Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
anti-BAFF (mouse), mAb (blocking) (Sandy-2)
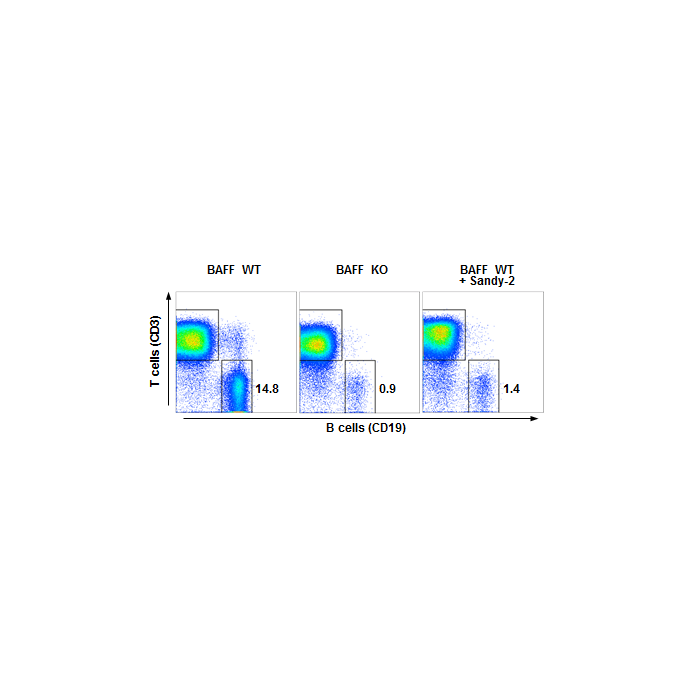
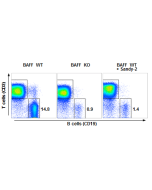
Method: Wild type C57BL/6 mice were treated i.p. at day 0 (single administration) with monoclonal antibody anti-BAFF (mouse), mAb (Sandy-2) (at 2mg/kg). Lymph nodes were prepared at week 2 and analyzed by FACS for the presence of T (CD3) and B (CD19) cells. Untreated BAFF WT and KO mice were analyzed in parallel.
Method: A) Immunofluorescence of IgA-positive plasma cells (pink) and DAPI-positive nuclei (blue) in gut jejunum sections of 10-week-old wild type C57/Bl6 mice treated with 4 weekly i.p. injections of the indicated antibodies at 2 mg/kg. B) Quantification of IgA-positive plasma cells in the gut (average of 2 sections/mouse) of mice treated with Isotype control (n=5), or with anti-APRIL Centotto-1 (n=5), or with anti-BAFF Sandy-2 (n=4) or with both Centotto-1 and Sandy-2 (n=5). One way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. ns: not significant. **** P<0.0001. Picture courtesy of Dr Mahya Eslami, Dr Pascal Schneider Lab, University of Lausanne, Switzerland
Method: A) Dot plots of CD3+ T cells versus B220+ B cells in lymph nodes of 12-week-old wild type C57/Bl6 mice treated with 4 weekly i.p. injections of the indicated antibodies at 2 mg/kg. B) Quantification of B cell to T cell ratio in lymph nodes of mice treated with Isotype control (n=5), or with anti-APRIL Centotto-1 (n=5), or with anti-BAFF Sandy-2 (n=4) or with both Centotto-1 and Sandy-2 (n=5). One way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. ns: not significant. * P < 0.05. ** P<0.01. *** P<0.001. **** P<0.0001.
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | BLyS; TALL-1; CD257; B Cell Activating Factor; TNFSF13B |
| Product Type | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Clone | Sandy-2 |
| Isotype | Mouse IgG1κ |
| Source/Host | Purified from concentrated hybridoma tissue culture supernatant. |
| Immunogen/Antigen | Recombinant mouse BAFF. |
| Application |
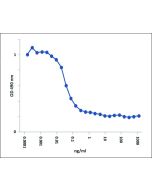
Functional Application: Inhibition of mouse BAFF binding to BAFF-R and TACI (BCMA not tested); blocks BAFF activity in mice. Injection of the anti-BAFF (mouse), mAb (Sandy-2) in mice creates a BAFF KO phenotype within 2 weeks, that can be maintained as long as necessary (> 6 months) by further injections of Sandy-2 every 2 weeks. |
| Crossreactivity | Mouse |
| Specificity |
Recognizes mouse BAFF. |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity Detail | Protein G-affinity purified. |
| Endotoxin Content | <0.01EU/μg purified protein (LAL test). |
| Concentration | 1mg/ml |
| Formulation | Liquid. In PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Other Product Data |
Note: BAFF and APRIL contribute to maintaining IgG, IgA, and IgM plasma cells in the bone marrow (BM), spleen, and intestine and rely mainly on three ligand/receptor pairs: APRIL-BCMA, BAFF-TACI, and APRIL-TACI. Together, these actors account for 90% of circulating antibodies. To efficiently target plasma cells, dual inhibition of BAFF (using blocking anti-BAFF (mouse), mAb (Sandy-2) (Prod. No. AG-20B-0063)) and APRIL (using blocking anti-APRIL (mouse), mAb (blocking) (Centotto-1) (Prod. No. AG-20B-0083PF) both developed at AdipoGen Life Sciences are required in a recently published study (see also Figure). |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Do not freeze. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
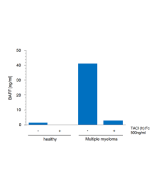
BAFF is a master regulator of peripheral B cell survival and, together with IL-6, promotes Ig class-switching and plasma cell differentiation. BAFF co-stimulates activated T cells. Increased levels of soluble BAFF have been detected in the serum of patients with various autoimmune diseases, such as Sjögren’s syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Furthermore, BAFF is found in inflammatory sites in which there is lymphoid neogenesis. BAFF levels are elevated in patients with multiple myeloma and B cell chronic lymphoid leukemia (B-CCL).
- The B cell-stimulatory cytokines BLyS and APRIL are elevated in human periodontitis and are required for B cell-dependent bone loss in experimental murine periodontitis: T. Abe, et al.; J. Immunol. 195, 1427 (2015)
- Antibodies that block or activate mouse B cell activating factor of the TNF family (BAFF) respectively induce B cell depletion or B cell hyperplasia: C. Kowalczyk-Quintas, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 291, 19826 (2016)
- Interactions between fibroblastic reticular cells and B cells promote mesenteric lymph node lymphangiogenesis: L.K. Dubey, et al.; Nat. Commun. 8, 367 (2017)
- The unknown aspect of BAFF: Inducing IL-35 production by a CD5+CD1dhiFcγRIIbhi regulatory B-Cell subset in lupus: Y. Zhang, et al.; J. Invest. Dermatol. 137, 2532 (2017)
- Berberine demonstrates anti-inflammatory properties in Helicobacter pylori-infected mice with chronic gastritis by attenuating the Th17 response triggered by the B cell-activating factor: X. Wu, et al.; J. Cell. Biochem. 119, 5373 (2018)
- A loop region of BAFF controls B cell survival and regulates recognition by different inhibitors: M. Vigolo, et al.; Nat. Commun. 9, 1199 (2018)
- Healthy donor polyclonal IgMs diminish B-lymphocyte autoreactivity, enhance regulatory T cell generation, and reverse type 1 diabetes in NOD mice: C.S. Wilson, et al.; Diabetes 67, 2349 (2018)
- B2-Lymphocyte responses to oxidative stress-derived antigens contribute to the evolution of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): S. Bruzzi, et al.; Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 124, 249 (2018)
- The Un-BLyS-Ful State: Blocking Factor VIII Inhibitor Development with BLyS Depletion: B.S. Doshi, et al.; Blood 132, 138 (2018)
- Depletion of BAFF cytokine exacerbates infection in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infected mice: D. Garic, et al.; J. Cyst. Fibr. 18, 349 (2019)
- No interactions between heparin and atacicept, an antagonist of B cell survival cytokines: C. Kowalczyk‐Quintas, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol. 176, 4019 (2019)
- Incorporating B cell activating factor (BAFF) into the membrane of rabies virus (RABV) particles improves the speed and magnitude of vaccine-induced antibody responses: J.R. Plummer & J.P. McGettigan; PLoS 13, e0007800 (2019)
- BAFF Blockade Attenuates Inflammatory Responses and Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction in a Murine Endotoxemia Model: R. Quan, et al.; Front. Immunol. 11, 570920 (2020)
- B cell-activating factor modulates the factor VIII immune response in hemophilia A: B.S. Doshi, et al.; J. Clin. Invst. 131, 142906 (2021)
- B cell activating factor antagonism attenuates the growth of experimental abdominal aortic aneurysm: M.D. Spinosa, et al.; Am. J. Pathol. 191, 2231 (2021)
- B cell activating factor regulates periodontitis development by suppressing inflammatory responses in macrophages: L. Wang, et al.; BMC Oral Health 21, 426 (2021)
- BAFF and APRIL counter-regulate susceptibility to inflammation-induced preterm birth: JR. Doll, et al.; Cell Rep. 42, 112352 (2023)
- B cell depletion with anti-CD20 promotes neuroprotection in a BAFF-dependent manner in mice and humans: A.A. Wang, et al.; Sci. Transl. Med. 16, eadi0295 (2024)
- Unique and redundant roles of mouse BCMA, TACI, BAFF, APRIL and IL-6 in supporting antibody-producing cells in different tissues: M. Eslami, et al.; PNAS 21, e2404309121 (2024)
- BAFF neutralization impairs the autoantibody-mediated clearance of dead adipocytes and aggravates obesity-induced insulin resistance: M.D. Lempicki, et al.; Front. Immunol. 15, 1436900 (2024)
- Lymphotoxin-dependent elevated meningeal CXCL13:BAFF ratios drive gray matter injury: I. Naouar, et al.; Nat. Immunol. 27, 48 (2026)