Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
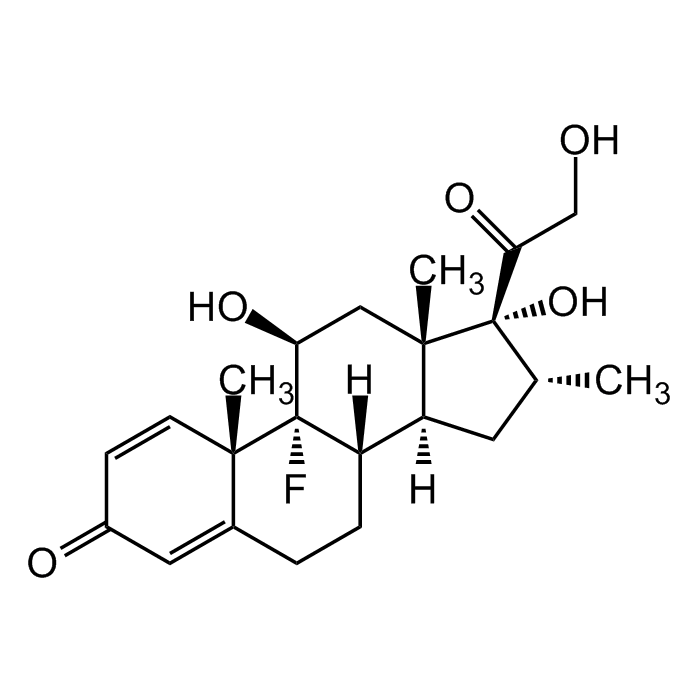
Dexamethasone
As low as
30
CHF
CHF 30.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3742-M05050 mgCHF 30.00
AG-CR1-3742-M500500 mgCHF 40.00
AG-CR1-3742-G0011 gCHF 80.00
AG-CR1-3742-G0055 gCHF 230.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | MK-125; NSC 34521; 9α-Fluoro-16α-methylprednisolone; 9-Fluoro-11β,17,21-trihydroxy-16α-methyl-pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C22H29FO5 |
| MW | 392.5 |
| CAS | 50-02-2 |
| RTECS | TU3980000 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (30mg/ml), ethanol (20mg/ml) or methanol (20mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | UREBDLICKHMUKA-CXSFZGCWSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C1C=C[C@@]2(C)C(CC[C@]3([H])[C@]2(F)[C@@H](O)C[C@@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])C[C@@H](C)[C@]4(O)C(CO)=O)=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Dexamethasone is a potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agent useful in a variety of inflammatory and autoimmune conditions.
- This synthetic glucocorticoid acts as an agonist of human glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and binds with a higher affinity than the natural ligand cortisol (Kd = 5nM versus 17nM, respectively). Through GR activation, dexamethasone has both transactivating and transrepressing effects on gene expression, resulting in anti-inflammatory properties. The anti-inflammatory effects are complex, but primarily via inhibition of inflammatory cells and suppression of expression of inflammatory mediators.
- Dexamethasone has been shown to regulate T cell survival, growth and differentiation. It induces the production of phospholipase A2 inhibitory protein (lipocortin) and inhibits the induction of nitric oxide synthase (IC50 = 5nM). Dexamethasone is used to study apoptosis, cell signaling pathways, cell differentiation and gene expression. It also has been shown to be an activator of IDO through the induction of the GITR-GITRL pathway.
- Reduces levels of activated NF-κB in immature dendritic cells (DCs) and inhibits differentiation into mature DCs. Induces differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Also induces autophagy in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cell lines.
- Dexamethasome is used in combination with several anticancer agents to improve the activity and has been shown to be useful in reducing the inflammatory factors in viral infections (EBV, RSV).
- The RECOVERY Trial recommended dexamethasone for use in COVID-19 patients with severe respiratory symptoms. Dexamethasone improves survival rates of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 by inhibiting cytokine storm.
Product References
- Differential effects of aspirin and dexamethasone on phospholipase A2 and C activities and arachidonic acid release from endothelial cells in response to bradykinin and leukotriene D4: M.A. Clark, et al.; Prostaglandins 32, 703 (1986)
- Inhibition of the Induction of Nitric Oxide Synthase by Glucocorticoids: Yet Another Explanation for Their Anti-Inflammatory Effects? S. Moncada & R.M. Palmer; TIPS 12, 130 (1991)
- Dexamethasone and etoposide induce apoptosis in rat thymocytes from different phases of the cell cycle: H.O. Fearnhead, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 48, 1073 (1994)
- Impaired cortisol binding to glucocorticoid receptors in hypertensive patients: P. Mulatero, et al.; Hypertension 30, 1274 (1997)
- Dexamethasone inhibits dendritic cell maturation by redirecting differentiation of a subset of cells: R. Matasic, et al.; J. Leukoc. Biol. 66, 909 (1999)
- SHP2 mediates the protective effect of interleukin-6 against dexamethasone-induced apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells: D. Chauhan, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 275, 27845 (2000)
- Regulation of nuclear factor-kappa B, activator protein-1, and glutathione levels by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and dexamethasone in alveolar epithelial cells: I. Rahman; Biochem. Pharmacol. 60, 1041 (2000) (Review)
- Crosstalk in inflammation: The interplay of glucocorticoid receptor-based mechanisms and kinases and phosphatases: I.M. Beck, et al.; Endocr. Rev. 30, 830 (2009) (Review)
- Reverse Signaling Through GITR Ligand Enables Dexamethasone to Activate IDO in Allergy: U. Grohmann, et al.; Nat. Med. 13, 579 (2007)
- Cell death induced by dexameth. in lymphoid leukemia is mediated through initiation of autophagy: E. Laane, et al.; Cell Death Differ. 16, 1018 (2009)
- Handbook of experimental pharmacology "dendritic cells": the use of dexamethasone in the induction of tolerogenic DCs: C. van Kooten, et al.; Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2009, 233 (2009) (Review)
- The Glucocorticoids Prednisone and Dexamethasone Differentially Modulate T Cell Function in Response to anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint Blockade: I.S. Okoye, et al.; Cancer Immunol. Immunother. (Epub ahead of print) (2020)
- Dexamethasone Prevents the Epstein-Barr Virus Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in A549 Cells: F. Zhang, et al.; J. Med. Virol. (Epub ahead of print) (2020)
- Low-cost dexamethasone reduces death by up to one third in hospitalised patients with severe respiratory complications of COVID-19: RECOVERY Trial (June 2020)
- Coronavirus Breakthrough: Dexamethasone Is First Drug Shown to Save Lives: H. Ledford; Nature (Epub ahead of print) (2020)