Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
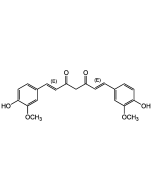
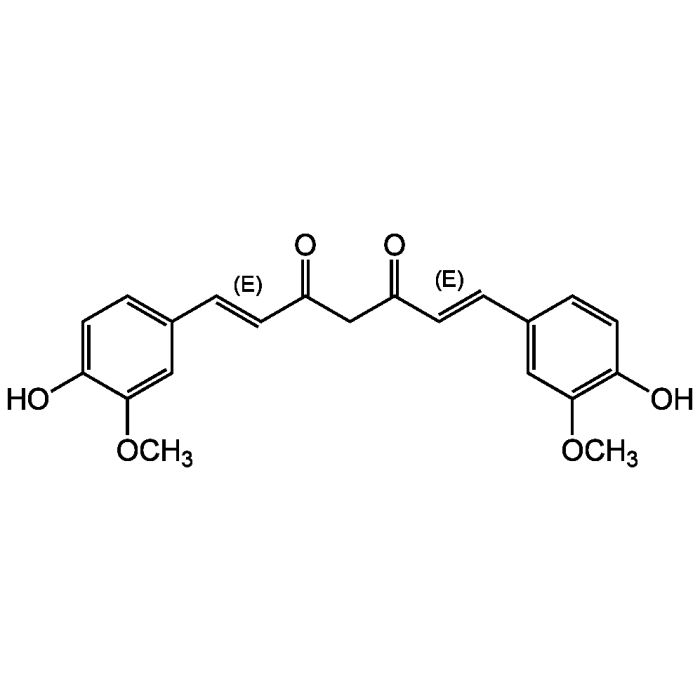
Curcumin (high purity)
As low as
45
CHF
CHF 45.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0059-M01010 mgCHF 45.00
AG-CN2-0059-M05050 mgCHF 95.00
AG-CN2-0059-M250250 mgCHF 340.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | BRN 2306965; CCRIS 3257; NSC 32982; NSC 687842; CI 75300 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C21H20O6 |
| MW | 368.4 |
| Merck Index | 14: 2673 |
| CAS | 458-37-7 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. Originally isolated from turmeric (Curcuma longa). |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Yellow-orange crystalline powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol, ethanol, ethyl acetate, acetone, methylene chloride, dimethylformamide or methyl ethyl ketone. |
| Other Product Data |
Note: This highly purified product is free of demethoxy- and bis-demethoxycurcumin and does not contain 30-40% bioactive impurities |
| InChi Key | VFLDPWHFBUODDF-FCXRPNKRSA-N |
| Smiles | COC1=CC(\C=C\C(=O)CC(=O)\C=C\C2=CC(OC)=C(O)C=C2)=CC=C1O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Curcumin is the major yellow pigment in turmeric and curry and has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, cardioprotective, antidiabetic, antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal, chemopreventive and antitumor activities. It interferes with multiple cell signaling pathways, including cell cycle (cyclin D1 and cyclin E), apoptosis (activation of caspases and down-regulation of anti-apoptotic gene products), proliferation (HER-2, EGFR and AP-1), survival (PI3K/AKT pathway), invasion (MMP-9 and adhesion molecules), angiogenesis (VEGF), metastasis (CXCR-4), tumorigenesis and development (Shh, Gli), metabolism (PPARγ, Nrf2), epigenetics (HDACs, HATs, DNA methyltransferase I and microRNAs) and inflammation (NLRP3, TLR4, NF-κB, TNF, IL-6, IL-1, COX-2 and 5-LOX).
- Anti-angiogenic. Anti-metastatic. Anti-invasive. Chemopreventive.
- Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling pathway modulator. Downregulates Shh and Gli1.
- Anti-inflammatory. Potent inhibitor of NF-κB, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), lipooxygenase (LOX), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS; NOSII). Downregulates the expression of various proinflammatory cytokines including TNF, IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12 and chemokines. Inhibits TLR4 and NLRP3 signaling.
- Modulates several key transcription factors. Down-regulate transcription factors NF-κB, AP-1 and Egr-1. Down-regulates the expression of COX-2, LOX, NOS, MMP-9, uPA, TNF, chemokines, cell surface adhesion molecules and cyclin D1. Down-regulate growth factor receptors (such as EGFR and HER2) and inhibits the activity of c-Jun N-terminal kinase, protein tyrosine kinases and protein serine/threonine kinases.
- Neuroprotective. Anti-amyloid activity.
- Cardioprotective. p300/CBP-HAT inhibitor.
- Regulates lipid metabolism and downregulates obesity. Activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) and Nrf2 cell-signaling pathways.
- Epigenetic agent. Interacts with histone deacetylases (HDACs), histone acetyltransferases (HATs), DNA methyltransferase I and microRNAs.
- Proteasome modulator/inhibitor.
Product References
- Anticancer potential of curcumin: preclinical and clinical studies: B.B. Aggarwal, et al.; Anticancer Res. 23, 363 (2003) (Review)
- Multiple biological activities of curcumin: a short review: R.K. Maheshwari, et al.; Life Sci. 78, 2081 (2006) (Review)
- Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin: V.P. Menon & A.R. Sudheer; Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 595, 105 (2007) (Review)
- Modulation of transcription factors by curcumin: S. Shishodia, et al.; Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 595, 127 (2007) (Review)
- Antitumor, anti-invasion, and antimetastatic effects of curcumin: G. Kuttan, et al.; Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 595, 173 (2007) (Review)
- Neuroprotective effects of curcumin: G.M. Cole, et al.; Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 595, 197 (2007) (Review)
- Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin, the anti-inflammatory agent, against neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic, autoimmune and neoplastic diseases: B.B. Aggarwal & K.B. Harikumar; Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 41, 40 (2009) (Review)
- Targeting inflammation-induced obesity and metabolic diseases by curcumin and other nutraceuticals: B.B. Aggarwal; Annu. Rev. Nutr. 30, 173 (2010) (Review)
- Development of curcumin as an epigenetic agent: S. Fu & R. Kurzrock; Cancer 116, 4670 (2010) (Review)
- The role of nutraceuticals in the regulation of Wnt and Hedgehog signaling in cancer: F.H. Sarkar, et al.; Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29, 383 (2010) (Review)
- Curcumin and obesity: evidence and mechanisms: L. Alappat & A.B. Awad; Nutr. Rev. 68, 729 (2010) (Review)
- Curcumin: a potential neuroprotective agent in Parkinson's disease: R.B. Mythri & M.M. Bharath; Curr. Pharm. Des. 18, 91 (2012) (Review)
- Targeting proteasomal pathways by dietary curcumin for cancer prevention and treatment: N. Hasima & B.B. Aggarwal; Curr. Med. Chem. 21, 1583 (2014)
- Curcumin as a MicroRNA Regulator in Cancer: A Review: A.A. Momtazi, et al.; Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 171, 1 (2016) (Review)
- Curcumin: A Natural Pan-HDAC Inhibitor in Cancer: S.S. Soflaei, et al.; Curr. Pharm. Des. 24, 123 (2018) (Review)
- Impact of curcumin on toll-like receptors: M. Boozari, et al.; J. Cell Physiol. 234, 12471 (2019) (Review)
- Curcumin: a modulator of inflammatory signaling pathways in the immune system: K.R. Kahkhaie, et al.; Inflammopharmacol. 27, 885 (2019) (Review)
- Antidiabetic Properties of Curcumin I: Evidence from In Vitro Studies: D.J.Den Hartogh, et al.; Nutrients 12, 118 (2020) (Review)
- Antidiabetic Properties of Curcumin II: Evidence from In Vivo Studies: D.J.Den Hartogh, et al.; Nutrients 12, 58 (2020) (Review)
- The Emerging Role of Curcumin in the Modulation of TLR-4 Signaling Pathway: Focus on Neuroprotective and Anti-Rheumatic Properties: M.A. Panaro, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 2299 (2020) (Review)
- Curcumin as an Antiviral Agent: M.R. Jennings & R.J. Parks; Viruses 12, 1242 (2020) (Review)
- COVID-19: A Case for Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome, Suppression of Inflammation with Curcumin? A.Saeedi-Boroujeni, et al.; Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 128, 37 (2021) (Review)