Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Targeting GLP-1R, GIPR & GCGR in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Research
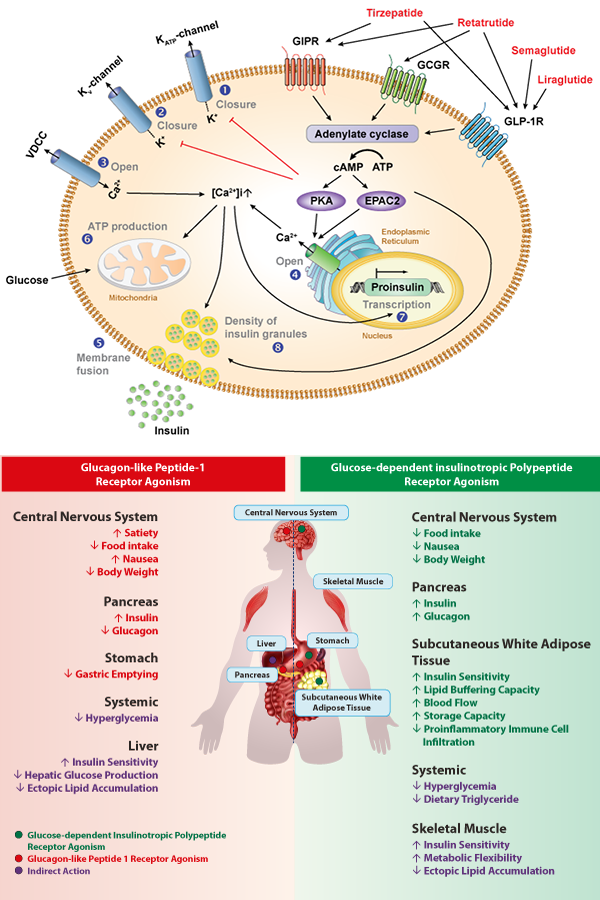
Incretins are gut-derived hormones, members of the glucagon superfamily. There are two main incretin hormones in humans: GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide; also known as gastric inhibitory peptide) and GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1). Both hormones are secreted by endocrine cells that are located in the epithelium of the small intestine and are secreted on ingestion of glucose or nutrients to stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic β cells. GIP and GLP-1 exert their effects by binding to their specific receptors, the GIP receptor (GIPR) and the GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R), which belong to the G-protein coupled receptor family. Receptor binding activates and increases the level of intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate in pancreatic β cells, thereby stimulating insulin secretion glucose-dependently. In addition to their insulinotropic effects, GIP and GLP-1 play critical roles in various biological processes in different tissues and organs that express GIPR and GLP-1R, including the pancreas, fat, bone and the brain. Within the pancreas, GIP and GLP-1 together promote β cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis, thereby expanding pancreatic β cell mass, while GIP enhances postprandial glucagon response and GLP-1 suppresses it. In adipose tissues, GIP but not GLP-1 facilitates fat deposition. In bone, GIP promotes bone formation while GLP-1 inhibits bone absorption. In the brain, both GIP and GLP-1 are thought to be involved in memory formation as well as the control of appetite.
Therefore, in addition to their effects on insulin secretion, GLP-1 and GIP also have other metabolic effects, such as reducing glucagon secretion from the pancreas, slowing down gastric emptying and promoting satiety.
GLP-1R agonists work by mimicking the effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). By activating GLP-1 receptors, GLP-1R agonists help to increase insulin release and lower blood sugar levels. They also slow down the emptying of food from the stomach, which can help to reduce post-meal spikes in blood sugar.
GIPR agonists work by targeting the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptor. By activating GIP receptors, GIP agonists can enhance insulin secretion and lower blood sugar levels. They may also reduce appetite and food intake, which can help to support weight loss.
Recently, GLP-1/GIP/Glucagon receptor triagonists have been in development and clinical trials. In addition to GLP-1R and GIPR, these agonists also act as Glucagon Receptor (GCGR) agonists. Glucagon (GCG), a hormone secreted from pancreatic α-cells, acts in opposition to insulin and plays as an essential regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism. GCGR plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels and energy balance. By decreasing glucagon release, these agonists support the body in maintaining more consistent blood sugar levels, which not only aids in weight loss but also provides overall metabolic benefits. Furthermore, the reduced glucagon levels can lead to a decrease in food intake and an increase in energy expenditure, resulting in a favorable shift toward weight loss. The synergistic action of these three important receptors provides a multifaceted approach to weight loss.
In addition, cagrilintide is now being developed in combination with the GLP-1 agonist semaglutide as "CagriSema" to achieve sustained weight loss in persons with overweight and obesity. Amylin, released with insulin from beta cells in the pancreas, induces its satiating effect via both the homoeostatic and hedonic regions of the brain. Semaglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, reduces appetite via GLP-1 receptors in the hypothalamus and increases the production of insulin, and reduces glucagon secretion, delaying gastric emptying. These separate, but related mechanisms of action of an amylin-analog and a GLP-1 receptor agonist appear to have an additive effect on appetite reduction.
Figures: GLP-1R and GIPR Signaling (adapted from Diabetes Ther. 10, 1645 (2019)) and GLP-1R and GIPR Agonists Effects (adapted from Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 31, 410 (2020)).
Literature References:
- How May GIP Enhance the Therapeutic Efficacy of GLP-1? R.J. Samms, et al.; Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 31, 410 (2020) (Review)
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Beyond Their Pancreatic Effects: X. Zhao, et al.; Front. Endocrinol. 12, 721135 (2021) (Review)
- GLP-1 and GIP receptor signaling in beta cells – A review of receptor interactions and co-stimulation: A. Mayendraray, et al.; Peptides 151, 170749 (2022) (Review)
- Bumps and humps in the success of Tirzepatide as the first GLP1 and GIP receptor agonist: R. Ali, et al.; Health Sci. Rev. 4, 100032 (2022) (Review)
- GLP-1a: Going beyond Traditional Use: L. Fornari Laurindo, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 739 (2022) (Review)
- Tirzepatide, a dual GIP/GLP‑1 receptor co‑agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes with unmatched effectiveness regarding glycaemic control and body weight reduction: M.A. Nauck & D.A. D'Alessio; Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 21, 169 (2022) (Review)
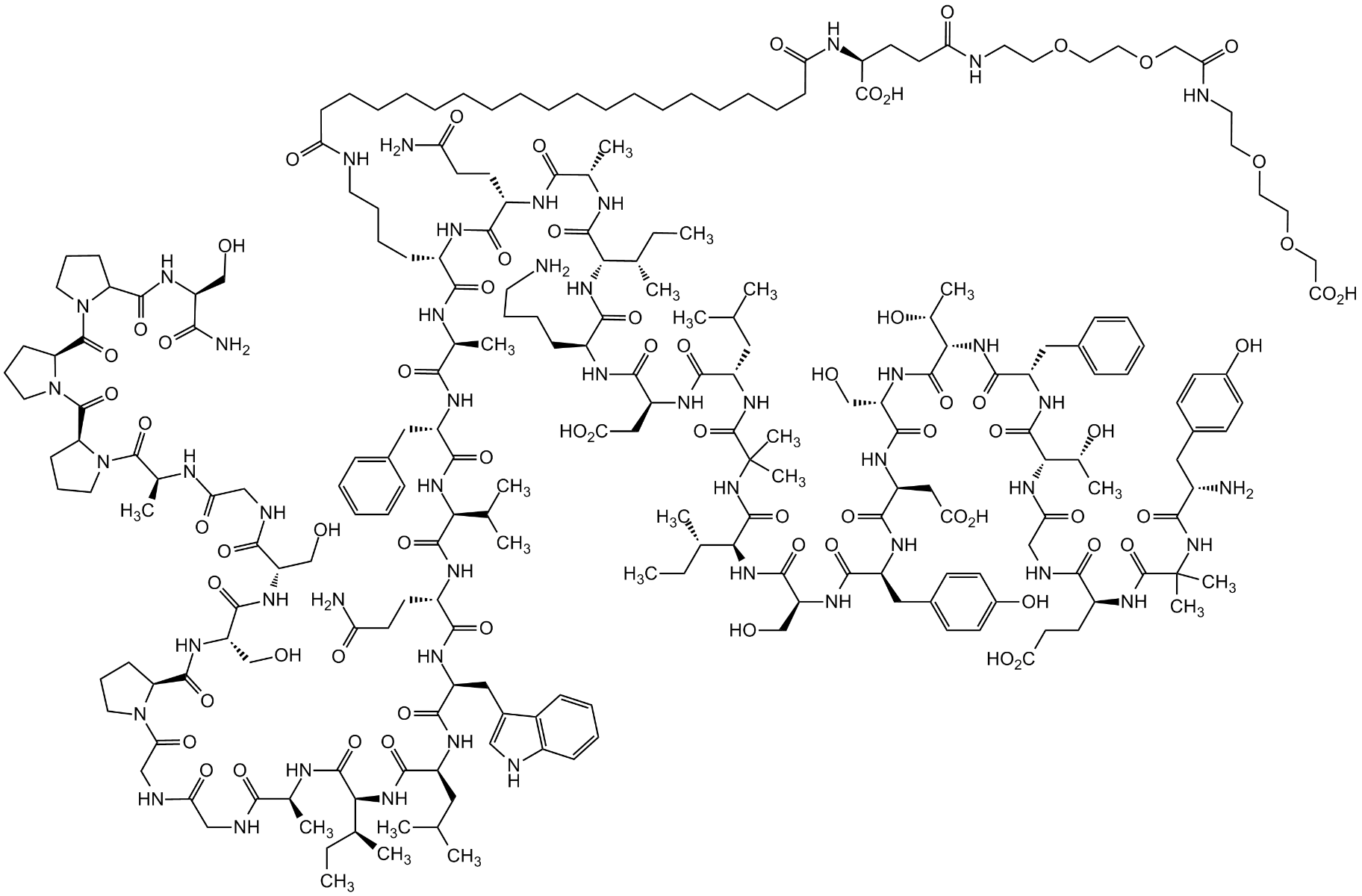
Retatrutide
Sequence: H-Tyr-(Aib)-Gln-Gly-Thr-Phe-Thr-Ser-Asp-Tyr-Ser-Ile-(α-Me-Leu)-Leu-Asp-Lys-(diacid-C20-gamma-Glu-(AEEA)-Lys)-Ala-Gln-(Aib)-Ala-Phe-Ile-Glu-Tyr-Leu-Leu-Glu-Gly-Gly-Pro-Ser-Ser-Gly-Ala-Pro-Pro-Pro-Ser-NH2
Retatrutide is a novel triple agonist peptide of the glucagon receptor (GCGR), glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R). Retatrutide potently activates the GLP-1R signaling pathway to stimulate glucose-dependent insulin secretion through activity at the GIP receptor (GIPR) or the GLP-1R. Retatrutide is a synthetic peptide with glucose-lowering effects. It is an antidiabetic agent against type 2 diabetes (T2D), stimulating insulin and suppressing glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent manner. Retatrutide was also shown to delay gastric emptying, lower fasting and postprandial glucose concentration, decrease food intake and reduce body weight in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Tirzepatide
Sequence: H-Tyr-{Aib}-Glu-Gly-Thr-Phe-Thr-Ser-Asp-Tyr-Ser-Ile-{Aib}-Leu-Asp-Lys-Ile-Ala-Gln-{diacid-γ-Glu-(AEEA)2-Lys}-Ala-Phe-Val-Gln-Trp-Leu-Ile-Ala-Gly-Gly-Pro-Ser-Ser-Gly-Ala-Pro-Pro-Pro-Ser-NH2
Tirzepatide is a novel dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. Tirzepatide potently activates the GLP-1R signaling pathway to stimulate glucose-dependent insulin secretion through activity at the GIP receptor (GIPR) or the GLP-1R. Tirzepatide has glucose-lowering effects. It is an antidiabetic agent against type 2 diabetes (T2D), stimulating insulin and suppressing glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent manner. Tirzepatide was also shown to delay gastric emptying, lower fasting and postprandial glucose concentration, decrease food intake and reduce body weight in patients with type 2 diabetes.
|
Product Information: CAS: 2023788-19-2 Formula: C225H348N48O68 MW: 4813.5 |
 |
|
|
Ask for BULK Prices - info@adipogen.com - Cagrilintide . AcOH - Liraglutide - Mazdutide - Retatrutide - Semaglutide - Semaglutide . AcOH - Survodutide - Tirzepatide Purity Specification for all: >98% HPLC |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| Liraglutide | AG-CP3-0034 | Liraglutide is a long-acting acylated glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. |
| Retatrutide . sodium salt | AG-CP3-0044 | Retatrutide is a novel triple agonist peptide of the glucagon receptor (GCGR), glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R). |
| Semaglutide | AG-CP3-0040 | Semaglutide is a longer-acting alternative glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist to Liraglutide. |
| Semaglutide . acetate | AG-CP3-0032 | Semaglutide is a longer-acting alternative glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist to Liraglutide. Salt form. |
| Tirzepatide | AG-CP3-0043 | Tirzepatide is a novel dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| GLP-1R (human) (rec.) (His) | AG-40B-0279 |
This protein binds to GLP-1, Semaglutide and Tirzepatide. It is of potential use for screening of new GLP-1R agonists. |
| GLP-1R (human) (rec.) (His) (Biotin) | AG-40B-0279B |
This protein can be used to block GLP-1 in vitro or for high-throughput screening (HTS) assays (binding of GLP-1 analogs). Potential use for screening of new GLP-1R agonists. |
| GLP-1R (human) (monomer):Fc (silent) InVivoKine™ | AG-40B-0272 |
This protein binds to GLP-1, Semaglutide and Tirzepatide. It is of potential use for screening of new GLP-1R agonists. Can be used to block GLP-1 in vivo. |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| Cagrilintide . acetate NEW | AG-CP3-0047 | Cagrilintide is a novel long-acting nonselective amylin receptors (AMYR) and calcitonin G protein-coupled receptor (CTR) agonist. |
| Mazdutide NEW | AG-CP3-0045 | Mazdutide is a novel long-acting dual glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor and glucagon receptor (GCGR) agonist. |
| Survodutide NEW | AG-CP3-0046 | Survodutide is a novel long-acting dual glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor and glucagon receptor (GCGR) agonist. |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| DMB [GLP-1R Agonist] | AG-CR1-3759 | DMB is a small molecule GLP-1 receptor agonist that exerts its activating effect by forming hydrogen bonds with the Tyr42, Cys71 and Ser84 residues of GLP-1R. |
| Linagliptin | AG-CR1-3618 | Highly potent and selective competitive inhibitor of dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (DPP4; DPP IV; CD26), an enzyme that degrades glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Prevents the inactivation of endogenous GLP-1 and GIP. |
| Metformin . HCl | AG-CR1-3689 | AMPK activator. Increases plasma concentrations of the glucose-lowering gut incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which may contribute to metformin's glucose-lowering effect. |
| Metformin Lipodisq Sterile Solution | IAX-700-103 | AMPK activator. Increases plasma concentrations of the glucose-lowering gut incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which may contribute to metformin's glucose-lowering effect. |
| Orlistat | AG-CN2-0050 | Hypolipemic cell permeable and irreversible pancreatic, gastric and carboxylester lipase inhibitor with anti-obesity activity. It promotes gastric emptying and secretion of gut peptides that modulate postprandial responses and attenuates the release of GIP. |
| Rebaudioside A | CDX-R0090 | Rebaudioside A is a glucosylated steviol glycoside studied and used as a non-glycemic sweetener. It is a α-glucosidase inhibitor and can inhibit ATP-sensitive K+-channels. In vitro rebaudioside A stimulated the insulin secretion from MIN6 cells in a dose- and glucose-dependent manner. It increases glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) secretion in a 2-dimensional mouse intestine model. |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| BRP [BRINP2-related Peptide] | AG-CP3-0048 |
Triggers central FOS activation and acts independently of leptin, GLP-1 receptor (GLP1R) and melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R). Instead, it activates the central CREB-FOS signaling pathway. BRP does not cause changes in pancreatic activity and does not affect blood glucose levels and insulin secretion. |
|
More Information
|
Downloadable Flyer
|
|
|
GLP-1R, GIPR & GCGR Agonists AdipoGen Life Sciences offers a broad range of peptide-based tools for Obesity & Diabetes Research. This includes many glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R), glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIPR) and glucagon receptor (GCGR) agonists.
|
Download |
