Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
SouthBayBio - Specialized in Bioassays, Enzymes and Advanced TR-FRET Technology
South Bay Bio, LLC, formed in 2016, provides expertise in the ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS) and other innovative research areas, like UPS related assay development, HTS, protein purification, bioconjugation and custom biochemistry services.
AdipoGen Life Sciences provides all SouthBayBio Reagents worldwide. Please contact us if you request further information.
For Product Inquiries: info@adipogen.com
Sensitive E3 Ligase TR-FRET Assays
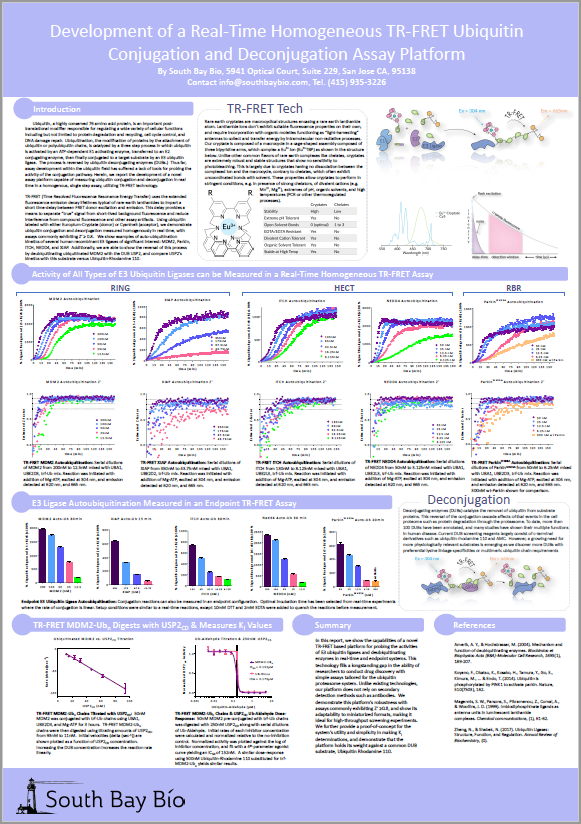
South Bay Bio's homogeneous Real-Time TR-FRET ubiquitin conjugation assays are simple; the format is 96 or 384 well low-volume plates (making them well suited for HTS). Using ubiquitin either labeled with Europium-Cryptate (donor) or Cyanine 5 (acceptor), for the first time ubiquitin conjugation and deconjugation can be measured homogenously in Real-Time (facilitating enzyme kinetics or endpoint if preferred), with assays commonly exhibiting Z’ 0.8 and a Signal to Noise of commonly >3000%.
Auto-ubiquitination kinetics of several human recombinant E3 ligases of significant interest, namely MDM2, MuRF1, ITCH and Parkin, along with ubiquitin conjugation on substrates such as p53 and s5a have been validated, as well as TR-FRET based deconjugation kinetics of several auto-ubiquitinated ligases using USP2cd and USP7. Coupled with the assays’ short development time (as no antibody development is required for assay optimization), the assay platform is ideally suited for a wide variety of academic and industry screening applications.
| Product Name | PID | Product description |
| ITCH E3 Ligase TR-FRET Kit | SBB-KF0035 | A fast and sensitive method monitoring ubiquitin conjugation onto ITCH in solution, resulting from an enzymatic ubiquitin cascade without the need of running and staining an SDS gel. The kit enables continuous TR-FRET detection of ubiquitin chain formation onto ITCH in a real-time detection setup, or in an end-point configuration if desired. |
| MDM2 E3 Ligase TR-FRET Kit | SBB-KF0030 | A fast and sensitive method monitoring ubiquitin conjugation onto GST-MDM2 in solution, resulting from an enzymatic ubiquitin cascade without the need of running and staining an SDS gel. The kit enables continuous TR-FRET detection of ubiquitin chain formation onto MDM2 in a real-time detection setup, or in an end-point configuration if desired. |
| Parkin E3 Ligase TR-FRET Kit | SBB-KF0036 | A fast and sensitive method monitoring ubiquitin conjugation onto both wild-type Parkin and a more active mutant W403A in solution, resulting from an enzymatic ubiquitin cascade without the need of running and staining an SDS gel. The kit enables continuous TR-FRET detection of ubiquitin chain formation onto Parkin in a real-time detection setup, or in an end-point configuration if desired. |
Labeled Ubiquitins for TR-FRET Experiments
Ubiquitin (Ub) is a highly conserved protein (from yeast to mammals) that plays a major role in the ubiquitination pathway. Ubiquitination, the conjugation of ubiquitin to other proteins is essential for many cellular process primarily linked to protein degradation. The ubiquitination process involves three steps with specific groups of enzymes in an ATP-dependent manner, which are activation with ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), conjugation with ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s) and ligation with ubiquitin ligases (E3s).
Good FRET pairs exhibit no overlapping spectrum between donor and acceptor, high quantum yields and red-shifted emission (e.g. Cy5) to minimize compound interference. The best donors are cryptates, comprised of rare-earth complexes (europium or terbium) with a lanthanide embedded in a macrocycle. They exhibit long-lived fluorescence, stability and robustness necessary to survive different assay conditions. Europium Cryptate-labeled Ubiquitin is ideal for measuring Ub-chain conjugation or deconjugation as a TR-FRET donor. Its ideal protein-based TR-FRET pair acceptor is Cy5-labeled Ubiquitin.
| Product Name | PID | Product description |
| Ubiquitin (human) (rec.) (Europium-Cryptate) | SBB-TR0014 | Human ubiquitin (aa1-76) (Accession Nr. P0CG47) is site-specifically conjugated to a single Europium-Cryptate moiety. All lysines are available along with a fully functional C-terminus, making it ideal for chain formation using the E1-E2 and E3 conjugation cascade. |
| Ubiquitin (human) (rec.) (Cy5) | SBB-TR0015 | Human ubiquitin (aa1-76) (Accession Nr. P0CG47) is site-specifically conjugated to a single Cyanine 5 (Cy5) moiety. All lysines are available along with a fully functional C-terminus, making it ideal for chain formation using the E1-E2 and E3 conjugation cascade. |
| Ubiquitin (human) (rec.) (6-FAM) | SBB-TR0016 | Human ubiquitin (aa1-76) (Accession Nr. P0CG47) is site-specifically conjugated to a single fluorescein (6-FAM) moiety. All lysines are available along with a fully functional C-terminus, making it ideal for chain formation using the E1-E2 and E3 conjugation cascade. |
| TRF-Ubiquitin Mix (100X) (2000 reactions) | SBB-TR0051-2K-1 | This product is a mix of Europium-Cryptate Ubiquitin (SBB-TR0014), Cy5-Ubiquitin (SBB-TR0015), and wild-type Ubiquitin (SBB-UP0013) in a ratio optimized for TR-FRET based conjugation experiments where long polyubiquitin chains are formed. Under conditions where short ubiquitin chains are formed, a different mix may be required to optimize signal to background ratio. Enzymatic incorporation of the labeled ubiquitins into chains conjugated onto a substrate protein leads to an increase in fluorescence emission at 665nm (Em-Acceptor) and decrease at emission wavelength 620nm (Em-Donor). |
Rhodamine-Labeled UB/UBL Derivatives - Protein Substrates
South Bay Bio's offers a growing list of Rhodamine 110-labeled protein substrates for Ubiquitin Research. These protein-based substrates have a typical working concentration range of 50-500nM. Hydrolysis of the conjugate results in fluorescence observable by excitation at 485nm and emission at 535nm.
| Product Name | PID | Product description |
| Ubiquitin (human) (rec.) (Rhodamine 110) | SBB-PS0001 | Human ubiquitin (aa1-76) (Accession Nr. P0CG47) conjugated at the C-terminus to a quenched Rhodamine 110 dye. |
| ISG15 (human) (rec.) (Rhodamine 110) | SBB-PS0002 | Human ISG15 (aa1-157) (Accession Nr. P05161) conjugated at the C-terminus to a quenched Rhodamine 110 dye. |
| NEDD8 (human) (rec.) (Rhodamine 110) | SBB-PS0003 | Human NEDD8 (aa1-76) (Accession Nr. Q15843) conjugated at the C-terminus to a quenched Rhodamine 110 dye. |
| SUMO1 (human) (rec.) (Rhodamine 110) | SBB-PS0028 | Human SUMO1 (aa1-97) (Accession Nr. P63165) conjugated at the C-terminus to a quenched Rhodamine 110 dye. |
| SUMO2 (human) (rec.) (Rhodamine 110) | SBB-PS0029 | Human SUMO2 (aa1-93) (Accession Nr. P61956) conjugated at the C-terminus to a quenched Rhodamine 110 dye. |
Active 20S Proteasome & 20S Immunoproteasome Proteins
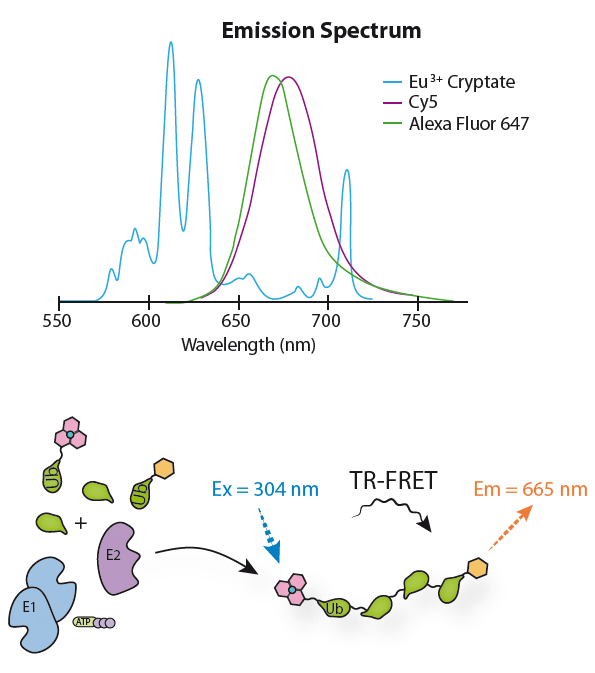
The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is the major proteolytic system in eukaryotic cells, where it catalyzes the selective degradation of short-lived regulatory proteins or the rapid turnover of misfolded proteins. One of the most important proteases in this pathway is the 26S proteasome, an ATP-dependent proteolytic complex, which is formed by the association of the barrel-shaped 20S proteasome (700kDa) and two 19S (700kDa) regulatory complexes. The 20S catalytic core is composed of 4 rings of 28 non-identical subunits; 2 rings are composed of 7 a-subunits and 2 rings are composed of 7 b-subunits. The 20S catalytic core is able to degrade a variety of peptide substrates and poly-ubiquitinated proteins involved in apoptosis, DNA repair, endocytosis and cell cycle control.
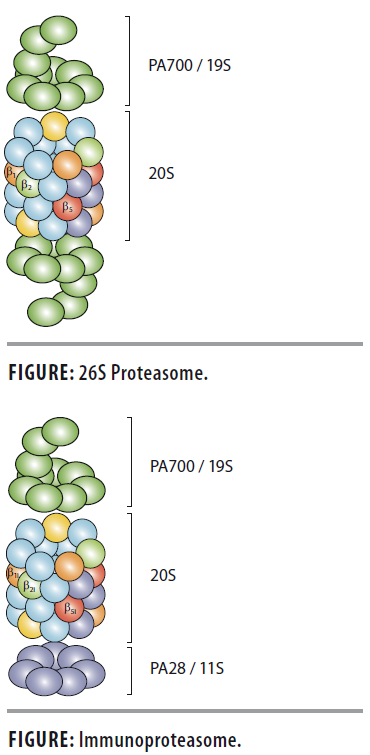
The immunoproteasome is structurally similar to constitutive 26S proteasome. The 20S core of immunoproteasome contains two outer rings composed of a-subunits and two internal 7-subunit containing rings each possessing 3 specific subunits responsible for proteasome catalytic activity. In the 20S immunoproteasome these subunits (b1, b2, b5) are replaced by three inducible subunits: PSMB9/LMP2, PSMB10/MECL1 and PSMB8/LMP7 (b1i, b2i, b5i). These stress-induced subunits allow for the production of MHC-1 associating peptides, which are displayed as antigens on the cell surface. These displayed peptides can then be recognized by immune surveillance CD8 T cells. The 20S immunoproteasome is recognized as a strong drug target for autoimmune disease and cancer. The 20S immunoproteasome is commonly associated with the 19S, PA28 a/b or the PA28g regulatory complexes.
| Product Name | PID | Product description |
| 20S Immunoproteasome (human) (untagged) | SBB-PP0004 | The 20S immunoproteasome is structurally similar to constitutive 26S proteasome. The 20S core of immunoproteasome contains two outer rings composed of α-subunits, and two internal 7-subunit containing rings each possessing 3 specific subunits responsible for proteasome catalytic activity. In immunoproteasomes these subunits (ß1, ß2, ß5) are replaced by three inducible subunits: PSMB9, PSMB10 and PSMB8, (ß1i, ß2i, ß5i). These stress-induced subunits allow for the production of MHC-1 associating peptides, which are displayed as antigens on the cell surface. These displayed peptides can then be recognized by immune surveillance CD8 T cells. 20S immunoproteasome is recognized as a strong drug target for autoimmune disease and cancer. |
| 20S Proteasome (human) (untagged) | SBB-PP0005 | The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is the major proteolytic system in eukaryotic cells, where it catalyzes the selective degradation of short-lived regulatory proteins or the rapid turnover of misfolded proteins. One of the most important proteases in this pathway is the 26S proteasome, an ATP-dependent proteolytic complex, which is formed by the association of the barrel-shaped 20S proteasome (700kDa) and two 19S (700kDa) regulatory complexes. The 20S catalytic core is composed of 4 rings of 28 non-identical subunits; 2 rings are composed of 7 α-subunits and 2 rings are composed of 7 β-subunits. The 20S catalytic core is able to degrade a variety of peptide substrates and poly-ubiquitinated proteins involved with apoptosis, DNA repair, endocytosis and cell cycle control. |
| More Information |
Product Catalog |
|
| Download the SouthBayBio Product Flyer 2017 | Download |