Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
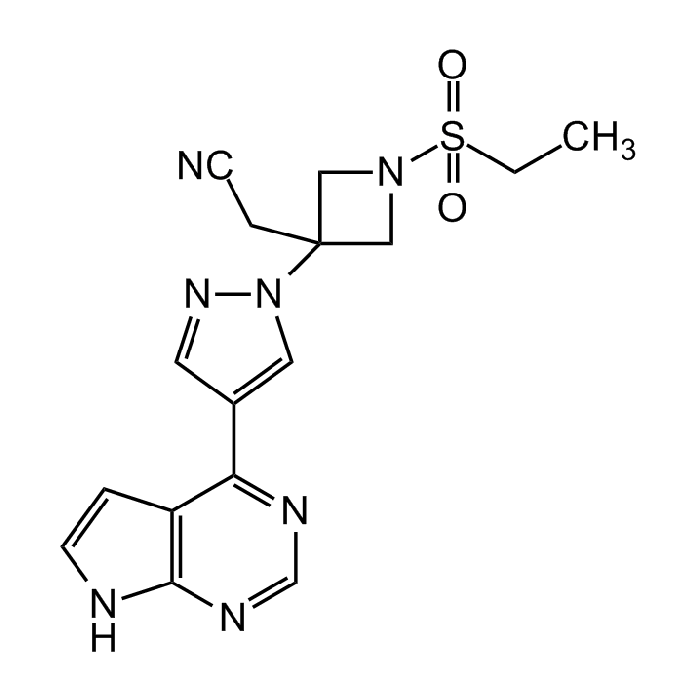
Baricitinib
As low as
40
CHF
CHF 40.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3734-M01010 mgCHF 40.00
AG-CR1-3734-M05050 mgCHF 80.00
AG-CR1-3734-M250250 mgCHF 220.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | LY3009104; INCB28050; 1-(Ethylsulfonyl)-3-[4-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl]-3-azetidineacetonitrile |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C16H17N7O2S |
| MW | 371.4 |
| CAS | 1187594-09-7 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (30mg/ml) or DMF (40mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | XUZMWHLSFXCVMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | CCS(N(C1)CC1(CC#N)N(N=C2)C=C2C3=NC=NC4=C3C=CN4)(=O)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Baricitinib is a selective orally bioavailable JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor with nanomolar potency against JAK1 (IC50 = 5.9nM) and JAK2 (IC50 = 5.7nM) and inhibits Tyk2 (IC50 = 53nM). It displays >100-fold selectivity for JAK1/2 over JAK3 (IC50 > 400nM). Janus kinases (JAKs) are non-receptor kinases and play important roles in the proinflammatory signaling pathways that are frequently over-activated in autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis. Upon binding of extracellular cytokines and growth factors, JAKs are phosphorylated and activate signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs). Via these signaling cascades, inflammatory cytokine and chemokine transcription is induced to form inflammatory mediators including IL-2, IL-6, IL-12, IL-15, IL-23.
- Baricitinib inhibits intracellular signaling of multiple proinflammatory cytokines including IL-6 and IL-23 at concentrations <50nM. It inhibits IL-6 receptor signaling, IL-6-induced STAT phosphorylation and subsequent pro-inflammatory chemokine (MPC-1) and cytokine (IL-17 and IL-22) production in PBMCs and T cells and displays anti-inflammatory and disease modifying effects in the rat adjuvant arthritis model. It also has been shown to block MSU-induced inflammasome activation.
- Baricitinib has potential application in various inflammatory disorders, including rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
- The majority of viruses enter cells through receptor mediated endocytosis. Baricitinib potently inhibits AP-2 associated protein kinase 1 (AAK1) and also binds cyclin G-associated kinase, both regulators of endocytosis. Inhibiting AAK1 might interrupt the passage of the SARS-CoV-2 virus into cells and also the intracellular assembly of virus particles. In addition the drug’s anti-inflammatory activity is expected to act on the inflammatory cascade associated with COVID-19.
Product References
- Selective inhibition of JAK1 and JAK2 is efficacious in rodent models of arthritis: Preclinical characterization of INCB028050: J.S. Fridman, et al.; J. Immunol. 184, 5298 (2010)
- Inhibition of Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) signalling pathway in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts using small molecule compounds: K. Migita, et al.; Clin. Exper. Immunol. 174, 356 (2013)
- Baricitinib for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: S. Kubo, et al.; Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 12, 911 (2016)
- Janus Kinase Inhibitor Baricitinib Modulates Human Innate and Adaptive Immune System: S. Kubo, et al.; Front. Immunol. 9, 1510 (2018)
- Baricitinib for systemic lupus erythematosus: J. Mucke & M. Schneider; Lancet 392, 190 (2018)
- Uric acid-mediated inflammasome activation in IL-6 primed innate immune cells is regulated by baricitinib: J. Temmoku, et al.; Mod. Rheumatol. (Epub ahead of print) (2020)
- Baricitinib as potential treatment for 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease: P. Richardson, et al.; Lancet 395, e30 (2020)
- Baricitinib therapy in COVID-19: A pilot study on safety and clinical impact: F. Cantini, et al.; J. Infect. 23, S0163 (2020)








