Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Innaxon
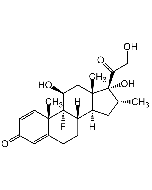
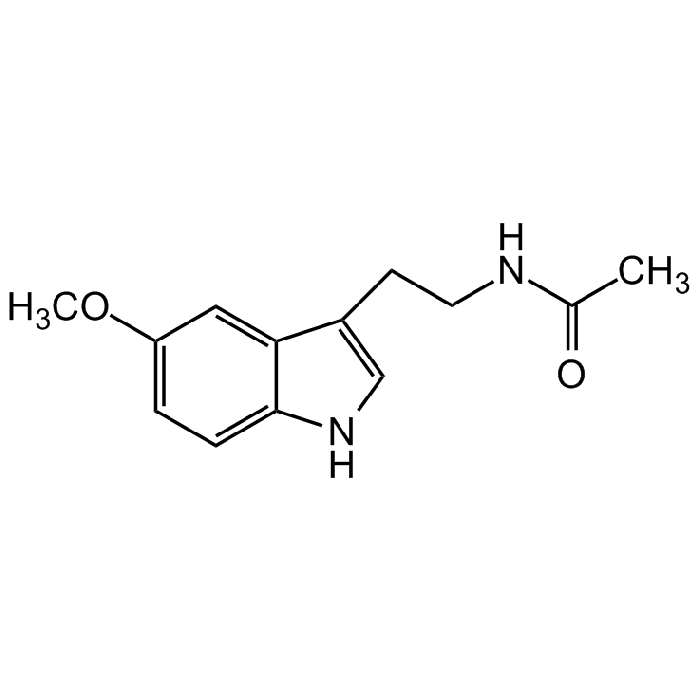
Melatonin Sterile Solution
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Melatonin Lipodisq™ Sterile Solution; N-Acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine; NSC 56423; NSC 113928; Regulin |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
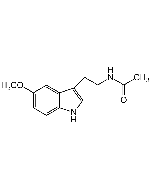
C13H16N2O2 |
| MW | 232.28 |
| CAS | 73-31-4 |
| RTECS | AC5955000 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Colourless clear aqueous solution |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, PBS, Tris and other physiological solutions as formulated in a proprietary, thermostable, aqueous lipid nanoparticulate formulation (Lipodisq). |
| Reconstitution | Avoid the use of buffers with divalent ions such as Ca or Mg or pH <6.5 or >8.0, which can cause particle instability. Unformulated melatonin is soluble in DMF, DMSO or ethanol. |
| Formulation | Liquid, detergent-free discoidal nano-formulation made of styrene-maleic acid lipid particles (SMALP), lecithin and sterile water. |
| Concentration | 1mg/ml (0.1% w/vol) |
| Biological Activity |
Discoidal nano-particles can incorporate hydrophobic, poorly water-soluble compounds, such as lipids, lipoproteins and glycolipids. - Cell culture tested (human macrophage cell line) (MTT). - Recommended starting dilution: 1:200 or higher. - Optimal working concentrations depend on the applications and need to be determined. - Published procedures using Lipodisq formulations (Curcumin and IAXO TLR4 antagonists) in vivo rodent models at 3-10mg/kg. Recommended route of administration is subcutaneous (s.c.) with oral or nasal application as a possible alternative, which needs to be optimized. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Innaxon. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet: Our product description may differ slightly from the original manufacturers product datasheet.
|
| InChi Key | DRLFMBDRBRZALE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | CC(NCCC1=CNC2=CC=C(OC)C=C21)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep sterile. Avoid skin and eye contact. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
- Melatonin (high purity) Sterile Solution is a ready-to-use nano-formulated aqueous solution.
- Melatonin, an evolutionarily ancient derivative of serotonin with hormonal properties, is the main neuroendocrine secretory product of the pineal gland. It regulates circadian rhythmicity and also exerts anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and anti-tumor capacities. Melatonin levels in individuals increase from birth and peak around puberty. Its synthesis and levels decline in middle-aged and most elderly individuals along with a simultaneous reduction in the urinary excretion of its metabolites. Moreover, it stimulates antioxidant defense systems in the brain. The decline in melatonin production in aged individuals is itself a significant factor that may contribute to age-related neurodegenerative disease processes and has been suggested as one of the primary reasons for the development of Alzheimer Disease (AD). Melatonin exerts antibacterial activities not only on classic Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, but also on members of other bacterial groups, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In recent years, an increasing number of studies have described the anticancer effects of melatonin. Melatonin is also a mitophagy regulator. It may exert an essential effect on mitochondrial physiology and facilitates mitochondrial function. A central mechanism by which melatonin protects mitochondria is by restoring the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) through blocking mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening under stress and activating uncoupling proteins (UCPs) to marginally decrease MMP under normal conditions.
- Melatonin Lipodisq is based on a nanoparticle (11-40nm) drug delivery system comprising a discoidal phospholipid bilayer membrane stabilized by a chaperone molecule annulus. Internal properties of the phospholipid membrane support the disposition and stabilization of drug molecule candidates and preserve the native conformation of membrane molecules. The resulting encapsulated actives are rendered water-soluble and specialised for intra-cellular penetration/delivery via endosomal uptake mechanisms. Lipodisq solutions show a good safety profile and are suitable for in vitro and in vivo investigations.
- Mechanisms of Melatonin in Alleviating Alzheimer’s Disease: M. Shukla, et al.; Curr. Neuropharmacol. 15, 1010 (2017)
- Cellular Mechanisms of Melatonin: Insight from Neurodegenerative Diseases: D Chen, et al.; Biomolecules 10, 1158 (2020)
- Melatonin and Pathological Cell Interactions: Mitochondrial Glucose Processing in Cancer Cells: R.F. Reiter, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 12494 (2021)
- Melatonin and Phytomelatonin: Chemistry, Biosynthesis, Metabolism, Distribution and Bioactivity in Plants and Animals—An Overview: G. Mannino, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 9996 (2021)
- Bacteriostatic Potential of Melatonin: Therapeutic Standing and Mechanistic Insights: F. He, et al.; Front. Immunol. 12, 683879 (2021)
- Melatonin: From Pharmacokinetics to Clinical Use in Autism Spectrum Disorder: S. Sebastien Lalanne, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 1490 (2021)
- Mechanisms of Melatonin in Obesity: A Review: Q. Guan; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 218 (2022)
- Protective Role of Melatonin and Its Metabolites in Skin Aging: G. Georgeta Bocheva, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 1238 (2022)
- Membrane Melatonin Receptors Activated Cell Signaling in Physiology and Disease: G. Nikolaev, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 471 (2022)
- New insights into the role of melatonin in diabetic cardiomyopathy: K. Huang, et al.; Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 10, e00904 (2022)
- Use of Melatonin in Cancer Treatment: Where Are We? L. Wang, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 3779 (2022)
General References for Lipodisq™ Technology:
- Responsive Hydrophobically Associating Polymers: A Review of Structure and Properties: S.R. Tonge & B.J. Tighe; Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 53, 109 (2001)
- Detergent-free formation and physico-chemical characterization of nanosized lipidpolymer complexes: Lipodisq; M.C. Orwick, et al.; Angew. Chem. 51, 4653 (2012)
- Physicochemical Characterization, Toxicity and In Vivo Biodistribution Studies of a Discoidal, Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Vehicle: Lipodisq Nanoparticles Containing Doxorubicin: M.L. Torgersen, et al.; J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 16, 41 (2020)
- Applications of Synthetic Polymer Discoidal Lipid Nanoparticles to Biomedical Research: M. Tanaka; Chem. Pharm. Bull. 70, 507 (2022)
- Mechanisms of Formation, Structure, and Dynamics of Lipoprotein Discs Stabilized by Amphiphilic Copolymers: A Comprehensive Review: P.S. Orekhov, et al.; Nanomaterials 12, 361 (2022)