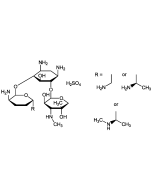Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
Puromycin . dihydrochloride
As low as
45
CHF
CHF 45.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0078-M02525 mgCHF 45.00
AG-CN2-0078-M100100 mgCHF 120.00
AG-CN2-0078-M250250 mgCHF 220.00
AG-CN2-0078-M500500 mgCHF 390.00
AG-CN2-0078-G0011 gCHF 670.00

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CL16,536; NSC 3055; Stylomycin |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C22H29N7O5 . 2HCl |
| MW | 471.5 . 72.9 |
| Merck Index | 14: 7943 |
| CAS | 58-58-2 |
| RTECS | AU7355000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Streptomyces alboniger. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR |
| Other Product Data |
NOTE: The working puromycin concentration for selection in mammalian cell lines ranges from 1-10 µg/ml. Prior to using the puromycin antibiotic, titrate the selection agent to determine the optimal concentration for target cell line. Use the lowest concentration that kills 100% of non-transfected cells in 3-5 days from the start of puromycin selection. See also online selection-protocol. |
| InChi Key | RXWNCPJZOCPEPQ-NIAQAADTBJ |
| Smiles | COC1=CC=C(C[C@H](N)C(=O)NC2[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]([C@H]2O)N2C=NC3=C2N=CN=C3N(C)C)C=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Protocols |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Aminonucleoside antibiotic.
- Protein synthesis inhibitor. Disrupts peptide transfer on ribosomes (acting as an acyl-tRNA analog) causing premature chain termination during translation. Translational inhibitor in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in both in vitro and in vivo systems.
- Inhibits the transport of proteins into the mitochondria in vitro.
- Reversible inhibitor of dipeptidyl-peptidase II (serine peptidase) and cytosol alanyl aminopeptidase (metallopeptidase).
- Apoptosis inducer.
- Inhibits the growth of Gram-positive bacteria, various animal and insect cells. Fungi and Gram-negative bacteria are resistant due to the low permeability to the antibiotic.
- Antineoplastic agent.
- Used in cell biology as selective agent in cell culture systems. It allows selection for cells that contain the resistance gene puromycin N-acetyl-transferase (PAC). Puromycin has a fast mode of action, causing rapid cell death at low antibiotic concentrations. Adherent mammalian cells are sensitive to concentrations of 2 to 5 µg/ml, while cells in suspension are sensitive to concentrations as low as 0.5 to 2 µg/ml. Puromycin-resistant stable mammalian cell lines can be generated in less than one week.
Product References
- Puromycin inhibition of protein synthesis: M.A. Darken; Pharmacol. Rev. 16, 223 (1964) (Review)
- Mechanism of puromycin action: fate of ribosomes after release of nascent polypeptide chains from polysomes: M.E. Azzam & D. Algranati; PNAS 70, 3866 (1973)
- Inhibition of aminopeptidase and acetylcholinesterase by puromycin and puromycin analogs: L.B. Hersh; J. Neurochem. 36, 1594 (1981)
- Isolation and properties of a puromycin acetyltransferase from puromycin-producing Streptomyces alboniger: S.Y. Paik, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 38, 1761 (1985)
- Biosynthesis of puromycin by Streptomyces alboniger. Characterization of puromycin N-acetyltransferase: J. Vara, et al.; Biochemistry 24, 8074 (1985)
- Molecular analysis of the pac gene encoding a puromycin-N-acetyl transferase from Streptomyces alboniger: R.A. Lacalle, et al.; Gene 79, 375 (1989)
- Use of puromycin N-acetyltransferase (PAC) as a new reporter gene in transgenic animals: E. Gomez Lahoz, et al.; Nucleic Acids Res. 19, 3465 (1991)
- Pac gene as efficient dominant marker and reporter gene in mammalian cells: S. De La Luna & J. Ortin; Meth. Enzymol. 216, 376 (1992)
- Puromycin reaction for the A site-bound peptidyl-tRNA: Y. Semenkov, et al.; FEBS Lett. 296, 207 (1992)
- Unexpected cytokinetic effects induced by puromycin include a G2-arrest, a metaphase-mitotic-arrest, and apoptosis: A.N. Davidoff & B.V. Mendelow; Leuk. Res. 16, 1077 (1992)
- Puromycin is a potent and specific inhibitor of tyrosine kinase activity in HL-60 cells: A.N. Davidoff & B.V. Mendelow; Anticancer Res. 12, 1761 (1992)
- Puromycin inhibits protein import into mitochondria by interfering with an intramitochondrial ATP-dependent reaction: J. Price & K. Verner; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1150, 89 (1993)
- Puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase. Sequence analysis, expression, and functional characterization: D.B. Constam, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 270, 26931 (1995)
- A simple assay for puromycin N-acetyltransferase: selectable marker and reporter: C. Mielke, et al.; Trends Genet. 11, 258 (1995)
- Cell proliferation and apoptosis of the glomerular epithelial cells in rats with puromycin aminonucleoside nephrosis: H. Shiiki, et al.; Pathobiology 66, 221 (1998)
- Puromycin Aminonucleoside Induces Glomerular Epithelial Cell Apoptosis: V. Sanwal, et al.; Exp. Mol. Pathol. 70, 54 (2001)
- Increased Apoptosis in Acute Puromycin Aminonucleoside Nephrosis: L. Fernandez, et al.; Exp. Nephrol. 9, 99 (2001)
- A puromycin-dependent activity-based sensing probe for histochemical staining of hydrogen peroxide in cells and animal tissues: K. Hoshi, et al.; Nature Protoc. 17, 1691 (2022)