Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
IL-2 Superkine (Fc)
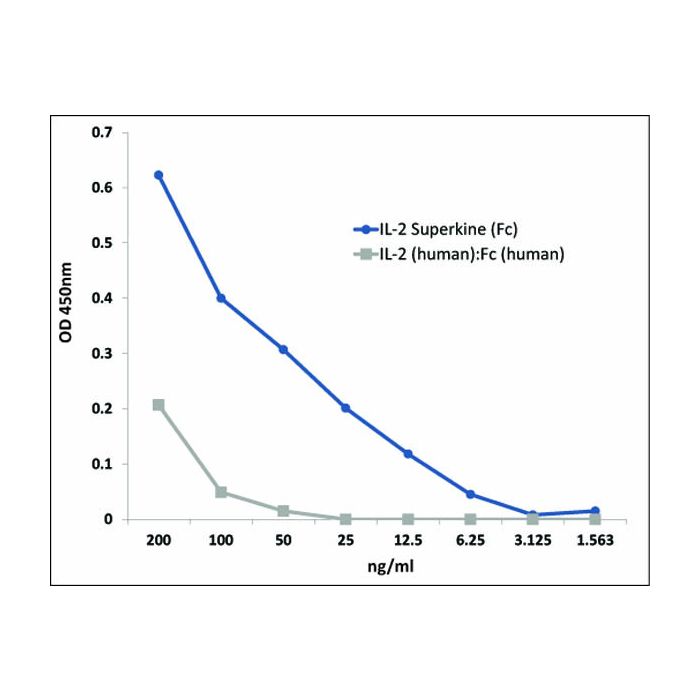
Methods: IL-2Rβ (human) was coated on an ELISA plate at 1μg/ml. After blocking and washing steps, indicated concentrations of IL-2 Superkine (Fc) or IL-2 (human):Fc (human) were added. Following incubation for 1 h at RT, the binding was detected using an anti-human Fc antibody (HRP).
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | IL-2 Superkine (H9) (human):Fc (human) (rec.); Interleukin-2; T Cell Growth Factor; TCGF; Aldesleukin; Super-2 |
| Product Type | Protein |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | HEK 293 cells |
| Sequence |
Human IL-2 (aa 21-153) (mutant H9 containing the mutations L80F / R81D / L85V / I 86V / I92F) is fused at the C-terminus to the Fc portion of human IgG2. |
| Crossreactivity |
Human Mouse |
| Application |
Triggers far greater antitumor responses than native IL-2 in vivo but with lower toxicity. |
| Specificity |
Binds to human and mouse IL-2R. |
| Biological Activity |
Triggers T cell proliferation at concentration <10ng/ml in the presence of 250ng/mL each of anti-CD3 (ANC-144-020) and anti-CD28 (ANC-177-020) antibodies. |
| MW | 42kDa |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Endotoxin Content | <0.01EU/μg protein (LAL test; Lonza). |
| Concentration | 0.1mg/ml after reconstitution. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute with 100μl sterile water. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Contains PBS. |
| Protein Negative Control | |
| Other Product Data |
Uniprot link P60568 : IL-2 (human) |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Centrifuge lyophilized vial before opening and reconstitution. PBS containing at least 0.1% BSA should be used for further dilutions. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. Working aliquots are stable for up to 3 months when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Application Note |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is a 133 amino acid glycoprotein with one intramolecular disulfide bond and variable glycosylation. It is secreted by activated T cells and induces proliferation and maturation of activated T cells, natural killer cells and lymphokine activated killer cells. IL-2 also stimulates proliferation of antibody-producing B cells, activates neutrophils and induces mononuclear cells to secrete IFN-γ and TNF-α and -β. Moreover, studies have shown that IL-2 is required for activation-induced apoptosis, an important homeostatic mechanism in the immune system, which is involved in the maintenance of peripheral tolerance to self-antigens.
IL-2 promotes T cell proliferation and particularly naive T cells. IL-2 signaling on activated T cells is effected through a quaternary high-affinity receptor complex consisting of IL-2, IL-2Rα (CD25), IL-2Rβ and IL-2Rγ. Naive T cells are relatively insensitive to IL-2 as they only express small amounts of IL-2Rβ and IL-2Rγ. They only acquire sensitivity after CD25 expression, which captures the cytokine and presents it to the IL-2Rβ and IL-2Rγ receptors. IL-2 Superkine (Fc) is an artificial variant of IL-2 containing mutations at positions L80F / R81D / L85V / I 86V / I92F. These mutations are located in the molecule's core that acts to stabilize the structure and to give it a receptor-binding conformation mimicking native IL-2 bound to CD25. These mutations effectively eliminate the functional requirement of IL-2 for CD25 expression and elicit proliferation of T cells. Compared to IL-2, the IL-2 superkine induces superior expansion of cytotoxic T cells, leading to improved antitumour responses in vivo, and elicits proportionally less toxicity by lowering the expansion of Tregulatory cells and reducing pulmonary oedema.
- Exploiting a natural conformational switch to engineer an interleukin-2 'superkine': AM. Levin, et al.; Nature 484, 529 (2012)






