Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Innaxon
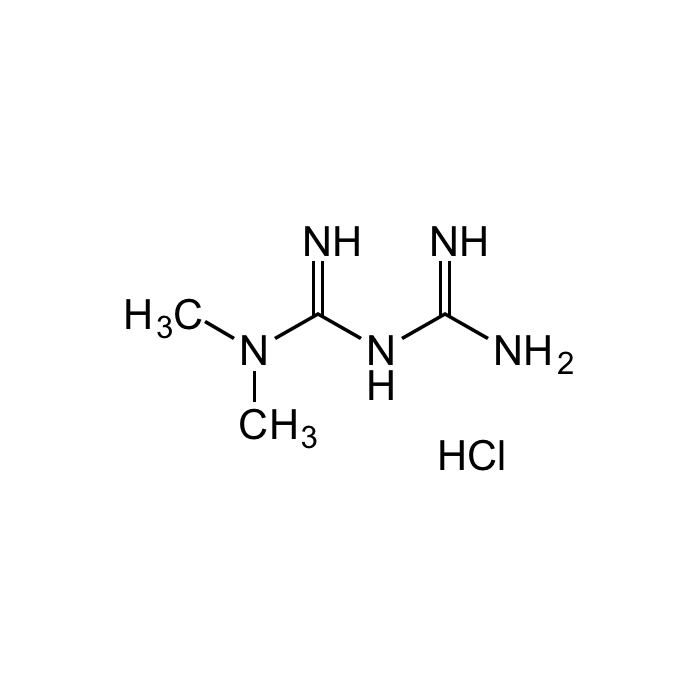
Metformin Sterile Solution
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Metformin Lipodisq™ Sterile Solution; 1,1-Dimethylbiguanide . HCl; NSC 91485; DMGG; LA 6023 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
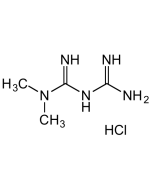
C4H11N5 . HCl |
| MW | 129.2 . 36.5 |
| CAS | 1115-70-4 |
| RTECS | DU1800000 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Colourless clear aqueous solution |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, PBS, Tris and other physiological solutions as formulated in a proprietary, thermostable, aqueous lipid nanoparticulate formulation (Lipodisq). |
| Reconstitution | Avoid the use of buffers with divalent ions such as Ca or Mg or pH <6.5 or >8.0, which can cause particle instability. Unformulated metformin is soluble in water or DMSO. |
| Formulation | Liquid, detergent-free discoidal nano-formulation made of styrene-maleic acid lipid particles (SMALP), lecithin and sterile water. |
| Concentration | 1mg/ml (0.1% w/vol) |
| Biological Activity |
Discoidal nano-particles can incorporate hydrophobic, poorly water-soluble compounds, such as lipids, lipoproteins and glycolipids. - Cell culture tested (human macrophage cell line) (MTT). - Recommended starting dilution: 1:200 or higher. - Optimal working concentrations depend on the applications and need to be determined. - Published procedures using Lipodisq formulations (Curcumin and IAXO TLR4 antagonists) in vivo rodent models at 3-10mg/kg. Recommended route of administration is subcutaneous (s.c.) with oral or nasal application as a possible alternative, which needs to be optimized. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Innaxon. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet: Our product description may differ slightly from the original manufacturers product datasheet.
|
| InChi Key | OETHQSJEHLVLGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | CN(C(NC(N)=N)=N)C.Cl |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Avoid skin and eye contact. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
- Metformin Sterile Solution is a ready-to-use nano-formulated aqueous solution.
- Metformin is an antihyperglycemic agent of the biguanide class, used for the management of type II diabetes and is currently prescribed to at least 120 million people worldwide. It is an AMPK activator and a mitochondrial electron transport chain complex I inhibitor, reducing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS). This antidiabetic and anti-hyperglycemic agent reduces blood glucose levels, improves insulin sensitivity, and decreases insulin resistance. Insulin sensitizer in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Increases plasma concentrations of the glucose-lowering gut incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which may contribute to metformin’s glucose-lowering effect. An anticancer agent with antiproliferative and proapoptotic activity in cancer cell lines. Autophagy activator. Targets brown adipose tissue (BAT) in vivo and reduces oxygen consumption. Anti-inflammatory agent by inhibition of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) via AMPK-dependent and independent pathways. Also described to inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome activation, subsequent caspase-1 cleavage and interleukin-1β secretion. Since the emergence of SARS-CoV-2, Metformin has been investigated as a prophylactic agent for the prevention of COVID-19.
- Metformin Lipodisq is based on a nanoparticle (11-40nm) drug delivery system comprising a discoidal phospholipid bilayer membrane stabilized by a chaperone molecule annulus. Internal properties of the phospholipid membrane support the disposition and stabilization of drug molecule candidates and preserve the native conformation of membrane molecules. The resulting encapsulated actives are rendered water-soluble and specialized for intra-cellular penetration/delivery via endosomal uptake mechanisms. Lipodisq solutions show a good safety profile and are suitable for in vitro and in vivo investigations.
- Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: an overview: B. Viollet, et al.; Clin. Sci. 122, 253 (2012)
- Metformin in 2019: J. Flory & K. Lipska; JAMA 321, 1926 (2019)
- Metformin Use Is Associated With Reduced Mortality in a Diverse Population With COVID-19 and Diabetes: A.B. Crouse, et al.; Front. Endocrinol. 11, 600439 (2021)
- Metformin inhibition of mitochondrial ATP and DNA synthesis abrogates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pulmonary inflammation: J. Flory & K. Lipska; Immunity 54, 1463 (2021)
- Metformin in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Y. Li, et al.; Front. Med. 8, 704666 (2021)
- Outpatient metformin use is associated with reduced severity of COVID-19 disease in adults with overweight or obesity: C.T. Bramante, et al.; J. Med. Virol. 93, 4273 (2021)
- Metformin inhibition of mitochondrial ATP and DNA synthesis abrogates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pulmonary inflammation: H. Xian, et al.; Immunity 54, 1463 (2021)
- Metformin and Covid-19: Focused Review of Mechanisms and Current Literature Suggesting Benefit: S. Ibrahim, et al.; Front. Endocrinol. 12, 587801 (2021)
General References for Lipodisq™ Technology:
- Responsive Hydrophobically Associating Polymers: A Review of Structure and Properties: S.R. Tonge & B.J. Tighe; Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 53, 109 (2001)
- Detergent-free formation and physico-chemical characterization of nanosized lipidpolymer complexes: Lipodisq; M.C. Orwick, et al.; Angew. Chem. 51, 4653 (2012)
- Physicochemical Characterization, Toxicity and In Vivo Biodistribution Studies of a Discoidal, Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Vehicle: Lipodisq Nanoparticles Containing Doxorubicin: M.L. Torgersen, et al.; J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 16, 41 (2020)
- Applications of Synthetic Polymer Discoidal Lipid Nanoparticles to Biomedical Research: M. Tanaka; Chem. Pharm. Bull. 70, 507 (2022)
- Mechanisms of Formation, Structure, and Dynamics of Lipoprotein Discs Stabilized by Amphiphilic Copolymers: A Comprehensive Review: P.S. Orekhov, et al.; Nanomaterials 12, 361 (2022)