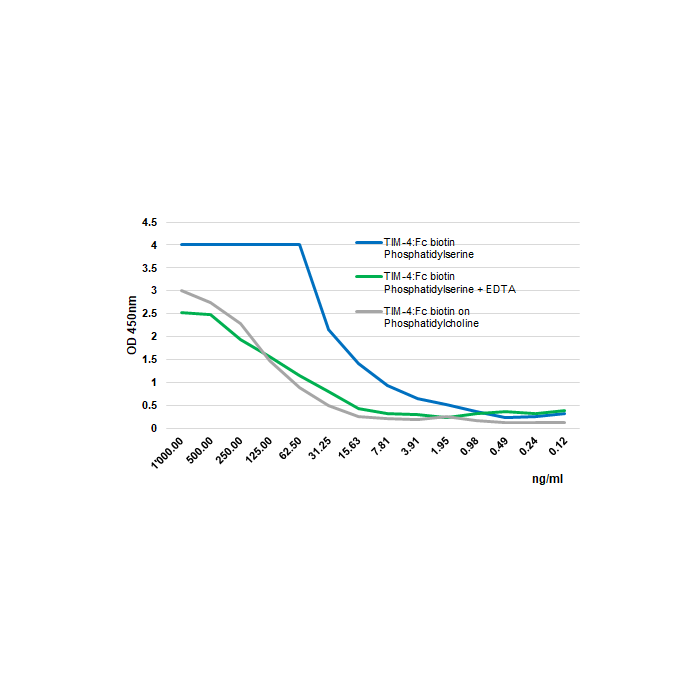
Methods: Phosphatidylserine or phosphatidylcholine (at 5µg/ml in methanol) are coated on polystyrene ELISA plate and air-dried overnight. After a blocking step in 2% BSA/PBS for 2 hours, Tim-4 (mouse):Fc (h) (rec.) (Biotin) is added (starting at 1000ng/ml with a twofold serial dilution) and incubated for 2 hours in the presence (green line) or absence of 5mM EDTA (blue line). The binding is detected using an HRP labeled anti-human Fc antibody.
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | TIM4; TIMD4; T Cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin Domain-containing Protein 4 |
| Product Type | Protein |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | CHO cells |
| Sequence |
The extracellular domain of mouse Tim-4 (aa 22-279) is fused to the N-terminus of the Fc region of human IgG1. |
| Crossreactivity |
Human Mouse |
| Application |
Function: - inhibits stimulated T cell proliferation |
| Label/Conjugates | Biotin |
| Specificity |
Tim-4 can isolate extracellular vesicles from different species (human, mouse, rat, etc.) containing phosphatidylserine (PS) at their surface. |
| Biological Activity |
Measured by its ability to inhibit anti-CD3-induced proliferation of stimulated human T cells. The Tim-4 (mouse):Fc (human) (rec.) (Biotin) is used with magnetic beads to isolate extracellular vesicles. 120ng of the protein is sufficient to isolate 1010 particles in a calcium-dependent manner. |
| MW | ~95kDa (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Endotoxin Content | <0.05EU/μg protein (LAL test). |
| Concentration | 0.1mg/ml after reconstitution. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute with 100 µl sterile water. |
| Accession Number | Q6U7R4 |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Contains PBS. |
| Protein Negative Control | |
| Other Product Data |
UniProt link: Tim-4 (mouse) |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Centrifuge lyophilized vial before opening and reconstitution. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. Working aliquots are stable for up to 3 months when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Protocols |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are released by a variety of cells into the cellular microenvironment and have the natural ability of delivering different cargos and carry bioactive molecules such as non-coding RNA, miRNAs, genomic DNA, lipids, growth factors and signaling molecules. EVs can be divided into exosomes (30-100nm), microvesicles (100-1000nm) and apoptotic bodies (>1000nm). EVs play substantial roles not only in the regulation of normal physiological processes but also in disease pathogenesis and their cargo reflects the status of parental cells at the time of secretion. Various studies are currently being conducted to develop therapeutic and diagnostic methods targeting or utilizing EVs. Therefore, developing ideal methods for isolating and quantifying EVs is an active area of research. EVs express phosphatidylserine (PS) on their outer lipid bilayer.
Tim-4 (T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein 4) is a single-pass type I membrane protein which belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and TIM family. Tim-4 contains one Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain. It is expressed on dendritic cells and macrophages. Tim-4 plays an important role in the proliferation of T helper type 2 (Th2) cells. Tim-4 binds to phosphatidylserine (PS) on the surface of apoptotic cells in a calcium-dependent manner and mediates phagocytosis of apoptotic cells.
EV membranes are rich in phosphatidylserine (PS) and Tim-4 binds to PS on the surface of EVs. A new protocol from the group of Prof. Rikinari Hanayama describes an affinity-based method for isolating EVs using streptavidin magnetic beads conjugated with Tim-4-biotin to capture EVs in a calcium-dependent manner [2]. This new protocol could replace ultracentrifugation, that is the most commonly used method for purifying EVs. This new Tim-4-dependent method gives good yield, high purity and allows isolation of all populations of EVs compared to other approaches (ultracentrifugation, PEG precipitation or selected antibodies immunoprecipitation).
See Reference 2 for a complete protocol (Download available).
- A novel affinity-based method for the isolation of highly purified extracellular vesicles: W. Nakai, et al.; Sci. Rep. 6, 33935 (2016)
- High purity isolation and sensitive quantification of extracellular vesicles using affinity to Tim-4: T. Yoshida, et al.; Curr. Prot. Cell Biol. 77, 3.45.1-3.45.18 (2017)
- Bifurcated Asymmetric Field Flow Fractionation of Nanoparticles in PDMS-Free Microfluidic Devices for Applications in Label-Free Extracellular Vesicle Separation: M. Priedols, et al.; Polymers 15, 789 (2023)






