Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
Fc (human):BAFF (human) (rec.)

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | BLyS; TALL-1; CD257; B Cell Activating Factor; TNFSF13B; Tumor Necrosis Factor Ligand Superfamily Member 13B |
| Product Type | Protein |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | CHO cells |
| Sequence |
The receptor-binding domain of human BAFF (aa 136-285) is fused at the N-terminus to the Fc portion of human IgG1. |
| Crossreactivity |
Human Mouse |
| Specificity |
Binds to human and mouse BAFF-R, TACI and BCMA. |
| Biological Activity |
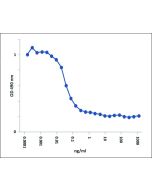
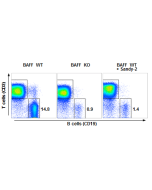
Rescues the production of mature follicular and marginal zone B cells. |
| MW |
~50kDa (SDS-PAGE; reducing conditions) ~100kDa (SDS-PAGE; non-reducing conditions) ~300kDa (SDS-PAGE; native conditions; multimerizes and forms hexamers) |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity Detail | Protein A affinity purified. |
| Endotoxin Content | <0.01EU/μg purified protein (LAL test; Lonza). |
| Concentration |
After reconstitution: for 10µg size: 0.1mg/ml for 500µg size: 1 mg/ml |
| Reconstitution |
10µg size: Reconstitute with 100µl sterile water. 500µg size: Reconstitute with 500µl sterile water. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Contains PBS. |
| Protein Negative Control | |
| Other Product Data |
UniProt link Q9Y275: BAFF (human) |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Centrifuge lyophilized vial before opening and reconstitution. PBS containing at least 0.1% BSA should be used for further dilutions. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. Working aliquots are stable for up to 3 months when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
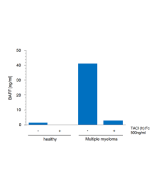
BAFF is mainly produced by innate immune cells such as neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, follicular dendritic cells. T cells, activated B cells, some malignant B cells and also non-lymphoid cells like astrocytes, synoviocytes and epithelial cells can also produce BAFF. BAFF binds three distinct receptors (BAFF-R, TACI and BCMA) expressed predominantly on B cells, although activated T cells also express BAFF-R. BAFF is a master regulator of peripheral B cell survival, and together with IL-6, promotes Ig class-switching and plasma cell differentiation. Besides its major role in B cell biology, BAFF co-stimulates activated T cells. Deregulated expression of BAFF leads to autoimmune disorders in mice. In humans, elevated levels of soluble BAFF have been detected in the serum of patients with various autoimmune diseases such as Sjoegren syndrome, Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Multiple sclerosis (MS) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). BAFF has also increased levels in some lymphoid cancers.
- Rescue of the mature B cell compartment in BAFF-deficient mice by treatment with recombinant Fc-BAFF: L.K. Swee, et al.; Immunol. Lett. 131, 40 (2010)
- Soluble BAFF levels inversely correlate with peripheral B cell numbers and the expression of BAFF receptors: M. Kreuzaler, et al.; J. Immunol. 188, 497 (2012)
- BAFF 60-mer, and differential BAFF 60-mer dissociating activities in human serum, cord blood and cerebrospinal fluid: M. Eslamy, et al.; Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8, 577662 (2020)