Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
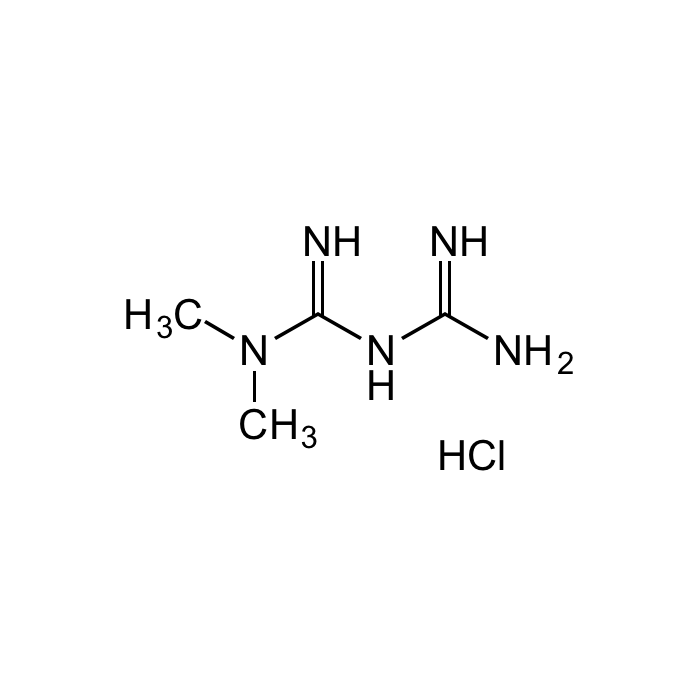
Metformin . hydrochloride
As low as
35
CHF
CHF 35.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3689-G0011 gCHF 35.00
AG-CR1-3689-G0055 gCHF 60.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 1,1-Dimethylbiguanide . HCl; NSC 91485; DMGG; LA 6023 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C4H11N5 . HCl |
| MW | 129.2 . 36.5 |
| CAS | 1115-70-4 |
| RTECS | DU1800000 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water (5mg/ml) or DMSO (5mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | OETHQSJEHLVLGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | CN(C(NC(N)=N)=N)C.Cl |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- AMPK activator.
- Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Reported to stimulate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), leading to the reduction in acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) activity and induction of fatty acid oxidation. Mitochondrial electron transport chain complex I inhibitor, reducing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS).
- Antidiabetic and anti-hyperglycemic agent that reduces blood glucose levels, improves insulin sensitivity and decreases insulin resistance. Its metabolic effects, including the inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis, are mediated in part by activation of the LKB1-AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) pathway.
- Used as weight-loss agent in obesity and as insulin sensitizer in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Leptin sensitizer to mediate the weight-loss effect in the brain.
- Increases plasma concentrations of the glucose-lowering gut incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which may contribute to metformin's glucose-lowering effect.
- Anticancer agent with antiproliferative and proapoptotic activity in cancer cell lines.
- Autophagy activator.
- Activates the aPKC-CBP pathway in neural precursors to promote neurogenesis.
- Targets brown adipose tissue (BAT) in vivo and reduces oxygen consumption.
- Anti-inflammatory agent. Described to suppress inflammatory responses by inhibition of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) via AMPK-dependent and independent pathways. Also described to inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome activation, subsequent caspase-1 cleavage and interleukin-1β secretion.
Product References
- Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action: G. Zhou, et al.; J. Clin. Invest. 108, 1167 (2001)
- Enhanced secretion of glucagon-like peptide 1 by biguanide compounds: N. Yasuda, et al.; BBRC 298, 779 (2002)
- The kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic effects of metformin: R.J. Shaw, et al.; Science 310, 1642 (2005)
- AMP-activated protein kinase in metabolic control and insulin signalling: M.C. Towler & D.G. Hardie; Circ. Res. 100, 328 (2007)
- Metformin activates an atypical PKC-CBP pathway to promote neurogenesis and enhance spatial memory formation: J. Wang, et al.; Cell Stem Cell 11, 23 (2012)
- Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: An overview: B. Viollet, et al.; Clin. Sci. 122, 253 (2012)
- Metformin in cancer: Translational challenges: R.J.O. Dowling, et al.; J. Mol. Endocrinol. 48, R31 (2012)
- Metformin and Inflammation: Its Potential Beyond Glucose-lowering Effect: Y. Saisho; Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 15, 196 (2015) (Review)
- Metformin increases hepatic leptin receptor and decreases steatosis in mice: X. Tang, et al.; J. Endocrinol. 230, 227 (2016)
- The AMP analog AICAR modulates the Treg/Th17 axis through enhancement of fatty acid oxidation: G.A. Gualdoni, et al. FASEB J. 30, 3800 (2016)
- Involvement of glucagon-like peptide-1 in the glucose-lowering effect of metformin: E. Bahne, et al.; Diabetes Obes. Metab. 18, 955 (2016) (Review)
- A guide to immunometabolism for immunologists: L.A. O'Neill, et al.; Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16, 553 (2016)
- The mechanisms of action of metformin: G. Rena, et al.; Diabetologia 60, 1577 (2017)
- Pharmacological modulation of autophagy: therapeutic potential and persisting obstacles; L. Galluzzi, et al.; Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 16, 487 (2017)
- Metformin targets brown adipose tissue in vivo and reduces oxygen consumption in vitro: P. Breining, et al.; Diabetes Obes. Metab. 20, (2264) (2018)
- Metformin improves depressive-like symptoms in mice via inhibition of peripheral and central NF-κB-NLRP3 inflammation activation: R.-W. Du & W.-G. Bu; Exp. Brain Res. (Epub ahead of print) (2020)
- AMPK regulation of Raptor and TSC2 mediate metformin effects on transcriptional control of anabolism and inflammation: J.L. Can Nostrand, et al.; Genes Dev. (Epub ahead of print) (2020)