Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
BAFF, Soluble (human) (60-mer) (rec.) (highly active)

A. BAFF (60-mer) was submitted to size fractionation on a Superdex 200 gel filtration column. The peak indicated with dotted red lines (60-mer) was isolated and processed to obtain purified BAFF, Soluble (human) (60-mer) (AG-40B-0112). Elution position of MW markers are indicated on the top of the figure.
B. For comparison, elution profile of the related product BAFF, Soluble (human) (3-mer).
Method: Jurkat T cells expressing a BCMA:Fas chimerical receptor (containing a extracellular domain of human BCMA and the intracellular domain of human Fas) were exposed for 16h to various concentrations of BAFF, Soluble (human) (60-mer). Cell viability was measured with the PMS/MTS assay.
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | BLyS; TALL-1; CD257; B Cell Activating Factor; TNFSF13B; Tumor Necrosis Factor Ligand Superfamily Member 13B |
| Product Type | Protein |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | E. coli |
| Sequence |
The extracellular domain of human BAFF (aa 134-285) is fused at the N-terminus to a His-tag. |
| Crossreactivity |
Human Mouse |
| Specificity |
Binds to human and mouse BAFF-R, TACI and BCMA. Relative binding affinity (EC50) for BAFF-R (human): ~3ng/ml. |
| Biological Activity |
Increases B cell survival/proliferation. Increases CD21/CD23 expression on B cells in vivo. Activates BAFF-R, TACI and BCMA receptors. Works at concentrations <20ng/ml. |
| MW |
~19kDa (under reduced conditions) ~1100kDa (under native conditions) |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Endotoxin Content | <0.01EU/μg purified protein (LAL test; Lonza). |
| Concentration | 0.1mg/ml after reconstitution. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute with 100μl sterile water. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Contains PBS. |
| Other Product Data |
UniProt link Q9Y275: BAFF (human) |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Centrifuge lyophilized vial before opening and reconstitution. PBS containing at least 0.1% BSA should be used for further dilutions. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. Working aliquots are stable for up to 3 months when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
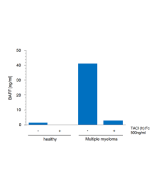
BAFF is mainly produced by innate immune cells such as neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, follicular dendritic cells. T cells, activated B cells, some malignant B cells and also non-lymphoid cells like astrocytes, synoviocytes and epithelial cells can also produce BAFF. BAFF binds three distinct receptors (BAFF-R, TACI and BCMA) expressed predominantly on B cells, although activated T cells also express BAFF-R. BAFF is a master regulator of peripheral B cell survival, and together with IL-6, promotes Ig class-switching and plasma cell differentiation. Besides its major role in B cell biology, BAFF co-stimulates activated T cells. Deregulated expression of BAFF leads to autoimmune disorders in mice. In humans, elevated levels of soluble BAFF have been detected in the serum of patients with various autoimmune diseases such as Sjoegren syndrome, Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Multiple sclerosis (MS) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). BAFF has also increased levels in some lymphoid cancers.
Processed human BAFF can either remain as a trimer, which is usual for TNF family ligands or assemble into 60-mer composed of 20 trimers. Mouse BAFF 60-mer has been identified in the serum of BAFF transgenic mice. Oligomerization of BAFF 3-mer into 60-mer in human BAFF is prevented by mutation of His218, a residue critical for 3-mer-to-3-mer interactions, but not for receptor binding. Despite the predominant functional role of processed BAFF in vivo, membrane-bound BAFF might also play a role. Indeed, soluble BAFF (3-mer) can trigger BAFF-R but not TACI or BCMA, whereas oligomeric forms of BAFF (BAFF 60-mer), which mimic membrane-bound BAFF, activate all BAFF receptors.
- TACI, unlike BAFF-R, is solely activated by oligomeric BAFF and APRIL to support survival of activated B cells and plasmablasts: C. Bossen, et al.; Blood 111, 1004 (2008)
- Mutation of the BAFF furin cleavage site impairs B-cell homeostasis and antibody responses: C. Bossen, et al.; Eur. J. Immunol. 41, 787 (2011)
- No evidence that soluble TACI induces signalling via membrane-expressed BAFF and APRIL in myeloid cells: J. Nys, et al.; PLoS One 8, e61350 (2013)
- BAFF 60-mer, and differential BAFF 60-mer dissociating activities in human serum, cord blood and cerebrospinal fluid: M. Eslamy, et al.; Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8, 577662 (2020)
- APRIL limits atherosclerosis by binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans: D. Tsiantoulas, et al.; Nature 597, 92 (2021)
- Ligand-independent oligomerization of TACI is controlled by the transmembrane domain and regulates proliferation of activated B cells: C.R. Smulski, et al.; Cell Rep. 38, 110583 (2022)
- BAFF antagonism via the BAFF receptor 3 binding site attenuates BAFF 60-mer-induced classical NF-κB signaling and metabolic reprogramming of B cells: M. Lempicki, et al.; Cell. Immunol. 381, 104603 (2022)
- Povetacicept, an Enhanced Dual APRIL/BAFF Antagonist that Modulates B Lymphocytes and Pathogenic Autoantibodies for the Treatment of Lupus and Other B Cell-Related Autoimmune Diseases: L.S. Evans, et al.; Arthritis Rheumatol. 75, 1187 (2023)
- Non-apoptotic FAS signaling controls mTOR activation and extrafollicular maturation in human B cells: J. Staniek, et al.; Sci. Immunol. 9, eadj5948 (2024)