Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Innaxon
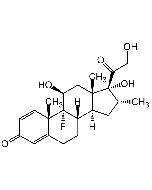
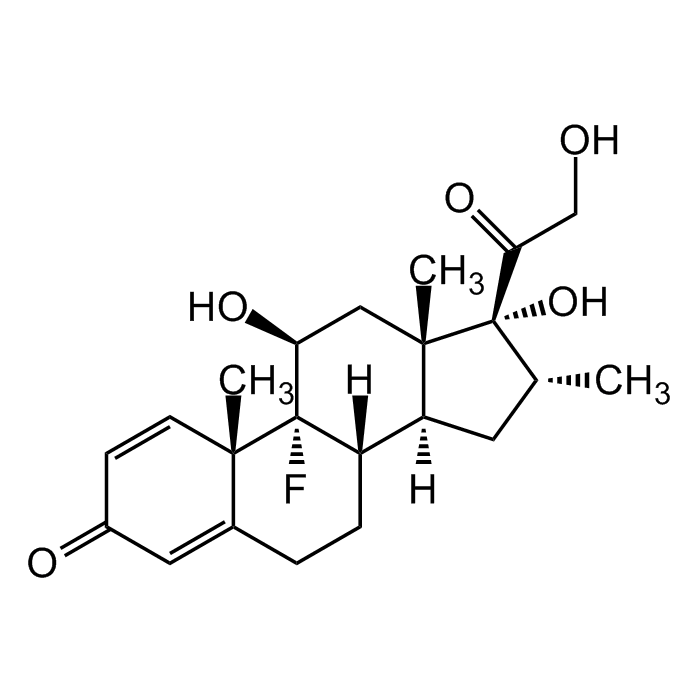
Dexamethasone Sterile Solution
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Dexamethasone Lipodisq™ Sterile Solution; MK-125; NSC 34521; 9α-Fluoro-16α-methylprednisolone; 9-Fluoro-11β,17,21-trihydroxy-16α-methyl-pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C22H29FO5 |
| MW | 392.5 |
| CAS | 50-02-2 |
| RTECS | TU3980000 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, PBS, Tris and other physiological solutions as formulated in a proprietary, thermostable, aqueous lipid nanoparticulate formulation (Lipodisq). |
| Reconstitution | Avoid the use of buffers with divalent ions such as Ca or Mg or pH <6.5 or >8.0, which can cause particle instability. Unformulated dexamethasone is soluble in DMSO, ethanol or methanol. |
| Formulation | Liquid, detergent-free discoidal nano-formulation made of styrene-maleic acid lipid particles (SMALP), lecithin and sterile water. |
| Concentration | 1mg/ml (0.1% w/vol) |
| Biological Activity |
Discoidal nano-particles can incorporate hydrophobic, poorly water-soluble compounds, such as lipids, lipoproteins and glycolipids. - Cell culture tested (human macrophage cell line) (MTT). - Recommended starting dilution: 1:200 or higher. - Optimal working concentrations depend on the applications and need to be determined. - Published procedures using Lipodisq formulations (Curcumin and IAXO TLR4 antagonists) in vivo rodent models at 3-10mg/kg. Recommended route of administration is subcutaneous (s.c.) with oral or nasal application as a possible alternative, which needs to be optimized. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Innaxon. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet: Our product description may differ slightly from the original manufacturers' product datasheet.
|
| InChi Key | UREBDLICKHMUKA-CXSFZGCWSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C1C=C[C@@]2(C)C(CC[C@]3([H])[C@]2(F)[C@@H](O)C[C@@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])C[C@@H](C)[C@]4(O)C(CO)=O)=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep sterile. Avoid skin and eye contact. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
- Dexamethasone Sterile Solution is a ready-to-use nano-formulated aqueous solution.
- Dexamethasone, developed in 1957 and granted FDA approval in 1958, is a corticosteroid structurally similar to hydrocortisone and prednisolone. Dexamethasone is used to treat conditions including: endocrine, rheumatic, collagen, dermatologic, allergic, ophthalmic, gastrointestinal, respiratory, hematologic, neoplastic, and edematous and most recently COVID-19.
- Dexamethasone Lipodisq is based on a nanoparticle (11-40nm) drug delivery system comprising a discoidal phospholipid bilayer membrane stabilized by a chaperone molecule annulus. Internal properties of the phospholipid membrane support the disposition and stabilization of drug molecule candidates and preserve the native conformation of membrane molecules. The resulting encapsulated actives are rendered water-soluble and specialized for intra-cellular penetration/delivery via endosomal uptake mechanisms. Lipodisq solutions show a good safety profile and are suitable for in vitro and in vivo investigations.
- Metabolic imbalance of T cells in COVID-19 is hallmarked by basigin and mitigated by dexamethasone: J.P. Siska, et al.; J. Clin. Invest. 131, e148225 (2021)
- Dexamethasone for Severe COVID-19: How Does It Work at Cellular and Molecular Levels? T. Kino, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 6764 (2021)
- Beyond Vaccines: Clinical Status of Prospective COVID-19 Therapeutics: S. Kumar, et al.; Front. Immunol. 12, 752227 (2021)
- Dexamethasone modulates immature neutrophils and interferon programming in severe COVID-19: S. Sinha, et al.; Nat. Med. 28, 201 (2022)
General References for Lipodisq™ Technology:
- Responsive Hydrophobically Associating Polymers: A Review of Structure and Properties: S.R. Tonge & B.J. Tighe; Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 53, 109 (2001)
- Detergent-free formation and physico-chemical characterization of nanosized lipidpolymer complexes: Lipodisq; M.C. Orwick, et al.; Angew. Chem. 51, 4653 (2012)
- Physicochemical Characterization, Toxicity and In Vivo Biodistribution Studies of a Discoidal, Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Vehicle: Lipodisq Nanoparticles Containing Doxorubicin: M.L. Torgersen, et al.; J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 16, 41 (2020)
- Applications of Synthetic Polymer Discoidal Lipid Nanoparticles to Biomedical Research: M. Tanaka; Chem. Pharm. Bull. 70, 507 (2022)
- Mechanisms of Formation, Structure, and Dynamics of Lipoprotein Discs Stabilized by Amphiphilic Copolymers: A Comprehensive Review: P.S. Orekhov, et al.; Nanomaterials 12, 361 (2022)