Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
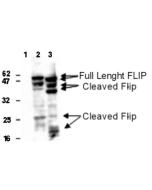
anti-FLIP (human), mAb (NF6)

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | I-FLICE; CLARP; CASPER; Usurpin, CASH; FLAME-1 |
| Product Type | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Clone | NF6 |
| Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Immunogen/Antigen | Recombinant human FLIP (aa 1-480). |
| Application |
Immunocytochemistry |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Specificity |
Recognizes short (FLIPS) and long (FLIPL) splice variants of human FLIP. This antibody recognizes an epitope in the N-terminal DED region (aa1-194). |
| Concentration | 1 mg/ml |
| Formulation | Liquid. In PBS containing 10% glycerol and 0.02% sodium azide. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
FLIP is an apoptosis regulator protein which functions as a crucial link between cell survival and cell death pathways in mammalian cells and acts as an inhibitor of TNFRSF6 mediated apoptosis. A proteolytic fragment (p43) is likely retained in the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) thereby blocking further recruitment and processing of caspase-8 at the complex. Full length and shorter isoforms have been shown either to induce apoptosis or to reduce TNFRSF-triggered apoptosis. FLIP lacks enzymatic (caspase) activity. FLIP is highly expressed in skeletal muscle, pancreas, heart, kidney, placenta and peripheral blood leukocytes.
- The role of c-FLIP in modulation of CD95-induced apoptosis: S. Scaffidi, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 274, 1541 (1999)
- An inducible pathway for degradation of FLIP protein sensitizes tumor cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis: Y. Kim, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 277, 22320 (2002)
- Caspase-10 is recruited to and activated at the native TRAIL and CD95 death-inducing signalling complexes in a FADD-dependent manner but can not functionally substitute caspase-8: M.R. Sprick, et al.; EMBO J. 21, 4520 (2002)
- Enhancement of Apo2L/TRAIL (tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand)-induced apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines by chemotherapeutic agents without correlation to the expression level of cellular protease: S. Frese, et al.; J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 123, 168 (2002)
- Lack of Proapoptotic Activity of Soluble CD95 Ligand Is Due to Its Failure to Induce CD95 Oligomers: S. Jang, et al.; J. Int. Cyt. Res. 23, 441 (2003)
- Proteasome inhibition results in TRAIL sensitization of primary keratinocytes by removing the resistance-mediating block of effector caspase maturation: M. Leverkus, et al.; Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 777 (2003)
- Suramin inhibits death receptor-induced apoptosis in vitro and fulminant apoptotic liver damage in mice: S.T. Eichhorst, et al.; Nature Med. 10, 602 (2004)
- The c-FLIP-NH2 terminus (p22-FLIP) induces NF-kappaB activation: A. Golks, et al.; J. Exp. Med. 203, 1295 (2006)
- Caspase-2 is activated at the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex in the course of CD95-induced apoptosis: I.N. Lavrik, et al.; Blood 108, 559 (2006)
- The role of CAP3 in CD95 signaling: new insights into the mechanism of procaspase-8 activation: A. Golks, et al.; Cell Death Diff. 13, 489 (2006)
- Expression of c-FLIP is primarily detected in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Hodgkin's lymphoma and correlates with lack of caspase 8 activation: I.S. van Houdt, et al.; Histopathology 51, 778 (2007)
- CD95 Stimulation Results in the Formation of a Novel Death Effector Domain Protein-containing Complex: I.N. Lavrik, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 283, 26401 (2008)
- A New C-terminal Cleavage Product of Procaspase-8, p30, Defines an Alternative Pathway of Procaspase-8 Activation: J.C. Hoffmann, et al.; Mol. Cell Biol. 29, 4431 (2009)
- Stoichiometry of the CD95 Death-Inducing Signaling Complex: Experimental and Modeling Evidence for a Death Effector Domain Chain Model: K. Schleich, et al.; Mol. Cell 47, 1 (2012)
- Opposing roles of TGF-β and EGF in the regulation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human breast epithelial cells: A. Cano-Gonzalez & A. Lopez-Rivas; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1863, 2104 (2016)
- The TRAIL-Induced Cancer Secretome Promotes a Tumor-Supportive Immune Microenvironment via CCR2: T. Hartwig, et al.; Mol. Cell 65, 730 (2017)
- c-FLIP is a target of the E3 ligase deltex1 in gastric cancer: T.S. Hsu, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 9, 135 (2018)
- Involvement of both caspase-8 and Noxa-activated pathways in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in triple-negative breast tumor cells: A. Cano-González, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 9, 134 (2018)
- TRAF2 Controls Death Receptor-Induced Caspase-8 Processing and Facilitates Proinflammatory Signaling; J. Kreckel, et al.; Front. Immunol. 10, 2024 (2019)
- Pevonedistat (MLN4924): mechanism of cell death induction and therapeutic potential in colorectal cancer: J. Ferris, et al.; Cell Death Discov. 6, 61 (2020)
- Potent pro-apoptotic combination therapy is highly effective in a broad range of cancers: A. Montinaro, et al.; Cell Death Differ. 29, 492 (2021)