Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
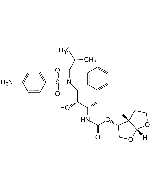
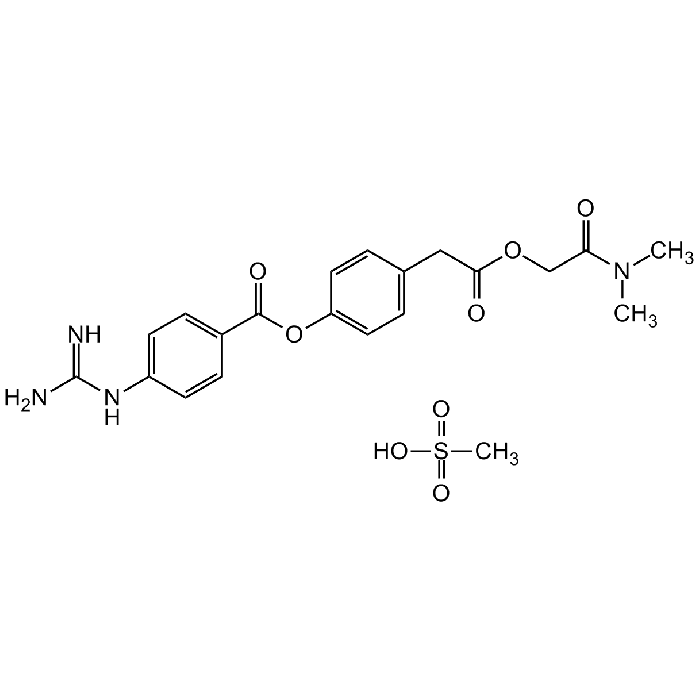
Camostat . mesylate
As low as
40
CHF
CHF 40.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3716-M01010 mgCHF 40.00
AG-CR1-3716-M05050 mgCHF 160.00
AG-CR1-3716-M250250 mgCHF 320.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | FOY 305; Foipan; FOY-S 980; Camostat mesilate |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C20H22N4O5 . CH4O3S |
| MW | 398.4 . 96.1 |
| CAS | 59721-29-8 |
| RTECS | CY1571620 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (25mg/ml), DMF (25mg/ml) or water (25mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | FSEKIHNIDBATFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | NC(NC1=CC=C(C(OC2=CC=C(CC(OCC(N(C)C)=O)=O)C=C2)=O)C=C1)=N.OS(=O)(C)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Camostat is an orally bioavailable trypsin-like protease inhibitor known to inhibit trypsin and various inflammatory proteases including plasmin, kallikrein and thrombin.
- Camostat has been shown to inhibit the production of TNF-α and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 by monocytes and to disrupt proliferation of pancreatic stellate cells in a rat model of pancreatic fibrosis. Protease regulation via camostat has also been reported to reversibly inhibit epithelial sodium channel function in human airway epithelial cell models.
- It is used in the treatment of some forms of cancer and is also effective against some viral infections (such as SARS, MERS or influenza), as well as inhibiting fibrosis in liver or kidney disease or pancreatitis. It suppresses pancreatitis-induced pain in rats following oral administration and is used to treat pancreatitis and reflux esophagitis after gastrectomy.
- It is an inhibitor of the enzyme transmembrane serine protease TMPRSS2 and partially blocks infection by SARS-CoV and human coronavirus NL63 in HeLa cells and entry of SARS-CoV2 (COVID-19) into lung cells in vitro.
Product References
- In vivo effects of camostat mesilate on plasma kallikrein, plasma kininase II and renal kallikrein of man: G. Bonner, et al.; Arzneimittelf. 37, 535 (1987)
- Suppressive effect of camostat mesilate (FOY 305) on acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE): T. Inuzuka, et al.; Neurochem. Res. 13, 225 (1988)
- Effect of camostat mesilate for the treatment of advanced diabetic nephropathy: M. Matsubara, et al.; J. Lab. Clin. Med. 116, 206 (1990)
- Gabexate and camostat, synthetic proteinase inhibitors, as direct inducing factors of water and bicarbonate secretion in the isolated and blood-perfused dog pancreas: A. Horiuchi, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 252, 320 (1990)
- Blocking effects of synthetic trypsin inhibitor (camostat) on pancreatic carcinogenesis in hamsters initiated with N-nitrosobis(2-oxopropyl)amine: F. Furukawa, et al.; Pancreas 9, 78 (1994)
- Evaluation of anti-influenza effects of camostat in mice infected with non-adapted human influenza viruses: M.G. Lee, et al.; Arch. Virol. 141, 1979 (1996)
- Camostat mesilate attenuates pancreatic fibrosis via inhibition of monocytes and pancreatic stellate cells activity: J. Gibo, et al.; Lab. Invest. 85, 75 (2005)
- The proteinase inhibitor camostat mesilate suppresses pancreatic pain in rodents: H. Ishikura, et al.; Life Sci. 80, 1999 (2007)
- Camostat attenuates airway epithelial sodium channel function in vivo through the inhibition of a channel-activating protease: K. Coote, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 329, 764 (2009)
- Simultaneous Treatment of Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells With Serine and Cysteine Protease Inhibitors Prevents Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Entry: M. Kawase, et al.; J. Virol. 86, 6537 (2012)
- The serine protease inhibitor camostat inhibits influenza virus replication and cytokine production in primary cultures of human tracheal epithelial cells: M. Yamaya, et al.; Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 33, 66 (2015)
- Protease Inhibitors Targeting Coronavirus and Filovirus Entry: Y. Zhou, et al.; Antiviral Res. 116, 76 (2015)
- SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically-proven protease inhibitor: M. Hoffmann, et al.; Cell (Epub ahead of print) (2020)