Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Ubiquitin Proteasome System (UPS)
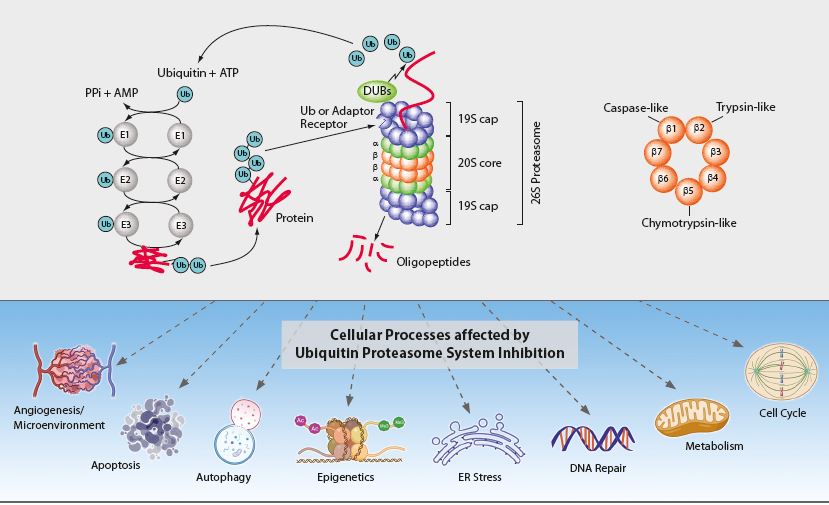
The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) and the autophagic-lysosomal pathway are the two major degradation systems for both native and misfolded proteins in eukaryotic cells. They do not act independently from each other. Defective autophagy results in the accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins, impacting the flux of the UPS, while dysfunction of the UPS can promote a compensatory induction of autophagy. Through protein degradation and the maintenance of protein homeostasis, the UPS regulates many normal cellular processes including signal transduction, cell cycle control, transcription and apoptosis (see Figure). The regulated proteolysis of bulk and misfolded proteins is strictly controlled by the 26S proteasome complex.
Figure: The Ubiquitin-Proteasome System Inhibition and affected Cellular Processes
The 26S proteasome complex recognizes polyubiquitinated proteins, which were marked for elimination by the E1, E2 and E3 ubiquitinating enzymes (see Figure). Upon recognition, unfolding and transfer of the de-ubiquitinated target protein by the 19S regulatory cap into the interior of the cylindrical 20S proteasome core particle, protein degradation is facilitated by catalytic β-subunits having nucleophilic N-terminal threonine (Thr1) residues. Although eukaryotic 20S proteasomes harbor seven different β-subunits in their two-fold symmetrical α7β7β7α7 stacked complexes, only three β-subunits per β-ring [subunits β1 (caspase-like), β2 (trypsin-like) and β5 (chymotrypsin-like)] are proteolytically active. These three β-subunits are major targets for small molecule proteasome inhibitors. Proteasome inhibition has implications in a number of human diseases such as cancer (e.g. multiple myeloma (MM)), inflammation and ischemic stroke and is an important therapeutic target.
Several components of the UPS have been validated as potential anticancer targets, including 20S proteasomes, 19S proteasome-associated deubiquitinases (DUBs) and ubiquitin ligases (E3s). One of the strategies to improve the current status of cancer treatment is to repurpose old drugs with UPS-inhibitory properties as new anticancer agents.
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| Bortezomib [PS-341] | AG-CR1-3602 | Inhibits chymotrypsin-like and caspase-like activity (IC50=3-5nM). |
| Carfilzomib [PR-171] | AG-CR1-3669 | Inhibits the chymotrypsin-like β5 subunit of the constitutive 20S proteasome (IC50=5.2nM) and the β5i subunit [LMP7] of the 20S immunoproteasome (IC50=14nM). |
| Delanzomib [CEP-18770] | AG-CR1-3673 | Inhibits the chymotrypsin-like β5 subunit of the constitutive 20S proteasome (IC50=3.8nM) and the caspase-like β1 subunit (IC50=~70nM). |
| (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate | AG-CN2-0063 | Inhibits chymotrypsin-like activity (IC50~200nm). |
| Epoxomicin | AG-CN2-0422 | Inhibits predominant chymotrypsin-like activity (IC50=4nM). |
| Ixazomib [MLN2238] | AG-CR1-3670 | Inhibits all the three catalytic activities of the constitutive 20S proteasome: chymotrypsin-like β5 subunit (IC50=3.4nM), trypsin-like β2 subunit (IC50=3.5μM) and the caspase-like β1 subunit (IC50=0.03μM). |
| Ixazomib citrate [MLN9708] | AG-CR1-3671 | Inhibits all the three catalytic activities of the constitutive 20S proteasome: chymotrypsin-like β5 subunit (IC50=3.4nM), trypsin-like β2 subunit (IC50=3.5μM) and the caspase-like β1 subunit (IC50=0.03μM). |
| clasto-Lactacystin β-lactone | AG-CN2-0442 | Chymotrypsin-like, trypsin-like and caspase-like activity inhibitor (IC50~1μM). |
| Lactacystin | AG-CN2-0104 | Chymotrypsin-like, trypsin-like and caspase-like activity inhibitor (IC50=4.8μM). |
| ONX 0914 | AG-CR1-3674 | Inhibits the β5i subunit [LMP7] of the 20S immunoproteasome (IC50=73nM) with minimal cross-reactivity to the chymotrypsin-like β5 subunit of the constitutive 20S proteasome (IC50=1.04μM). |
| Oprozomib [ONX 0912] | AG-CR1-3672 | Inhibits the chymotrypsin-like β5 subunit of the constitutive 20S proteasome (IC50=36nM) and the β5i subunit [LMP7] of the 20S immunoproteasome (IC50=82nM). |
| PI-1840 [Proteasome Inhibitor] | AG-CR1-3675 | Inhibits the chymotrypsin-like β5-subunit of the constitutive 20S proteasome (IC50=27nM), with minimal trypsin-like (β2) and caspase-like (β1) activity (IC50= >100μM, for both). |
| Piperlongumine | AG-CN2-0024 | Inhibits the β5i subunit (LMP7) (IC50=15μM) with minimal inhibition of the human constitutive 20S proteasome. |
| Salinosporamide A [Marizomib] | AG-CN2-0444 | Inhibits all the three catalytic activities of the constitutive 20S proteasome: chymotrypsin-like (IC50=3.5nm); trypsin-like (IC50=28nm); caspase-like (IC50=430nm). |
| VR23 [Proteasome Inhibitor] | AG-CR1-3676 | Inhibits all the three catalytic activities of the constitutive 20S proteasome: chymotrypsin-like (IC50=50-100nm); trypsin-like (IC50=1nm); caspase-like (IC50=3μm). |
| Z-Leu-Leu-Phe-CHO [MG-110] | AG-CP3-0021 | Chymotrypsin-like activity inhibitor. |
| Z-Leu-Leu-Nva-CHO [MG-115] | AG-CP3-0015 | Chymotrypsin-like activity inhibitor. |
| Z-Leu-Leu-Leu-CHO [MG-132] | AG-CP3-0011 | Chymotrypsin-like and caspase-like activity inhibitor (IC50~1μM). |
| Z-Leu-Leu-Leu-B(OH)2 [MG-262] | AG-CP3-0024 | Chymotrypsin-like and caspase-like activity inhibitor (IC50~150nM). |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| Apigenin | CDX-A0438 | Inhibits chymotrypsin-like and trypsin-like proteasome catalytic activity. |
| Betulinic acid (>99%) | AG-CN2-0415 | Chymotrypsin-like activity activator at low micromolar concentration. |
| Betulinic acid (>97%) | AG-CN2-0417 | Chymotrypsin-like activity activator at low micromolar concentration. |
| Celastrol | AG-CN2-0460 | Inhibits 20S proteasome chymotrypsin-like activity. |
| Curcumin (high purity) | AG-CN2-0059 | Inhibits all three catalytic activities (IC50~10μM). Inhibits DUB activity. |
| Kendomycin | BVT-0001 | Inhibits 20S proteasome chymotrypsin-like activity. |
| Luteolin | AG-CN2-0098 | Inhibits chymotrypsin-like and trypsin-like proteasome catalytic activity. |
| Nelfinavir . mesylate | AG-CR1-3726 | Pan-proteasome inhibition in AMO-1 and U266 myeloma cells; 60 % inhibition of the chymotrypsin-like activity of 26S proteasome at 5μM. |
| Quercetin . dihydrate | AG-CN2-0409 | Inhibits all three catalytic activities (IC50~15μM). |
| Ritonavir | AG-CR1-3683 | Inhibits 20S proteasome chymotrypsin-like activity. |
| Saquinavir . mesylate | AG-CR1-3727 | Inhibits chymotrypsin-like and caspase-like activity of the 26S proteasome and purified 20S proteasome. |
| Shikonin | AG-CN2-0487 | Proteasome inhibitor. |
| Terrein | BVT-0193 | Inhibits chymotrypsin- and trypsin-like activity (IC50~0.3mM). |
| Withaferin A | AG-CN2-0490 | Inhibits 20S proteasome β5 subunit chymotrypsin-like activity. |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| Ac-Ala-Asn-Trp-AMC | AG-CP3-0037 | Fluorogenic substrate for specifically measuring chymotrypsin-like activity of the 20S immunoproteasome. |
| Ac-Arg-Leu-Arg-AMC | AG-CP3-0013 | Fluorogenic substrate for measuring the trypsin-like peptidase activity of the 20S proteasome. |
| Ac-Pro-Ala-Leu-AMC | AG-CP3-0036 | Fluorogenic substrate for specifically measuring caspase-like activity of the 20S immunoproteasome. |
| Ac-Trp-Leu-Ala-AMC | AG-CP3-0035 | Fluorogenic substrate for measuring the chymotrypsin-like peptidase activity of the 20S proteasome, calpains and other chymotrypsin-like proteases. |
| Boc-Leu-Arg-Arg-AMC | AG-CP3-0014 | Fluorogenic substrate for measuring the trypsin-like peptidase activity of the 20S proteasome. |
| Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-AMC | AG-CP3-0016 | Fluorogenic substrate for measuring the chymotrypsin-like peptidase activity of the 20S proteasome, calpains and other chymotrypsin-like proteases. |
| Suc-Leu-Tyr-AMC | AG-CP3-0017 | Fluorogenic substrate for measuring the chymotrypsin-like peptidase activity of the 20S proteasome. |
| Z-Leu-Leu-Leu-AMC | AG-CP3-0019 | Fluorogenic substrate for measuring the chymotrypsin-like peptidase activity of the 20S proteasome. |
| Z-Leu-Leu-Glu-AMC | AG-CP3-0022 | Fluorogenic substrate for measuring the caspase-like activity of the 20S proteasome. |
| Z-Leu-Arg-Gly-Gly-AMC | AG-CP3-0023 | Preferred substrate sequence of the human deSUMOylating enzymes SENP6 and SENP7. |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| Apcin | AG-CR1-3603 | APC/C E3 ubiquitin ligase inhibitor. |
| Auranofin | AG-CR1-3611 | Proteasomal deubiquitinase (DUB) inhibitor. |
| BAY 11-7082 | AG-CR1-0013 | RBR E3 ligase inhibitor. Effects by inactivating the E2-conjugating enzymes Ubc13 and UbcH7 and the E3 ligase LUBAC, preventing the formation of Lys63-linked and linear polyubiquitin chains. |
| Lovastatin | AG-CN2-0051 | SKP2 E3 ligase inhibitor. |
| NSC697923 | AG-CR1-3519 | Selective Ub-conjugating enzyme (E2) complex Ubc13-Uev1A inhibitor. Inhibits the formation of the Ubc13~Ub conjugate. |
| Oridonin | CDX-O0131 | CRL/SCF RING E3 activator. Activates Fbw7 an E3 ubiquitin ligase (CRL/SCF RING) of c-Myc and promotes proteasomal degradation. |
| Simvastatin | AG-CN2-0052 | SKP2 E3 ligase inhibitor. |
| Suramin . hexasodium salt | AG-CR1-3575 | Cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase inhibitor. |
| Vitexin | AG-CN2-0425 | Inhibits polyubiquitin synthesis by the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2-25K. |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| Anacardic acid | AG-CR1-0046 | SUMOylation inhibitor. |
| MLN4924 [NAE Inhibitor] | AG-CR1-3703 | Inhibits ubiquitin-activating enzyme (UAE) and SUMO-activating enzyme (SAE) with IC50 values of 1.5 and 8.2μM, respectively. |
| MLN4924 [NAE Inhibitor] Solution | AG-CS1-0103 | Inhibits ubiquitin-activating enzyme (UAE) and SUMO-activating enzyme (SAE) with IC50 values of 1.5 and 8.2μM, respectively. |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| 20S Immunoproteasome Assay Kit | SBB-KP0037 | Designed to test for specific activity of 20S immunoproteasome. |
| 20S Constitutive Proteasome Assay Kit | SBB-KP0038 | Designed to test for specific activity of 20S proteasome. |
| 20S Immunoproteasome (human) (untagged) | SBB-PP0004 | 20S immunoproteasome is most active against Suc-LLVY-AMC (AG-CP3-0016), Ac-PAL-AMC (AG-CP3-0036), and Ac-ANW-AMC (AG-CP3-0037) substrates. |
| 20S Immunoproteasome (mouse) (untagged) | SBB-PP0083 | 20S immunoproteasome is most active against Suc-LLVY-AMC (AG-CP3-0016), Ac-PAL-AMC (AG-CP3-0036), and Ac-ANW-AMC (AG-CP3-0037) substrates. |
| 20S Immunoproteasome (rat) (untagged) | SBB-PP0046 | 20S immunoproteasome is most active against Suc-LLVY-AMC (AG-CP3-0016), Ac-PAL-AMC (AG-CP3-0036), and Ac-ANW-AMC (AG-CP3-0037) substrates. |
| 20S Proteasome (human) (untagged) | SBB-PP0005 | 20S Proteasome is most active against Suc-LLVY-AMC (AG-CP3-0016), Z-LLE-AMC (AG-CP3-0022), and Ac-WLA-AMC (AG-CP3-0035) substrates. |
| 20S Proteasome (mouse) (untagged) | SBB-PP0047 | 20S Proteasome is most active against Suc-LLVY-AMC (AG-CP3-0016), Z-LLE-AMC (AG-CP3-0022), and Ac-WLA-AMC (AG-CP3-0035) substrates. |
| 20S Proteasome (rat) (untagged) | SBB-PP0086 | 20S Proteasome is most active against Suc-LLVY-AMC (AG-CP3-0016), Z-LLE-AMC (AG-CP3-0022), and Ac-WLA-AMC (AG-CP3-0035) substrates. |
| Angiocidin (human) (rec.) | AG-40B-0061 | Angiocidin shows sequence similarity with proteasome components and is also being referred to as 26A proteasome regulatory subunit S5A. |
| Ubiquitin (human) (rec.) (Europium-Cryptate) | SBB-TR0014 | Human ubiquitin (aa1-76) is site-specifically conjugated to a single Europium-Cryptate moiety. |
| Ubiquitin (human) (rec.) (Cy5) | SBB-TR0015 | Human ubiquitin (aa1-76) is site-specifically conjugated to a single Cyanine 5 (Cy5) moiety. |
| Ubiquitin (human) (rec.) (6-FAM) | SBB-TR0016 | Human ubiquitin (aa1-76) is site-specifically conjugated to a single fluorescein (6-FAM) moiety. |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| D-Biotin p-nitrophenyl ester (Biotin-ONP; BNP) | CDX-B0307 | Exploits the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins. D-Biotin p-nitrophenyl ester is commonly used as a biotin-tagged photoaffinity probe and an alkyl chain-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs. |
| Lipoyl-TRIM21 (human) (rec.) (His) | AG-40B-0182 | TRIM21 (tripartite motif-containing protein 21) is a cytosolic Fc receptor induced by interferon (IFN). TRIM21 functions as a E3 ligase. During infection, antibodies are delivered efficiently to the cytosol when bound to intracellular pathogens such as viruses and bacteria. The antibody-pathogen complex in the cytosol upon engagement of the protein TRIM21 is ubiquitinylated and degraded by the proteasome machinery. |
| Product Name | PID | Product Description |
| AMC Standard Solution | SBB-RB0128 | A fluorogenic standard useful for quantitating assays monitoring 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin (AMC) release. |
| AFC Standard Solution | SBB-RB0129 | A fluorogenic standard useful for quantitating assays monitoring 7-amino-4-trifluoromethylcoumarin (AFC) release. |
| Loading Buffer (5X) | SBB-RB0126 | Loading buffer for separation and visualization of proteins with SDS-PAGE and western blot analysis. |
| MgATP (100X) Solution | SBB-RB0127 | Pre-coupled Mg-ATP is an ideal energy source for semi-purified conjugation/degradation reactions. |