Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
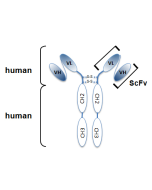
anti-Polyglutamate chain (polyE), pAb (IN105)

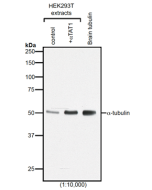
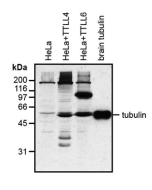
Method: HEK-293T cells are grown in standard culture conditions, transfected with plasmids expressing the tubulin glutamylases TTLL4 and TTLL6 (J. van Dijk, et al.; Mol. Cell 2007) and are lysed in SDS sample buffer and run on a 10% SDS-PAGE. Brain tubulin was prepared following standard procedures (M. Castoldi & A.V. Popov; Protein Expr. Purif. 2003). Different C-terminally modified variants of GST-telokin were produced in bacteria as described before (K. Rogowski, et al.; Cell 2010). The proteins are transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane and detected by standard immunoblot protocol using the anti-polyE, pAb (IN105) (1:2'000) in TBS containing 0.1% Tween-20 for washing steps and 2.5% fat free milk for antibody incubation. The same samples were probed with the anti-Polyglutamylation Modification, mAb (GT335) (Prod. No. AG-20B-0020) for comparison. In the normal HEK-293T cell extracts, no tubulin detection is observed, even on high exposure. Expression of TTLL4 glutamylase does not lead to detection with anti-polyE, pAb (IN105) while glutamylation is observed with GT335. This indicates that TTLL4 generates short glutamate chains on tubulin. Expression of TTLL6 generates long glutamate chains (J. van Dijk, et al.; Mol. Cell 2007), which are detected by anti-polyE, pAb (IN105). Brain tubulin is a heterogenous mixture of different glutamylation states of tubulin (B. Edde, et al.; Science 1990) and therefore strongly detected by anti-polyE, pAb (IN105) and mAb GT335. Anti-polyE, pAb (IN105) also detects gene-encoded linear C-terminal glutamate chains. To illustrate the specificity of anti-polyE, pAb (IN105), recombinant GST-telokin proteins are included in the western blot analysis. Anti-polyE, pAb (IN105) specifically detects glutamate-chains of four and more glutamates. In contrast, GT335 cannot detect such chains (K. Rogowski, et al.; Cell 2010).
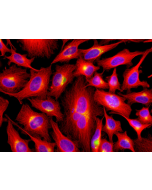
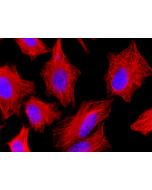
Picture courtesy of Dr. Sudarshan Gadadhar & Dr. Carsten Janke, Curie Institute, Paris
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Polyclonal Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | Rabbit |
| Immunogen/Antigen | Polyglutamate peptide. |
| Application |
Immunocytochemistry: (1:5'000) |
| Crossreactivity | All |
| Specificity |
Recognizes C-terminally located linear alpha-glutamate chains of 4 and more glutamate residues. |
| Purity Detail | Epitope-affinity purified. |
| Concentration | Lot dependent |
| Formulation | Liquid. In PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Do not freeze. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Microtubules are key elements of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton that dynamically assemble from heterodimers of α- and β-tubulin. Two different mechanisms can generate microtubule diversity: the expression of different α- and β-tubulin genes, referred to as tubulin isotypes, and the generation of posttranslational modifications (PTMs) on α- and β-tubulin. Tubulin PTMs include the well-known acetylation or phosphorylation, and others that have so far mostly been found on tubulin, detyrosination/tyrosination, polyglutamylation and polyglycylation. These PTMs might have evolved to specifically regulate tubulin and microtubule functions. Polyglutamylation is a PTM that occurs when secondary glutamate side chains are formed on γ-carboxyl groups of glutamate residues in a protein. Enzymes catalyzing polyglutamylation belong to the TTL-like (TTLL; Tubulin tyrosine ligase-like) family of glutamylases. Deglutamylases, the enzymes that reverse polyglutamylation, were identified within a novel family of CCPs (cytosolic carboxypeptidase). Subtle differences in polyglutamylation can be seen on diverse microtubules in different cell types. The functions of these modifications remain to be studied. However, its wide distribution strengthens the idea that it could be involved in fine-tuning a range of microtubule functions. PolyE labels centrioles as they mature, such that two foci are present throughout the cell cycle.
- Tubulin polyglutamylation stimulates spastin-mediated microtubule severing: B. Lacroix, et al.; J. Cell Biol. 189, 945 (2010)
- Microtubule detyrosination guides chromosomes during mitosis: M. Barisic, et al.; Science 348, 6236 (2015) (Supplement)
- Zika virus causes supernumerary foci with centriolar proteins and impaired spindle positioning: B. Wolf, et al.; Open Bio 7, 160231 (2017)
- Alterations in the balance of tubulin glycylation and glutamylation inphotoreceptors leads to retinal degeneration: M. Bosch Grau, et al.; J. Cell. Sci. 130, 938 (2017)
- Spastin regulates VAMP7-containing vesicles trafficking in cortical neurons: C. Plaud, et al.; BBA - Molecular Basis of Disease 1863, 1666 (2017)
- iPSCs from a Hibernator Provide a Platform for Studying Cold Adaptation and Its Potential Medical Applications: J. Ou, et al.; Cell 173, 1 (2018)
- Imaging cellular ultrastructures using expansion microscopy (U-ExM): D. Gambarotto, et al.; Nat. Methods 16, 71 (2018)
- Essential function of the alveolin network in the subpellicular microtubules and conoid assembly in Toxoplasma gondii: N. Tosetti, et al.; eLife, Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 9, e56635 (2020)
- Mutation of NEKL-4/NEK10 and TTLL genes suppress neuronal ciliary degeneration caused by loss of CCPP-1 deglutamylase function: K.M. Power, et al.; PLoS Genet. 16, e1009052 (2020)
- Light microscopy of proteins in their ultrastructural context: O. M'Saad & J. Bewersdorf; Nat. Commun. 11, 3850 (2020)
- Tubulin glycylation controls axonemal dynein activity, flagellar beat, and male fertility: S. Gadadhar, et al.; Science 371, eabd4914 (2021)
- Essential function of the alveolin network in the subpellicular microtubules and conoid assembly in Toxoplasma gondii: N. Tosetti, et al.; eLife 9, e56635 (2021)
- Proteomic analysis of Giardia lamblia and Trichomonas vaginalis flagella reveal unique post-translational modifications in tubulin that provide clues to regulation of their motilities: A. Sudhakar, et al.; Proteomics e2100004 (2021)
- Regulators of tubulin polyglutamylation control nuclear shape and cilium disassembly by balancing microtubule and actin assembly: L. Wang, et al.; Nature Cell Res. 32, 190 (2022)
- Septin-microtubule association via a motif unique to the isoform 1 of septin 9 tunes stress fibers: M. Kuzmic, et al.; J. Cell Sci. 135, 258850 (2022)
- ER proteins decipher the tubulin code to regulate organelle distribution: P. Zheng, et al.; Nature 601, 132 (2022)
- TissUExM enables quantitative ultrastructural analysis in whole vertebrate embryos by expansion microscopy: E. Steib, et al.; Cell Rep. Methods 2, 100311 (2022)
- Visualizing the native cellular organization by coupling cryofixation with expansion microscopy (Cryo-ExM): M.H. Laporte, et al.; Nat. Meth. 19, 216 (2022)
- Choroid plexuses carry nodal-like cilia that undergo axoneme regression from early adult stage: KH. Ho, et al.; Dev. Cell 58, 2641 (2023)
- Polyglutamylation of microtubules drives neuronal remodeling: A. Gavoci, et al.; Nat. Commun. 16, 5384 (2025)