Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Resiniferatoxin (RTX) - Potent TRPV1 Agonist for Pain Relief
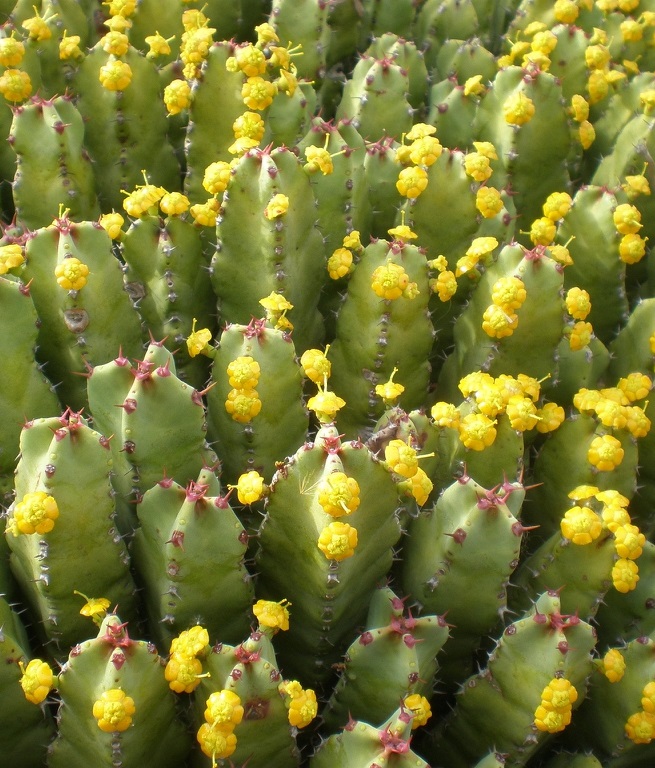

The plant Euphorbia resinifera (Resin spurge) contains a milky latex, which in the dried form is called Euphorbium. It is the most potent irritant known so far and was used in ancient traditional medicine for its analgesic properties. The irritant principle of the cactus-like plant was isolated and identified as resiniferatoxin (RTX). RTX is an ultrapotent capsaicin analog with a unique spectrum of biological activities resulting from its agonist activity at the vanilloid receptor subtype 1 (VR-1 or TRPV1) and has shown to be several thousand times more potent than capsaicin from hot chili in many assays. TRPV1, a member of the transient receptor potential channel (TRP) superfamily, is a heat- and chemo-sensitive calcium/sodium ion channel that is selectively expressed in a subpopulation of pain-sensing primary afferent neurons.
The TRPV1 agonist RTX can interact with a vanilloid receptor on primary sensory neurons mediating pain (nociception) and neurogenic inflammation. Several companies are conducting clinical trials to establish the clinical efficacy of RTX in treating severe pain in cancer and knee osteoarthritis. By injecting RTX at a discrete location, it physically deletes TRPV1-expressing Aδ and C-fiber cells in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG). When you eliminate the sensory neurons, you effectively stop pain transmission along the spinal cord and up to the brain before it begins. The treatment of sensory neurons with RTX causes calcium cytotoxicity that rapidly sutures and selectively deletes TRPV1(+) neurons. In addition, RTX has been investigated for the treatment of urinary bladder hyperreflexia, interstitial cystitis, rhinitis and chronic pain conditions. RTX has also been shown anti-inflammatory activity in T. spiralis infection, by inhibiting the Th1 immune response through the inhibition of Th1 cytokines in the intestinal phase.
Figure: Euphorbia resinifera
Literature References:
-
Resiniferatoxin, a phorbol-related diterpene, acts as an ultrapotent analog of capsaicin, the irritant constituent in red pepper: A. Szallasi & P.M. Blumberg; Neurosci. 30, 515 (1989)
-
The vanilloid agonist resiniferatoxin for interventional-based pain control: M.J. Iadarola & A.J. Mannes; Curr. Top Med. Chem. 11, 2171 (2011) (Review)
-
Regulation of Pain Genes—Capsaicin vs Resiniferatoxin: Reassessment of Transcriptomic Data: R.K. Singla, et al.; Front. Pharmacol. 11, 551786 (2020)
-
Human TRPV1 and TRPA1 are receptors for bacterial quorum sensing molecules: N. Tobita, et al.; J. Biochem. 170, 775 (2021)
-
The effects of vanilloid analogs structurally related to capsaicin on the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 channel: Y. Oka, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 30, 101243 (2022)
-
TRP channels in cancer pain: A. Spring de Almeida, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 904, 174185 (2023) (Review)
Resiniferatoxin (RTX) Highly Pure - Highly Active
AG-CN2-0534 (0.1 mg and 0.5 mg sizes from stock)
RTX is a phorbol-related diterpene ester analog of capsaicin. RTX is a highly potent transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) agonist (Ki=43pM) and acts as a selective modulator of primary afferent neurons. The primary action of RTX is to activate sensory neurons responsible for the perception of pain. The mode of action of Resiniferatoxin (RTX) is to bind and activate the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1), a non-selective cation channel in the plasma membrane of primary afferent sensory neurons. This increases the permeability to cations and leads to an influx of calcium and sodium ions. The influx of cations causes the neuron to depolarize, transmitting signals similar to those that would be transmitted if the innervated tissue were being burned or damaged. This stimulation is followed by desensitization and analgesia, in part because the nerve endings die from calcium overload. Inflammation and nerve damage result in the up-regulation of TRPV1 transcription and therefore, modulators of TRPV1 channels are potentially useful in the treatment of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. RTX is a very potent natural compound with a high affinity for afferent sensory pain neurons that leaves other sensory neurons unaffected.
AdipoGen Life Sciences is an original Manufacturer of Resiniferatoxin. Available from stock. Ask for BULK quantities!
|
Product Specifications: CAS: 57444-62-9Source: Isolated from Euphorbia resinifera Purity: >98% HPLC Identity: Determined by MS
Contact us at info@adipogen.com and inquire about BULK Pricing! |
 |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| Capsaicin | CDX-C0941 | TRPV1 agonist |
| Dihydrocapsiate | CDX-D0419 | TRPV1 agonist |
| Nordihydrocapsiate | CDX-N0121 | TRPV1 and hTRPA1 agonist |
| N-Vanillylnonanamide | CDX-N0181 | TRPV1 agonist (analog of capsaicin) |
| N-(3-Oxododecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone | CDX-O0031 | TRPV1 agonist |
| N-Octanyol-DL-homoserine lactone | CDX-O0062 | TRPV1 and TRPA1 agonist |
| N-Decanyol-DL-homoserine lactone | CDX-D0388 | TRPV1 and TRPA1 agonist |
| Shogaol | CDX-S0279 | TRPV1 and TRPA1 agonist |
| Incensol | AG-CN2-0482 | TRPV3 agonist |
| Incensol acetate | AG-CN2-0484 | TRPV3 agonist |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| SB366791 | AG-CR1-0034 | Potent and selective TRPV1 antagonist |
| Pellitorine | AG-CN2-0009 | TRPV1 antagonist |
| Osthole | CDX-O0097 | TRPV3 antagonist |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| Paeoniflorin | CDX-P060 | NMDA and TRPV1 modulator |
|
More Information
|
Downloadable Flyer
|
|
|
Resiniferatoxin (RTX) - Potent TRPV1 Agonist for Pain Relief AdipoGen Life Sciences offers a broad range of TRPV modulators and is a manufacturer of the highly potent TRPV1 agonist, Resiniferatoxin (RTX). AdipoGen’s RTX is isolated from cultivated plants from European plant nurseries in compliance with the CITES regulation, and it is available in BULK quantities.
|
Download |
