Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
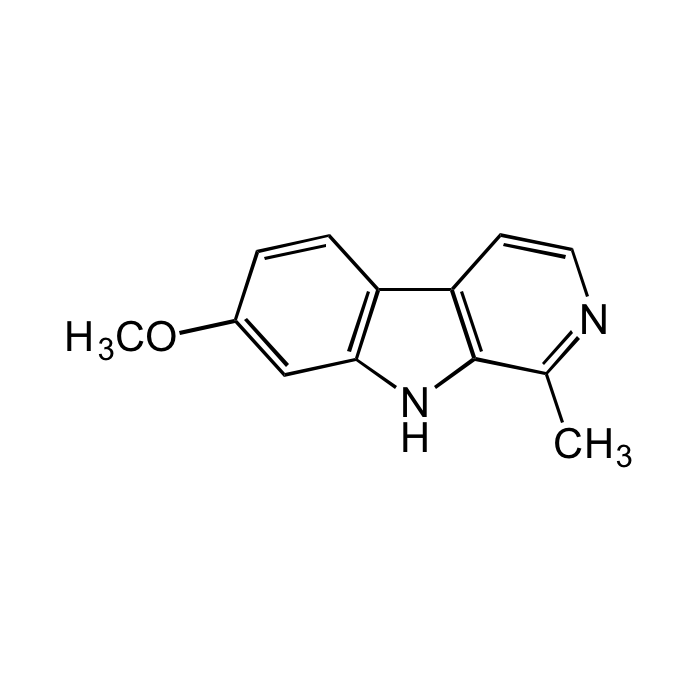
Harmine
As low as
30
CHF
CHF 30.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0510-M01010 mgCHF 30.00
AG-CN2-0510-M05050 mgCHF 50.00
AG-CN2-0510-M250250 mgCHF 80.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 7-Methoxy-1-methyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole; Banisterine; Leucoharmine; Telepathine; Yageine; BRN0178813 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C13H12N2O |
| MW | 212.3 |
| CAS | 442-51-3 |
| RTECS | UV0175000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. Originally isolated from the seeds of Peganum harmala (Syrian rue). |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% |
| Appearance | White ot off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO. Slightly soluble in ethanol. Insoluble in water. |
| Other Product Data |
Stock Solution: Prior to performing biological experiments the stock solution should be further diluted into water or other aqueous buffers to ensure that the residual amount of DMSO/ethanol is insignificant, since DMSO and ethanol may have physiological effects at high concentrations. |
| InChi Key | BXNJHAXVSOCGBA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | CC1=NC=CC2=C1NC3=C2C=CC(OC)=C3 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light. Protect from moisture and oxygen. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Fluorescent β-carboline alkaloid.
- Potent ATP-competitive and selective inhibitor of DYRK1A, DYRK2 and DYRK3 with IC50 values of 0.08, 0.9 and 0.8µM. Shown to inhibit CLK2, PIM3 (at 4.3µM) and CK1 at 1.5µM as well. Inhibits DYRK1A-mediated tau phosphorylation.
- Competitive and reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) that reversibly inhibits MAO-A (monoamine oxidase A) but has no effect on MAO-B.
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (AChEI). Could potentially ameliorate impaired memory.
- Useful fluorescent pH indicator. Shows a color change from pH 7.2 (blue fluorescence) to pH 8.9 (yellow fluorescence). With the radioisotope carbon-11, used in positron emission tomography neuroimaging to examine its binding to MAO-A.
- Antiviral and antileishmanial compound.
- Antiangiogenic and antitumor agent. Inhibits cellular proliferation, migration, invasion and induced apoptosis in vitro, as well as inhibited tumor growth in vivo.
- Antidiabetic. Unique regulator of PPARγ expression that acts by inhibiting the Wnt signaling pathway in a cell-specific manner. Induces pancreatic β-cell proliferation. Reduced blood glucose, free fatty acids and triglyceride levels, delayed hyperglycemia and improved insulin sensitivity.
- Able to expand human β-cell numbers and stimulate insulin-producing human β-cell regeneration by transforming cycling α-cells into insulin-producing β- cells. DYRK1A inhibitors may act via a combination of α-cell precursor replication followed by α-to-β cell transdifferentiation.
- Shown to induce adipocyte thermogenesis through the RAC1-MEK-ERK-CHD4 axis. CHD4 directly binds the proximal promoter region of UCP1, serving as a negative modulator of UCP1 and inducing browning in brown (BAT) and white adipose tissue (WAT).
- Inhibits DNA topoisomerases and interferes with DNA synthesis. Interacts with DNA via both groove binding and intercalative modes and cause major DNA structural changes.
- Shown to promote differentiation of osteoblasts (bone-forming cells) and chondrocytes (cells in the cartilage) and to inhibit osteoclastogenesis (the formation of bone resorbing cells).
- Antimalarial by inhibiting the Plasmodium falciparum heat shock protein 90 (PfHSP90) ATP-binding domain.
Product References
- The pH-dependence of the absorption and fluorescence spectra of harmine and harmol: drastic differences in the tautomeric equilibria of ground and first excited singlet state: O.S. Wolfbeis & E. Furlinger; Z. Physik. Chem. 129, 171 (1982)
- Antiviral effect of harmine, a photoactive beta-carboline alkaloid: J.B. Hudson, et al.; Photochem. Photobiol. 43, 21 (1986)
- Harmine as a substitute for 33258 Hoechst in the FPG technique: M.G. Gutierrez-Gonzalvez, et al.; Histochemistry 89, 199 (1988)
- Effect of moclobemide on rat brain monoamine oxidase A and B: comparison with harmaline and clorgyline: J. Gerardy; Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 18, 793 (1994)
- 11C-harmine as a tracer for monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A): in vitro and in vivo studies: M. Bergstrom, et al.; Nucl. Med. Biol. 24, 287 (1997)
- Antitumor agents 201. Cytotoxicity of harmine and beta-carboline analogs: J. Ishida, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 9, 3319 (1999)
- Harmine: evaluation of its antileishmanial properties in various vesicular delivery systems: S. Lala, et al.; J. Drug Target 12, 165 (2004)
- The small molecule harmine is an antidiabetic cell-type-specific regulator of PPARgamma expression: H. Waki, et al.; Cell Metab. 5, 357 (2007)
- The selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors: a further update: J. Bain, et al.; Biochem. J. 408, 297 (2007)
- DYRK1A phosphorylates caspase 9 at an inhibitory site and is potently inhibited in human cells by harmine: A. Seifert, et al.; FEBS J. 275, 6268 (2008)
- Harmine specifically inhibits protein kinase DYRK1A and interferes with neurite formation: N. Gockler, et al.; FEBS J. 276, 6324 (2009)
- β-Carboline alkaloids bind DNA: S. Nafisi, et al.; J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol. 100, 84 (2010)
- Harmine, a β-carboline alkaloid, inhibits osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption in vitro and in vivo: T. Yonezawa, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 650, 511 (2011)
- Harmine is an ATP-competitive inhibitor for dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (Dyrk1A): T. Adayev, et al.; Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 507, 212 (2011)
- The small molecule harmine regulates NFATc1 and Id2 expression in osteoclast progenitor cells: H. Egusa, et al.; Bone 49, 264 (2011)
- β-carboline compounds, including harmine, inhibit DYRK1A and tau phosphorylation at multiple Alzheimer's disease-related sites: D. Frost, et al.; PLoS One 6, e19264 (2011)
- Harmine is a potent antimalarial targeting Hsp90 and synergizes with chloroquine and artemisinin: D. Shahinas, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 56, 4207 (2012)
- Harmine induces apoptosis and inhibits tumor cell proliferation, migration and invasion through down-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in gastric cancer: H. Zhang, et al.; Phytomedicine 21, 348 (2014)
- A high-throughput chemical screen reveals that harmine-mediated inhibition of DYRK1A increases human pancreatic beta cell replication: P. Wang, et al.; Nat. Med. 21, 383 (2015)
- Effects of harmine, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, on spatial learning and memory of APP/PS1 transgenic mice and scopolamine-induced memory impairment mice: D. He, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 768, 96 (2015)
- Selectivity profiling and biological activity of novel β-carbolines as potent and selective DYRK1 kinase inhibitors: K. Ruben, et al.; PLos One 10, e0132453 (2015)
- Harmine induces cell cycle arrest and mitochondrial pathway-mediated cellular apoptosis in SW620 cells via inhibition of the Akt and ERK signaling pathways: J. Liu, et al.; Oncol. Rep. 35, 3363 (2016)
- Harmine Induces Adipocyte Thermogenesis through RAC1-MEK-ERK-CHD4 Axis: T. Nie,et al.; Sci. Rep. 6, 36382 (2016)
- Comparative Efficacy and Selectivity of Pharmacological Inhibitors of DYRK and CLK Protein Kinases: M.F. Lindberg, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 66, 4106 (2023)
- Cycling alpha cells in regenerative drug-treated human pancreatic islets may serve as key beta cell progenitors: E. Karakose, et al.; Cell Rep. Med. 5, 101832 (2024)