Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
anti-TNF-α (mouse), mAb (blocking) (V1q) (preservative free)

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Tumor Necrosis Factor Ligand Superfamily Member 2; TNFSF2; Cachectin |
| Product Type | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Clone | V1q |
| Isotype | Rat IgG |
| Source/Host | Purified from concentrated hybridoma tissue culture supernatant. |
| Immunogen/Antigen | Cytotoxin purified from ConA induced T cell clone 29. |
| Label/Conjugates | Preservative Free |
| Application |
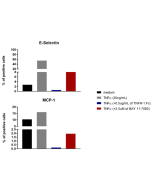
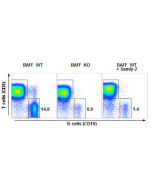
Functional Application: Inhibition of mouse TNF-α function in vivo (in mice). 20µg of antibody/mouse is sufficient to block the activity of endogenous mouse TNF-α. |
| Crossreactivity |
Human Mouse |
| Specificity |
Recognizes mouse TNF-α. Reacts with both natural and recombinant mouse TNF-α. Cross-reacts with recombinant human TNF-α in an ELISA-binding assay (blocking not tested). Does not cross-react with TNF-β (Lymphotoxin-α) |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity Detail | Protein G-affinity purified. |
| Endotoxin Content | <0.01EU/μg purified protein (LAL test). |
| Concentration | 1mg/ml |
| Formulation | Liquid. In PBS. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Accession Number | P06804 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After opening, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin or cachectin and formerly known as tumor necrosis factor-α) is a cytokine involved in systemic inflammation and metabolism and is a member of a group of cytokines that stimulate the acute phase reaction. It causes tumor necrosis in vivo and shows also cytolytic activity against tumors. Signal transduction occurs via two types of TNF-receptors, the TNF-receptors 1 and 2. The receptor TNF-R1 is activated by both the membrane-bound and soluble trimeric forms of TNF-α, whereas the receptor TNF-R2 only responds to the membrane-bound form of TNF-α. The monoclonal antibody V1q recognizes endogenous mouse TNF-α.
- Requirement of endogenous tumor necrosis factor/cachectin for recovery from experimental peritonitis: B. Echtenacher, et al.; J. Immunol. 145, 3762 (1990)
- Pharmacologic Inhibitors of Tumor Necrosis Factor Production Exert Differential Effects in Lethal Endotoxemia and in Infection with Live Microorganisms in Mice: M.G. etea, et al.; J. Inf. Dis. 171, 393 (1995)
- A monoclonal antibody against tumour necrosis factor-alpha improves survival in experimental multiple organ dysfunction syndrome: M.J. Jansen, et al.; Cytokine 10, 904 (1998)
- Anti-inflammatory effects of systemic anti-tumour necrosis factor α treatment in human/murine SCID arthritis: H. Schadlich, et al.; Ann. Rheum. Dis. 58, 428 (1999)
- Therapeutic neutralization of CD95-ligand and TNF attenuates brain damage in stroke: A. Martin-Villablba, et al.; Cell Death Diff. 8, 679 (2001)
- Roles of tumor necrosis factor p55 and p75 receptors in TNF-a-induced vascular permeability: E. Ferrero, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 281, C1173 (2001)
- Improving chemotherapeutic drug penetration in tumors by vascular targeting and barrier alteration: F. Curnis, et al.; J. Clin. Invest. 110, 475 (2002)
- An Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Antibody Inhibits the Development of Experimental Skin Tumors: K.A. Scott, et al.; Mol. Cancer Therap. 2, 445 (2003)
- Neutralization of CD95 ligand promotes regeneration and functional recovery after spinal cord injury: D. Demjen, et al.; Nat. Med. 10, 389 (2004)
- Blockade of TNF-α Decreases Both Inflammation and Efficacy of Intrapulmonary Ad.IFNβ Immunotherapy in an Orthotopic Model of Bronchogenic Lung Cancer: M.J. Wilderman, et al.; Mol. Ther. 13, 910 (2006)
- Severely impaired insulin signaling in chronic wounds of diabetic ob/ob mice: a potential role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: I. Goren, et al.; Am. J. Pathol. 168, 765 (2006)
- Systemic Anti-TNFα Treatment Restores Diabetes-Impaired Skin Repair in ob/ob Mice by Inactivation of Macrophages: I. Goren, et al.; J. Clin. Invest. 127, 2259 (2007)
- Tumor Necrosis Factor a Sensitizes Primary Murine Hepatocytes to Fas/CD95-Induced Apoptosis in a Bim- and Bid-Dependent Manner: K. Schmich, et al.; Hepatol. 53, 282 (2011)
- TNF signaling drives myeloid-derived suppressor cell accumulation: X. Zhao, et al.; J. Clin. Invest. 122, 4094 (2012)
- Long-term amelioration of established collagen-induced arthritis achieved with short-term therapy combining anti-CD3 and anti-tumor necrosis factor treatments: F. Depis, et al.; Arthr. Rheumatol. 64, 3189 (2012)
- Targeting Endothelial CD146 Attenuates Colitis and Prevents Colitis-Associated Carcinogenesis: S. Xing, et al.; Am. J. Pathol. 184, 1604 (2014)