Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
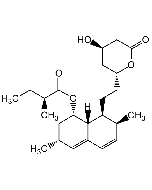
Orlistat
As low as
35
CHF
CHF 35.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0050-M05050 mgCHF 35.00
AG-CN2-0050-M250250 mgCHF 135.00

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Tetrahydrolipstatin; Xenical; Alli; Ro-18-0647 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C29H53NO5 |
| MW | 495.7 |
| Merck Index | 14: 6869 |
| CAS | 96829-58-2 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. Originally isolated from Streptomyces sp. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (NMR) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, ethanol or DMF. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | AHLBNYSZXLDEJQ-FWEHEUNISA-N |
| Smiles | [H]C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)O[C@@H](CCCCCCCCCCC)C[C@@H]1OC(=O)[C@H]1CCCCCC |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Hypolipemic cell permeable and irreversible pancreatic, gastric and carboxylester lipase inhibitor [1-3].
- Anti-obesity and antihypercholesterolemic compound [2, 5, 11].
- Antitumor compound by inhibition of the thioesterase domain of fatty acid synthase (FASN) [4, 6, 9, 10].
- Anti-proliferative [4, 6, 9, 10].
- Causes cell cycle arrest at G1 phase. Apoptosis inducer through caspase-3 activation [6, 10].
- Sn-1-selective-diacylglycerol lipases α (DAGLα) inhibitor. Targets serine hydrolases in the nervous system, such as diacylglycerol lipase (DAGL), which is responsible for the conversion of DAG to 2-AG [7].
- Partially inhibits the hydrolysis of triglycerides and lowers the absorption of dietary fat, promoting weight loss [8].
- Promotes the sensitivity to TRAIL in cancer cells by ROS-mediated pathways [11].
Product References
- Interactions of lipoprotein lipase with the active-site inhibitor tetrahydrolipstatin (Orlistat): A. Lookene, et al.; Eur. J. Biochem. 222, 395 (1994)
- Mode of action of orlistat: R. Guerciolini; Int. J Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2, S12 (1997) (Review)
- Degree of in vivo inhibition of human gastric and pancreatic lipases by Orlistat (Tetrahydrolipstatin, THL) in the stomach and small intestine: B. Sternby, et al.; Clin. Nutr. 21, 395 (2002)
- Orlistat is a novel inhibitor of fatty acid synthase with antitumor activity: S.J. Kridel, et al.; Cancer Res. 64, 2070 (2004)
- The use of orlistat in the treatment of obesity, dyslipidaemia and Type 2 diabetes: R.H. Nelson & J.M. Miles; Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 6, 2483 (2005) (Review)
- Antitumoral actions of the anti-obesity drug orlistat (XenicalTM) in breast cancer cells: blockade of cell cycle progression, promotion of apoptotic cell death and PEA3-mediated transcriptional repression of Her2/neu (erbB-2) oncogene: J.A. Menendez, et al.; Ann. Oncol. 16, 1253 (2005)
- Development of the first potent and specific inhibitors of endocannabinoid biosynthesis: T. Bisogno, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1761, 205 (2006)
- Orlistat accelerates gastric emptying and attenuates GIP release in healthy subjects: F.Y. Enc, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 296, G482 (2008)
- Fatty acid synthase inhibition with Orlistat promotes apoptosis and reduces cell growth and lymph node metastasis in a mouse melanoma model: M.A. Carvalho, et al.; Int. J. Cancer. 123, 2557 (2008)
- Antitumor effect of orlistat, a fatty acid synthase inhibitor, is via activation of caspase-3 on human colorectal carcinoma-bearing animal: H.Y. Chuang, et al.; Biomed. Pharmacother. 65, 286 (2011)
- The anti-obesity drug orlistat promotes sensitivity to TRAIL by two different pathways in hormone-refractory prostate cancer cells: J. Fujiwara, et al.; Int. J. Oncol. 48, 854 (2016)
- The oncogene-dependent resistance to reprogramming unveils cancer therapeutic targets: K. Ito, et al.; Cell Rep. 39, 110721 (2022)