Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
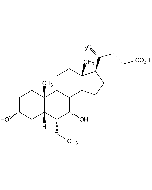
Stigmasterol
As low as
60
CHF
CHF 60.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0412-G0011 gCHF 60.00
AG-CN2-0412-G0055 gCHF 240.00

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Stigmasterin; Phytosterol; β-Stigmasterol; Serposterol; Wulzen anti-stiffness Factor; NSC8095 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C29H48O |
| MW | 412.7 |
| CAS | 83-48-7 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. Originally isolated from various plants and marine organisms. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (NMR) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, ethanol or dimethylformamide. Sparingly soluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1-H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | HCXVJBMSMIARIN-PHZDYDNGSA-N |
| Smiles | [H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])CC=C4C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)[C@H](C)\C=C\[C@@H](CC)C(C)C |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Anti-hypercholestrolemic compound [1, 7].
- Anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating effects [2, 4].
- Anticancer compound. Chemopreventive [3, 12, 13].
- Cytostatic. Cell growth inhibitor [5].
- Antimutagenic [6].
- Potent in vitro antagonist of FXR (farnesoid X receptor) [8].
- DNA polymerase β inhibitor [9].
- Potent antioxidant, hypoglycemic and thyroid inhibiting agent [10].
- Anti-osteoarthritic. Decreases the expression of matrix metalloproteinases [11].
- Neuroprotective [15].
- Is used as a precursor for synthetic progesterone and vitamin D3 and is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of androgens, estrogens and corticoids [14].
Product References
- Antihypercholesterolemic studies with sterols: beta-sitosterol and stigmasterol: R.F. Chandler, et al.; J. Pharm. Sci. 68, 245 (1979)
- Topical antiinflammatory activity of phytosterols isolated from Eryngium foetidum on chronic and acute inflammation models: M.D. Garcia, et al.; Phytother. Res. 13, 78 (1999)
- Phytosterols as anticancer dietary components: evidence and mechanism of action: A.B. Awad & C.S. Fink; J. Nutr. 130, 2127 (2000) (Review)
- Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulating Properties of a Sterol Fraction from Sideritis foetens CLEM: N. Antonio, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 24, 470 (2001)
- Cyostatic activity of Achillea ageratum L.: M.A. Gomez, et al.; Phytother. Res. 15, 633 (2001)
- Antimutagenic Constituents from the Thorns of Gleditsia sinensis: L. Jae-Chul, et al.; Chem. Pharm. Bull. 53, 561 (2005)
- Stigmasterol reduces plasma cholesterol levels and inhibits hepatic synthesis and intestinal absorption in the rat: A.K. Batta, et al.; Metabolism 55, 292 (2006)
- Stigmasterol, a soy lipid-derived phytosterol, is an antagonist of the bile acid nuclear receptor FXR: B.A. Carter, et al.; Pediatr. Res. 62, 301 (2007)
- Inhibitors of DNA polymerase β: Activity and mechanism: G. Zhijie, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16, 4331 (2008)
- Thyroid inhibitory, antiperoxidative and hypoglycemic effects of stigmasterol isolated from Butea monosperma: S. Panda, et al.; Fitoterapia 80, 123 (2009)
- Stigmasterol: a phytosterol with potential anti-osteoarthritic properties: O. Gabay, et al.; Osteoarthritis Cartilage 18, 106 (2010)
- Cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of the oxidized derivatives of stigmasterol in the U937 human monocytic cell line: Y.C. O'Callaghan, et al.; J. Agric. Food Chem. 58, 10793 (2010)
- Phytosterols: perspectives in human nutrition and clinical therapy: S.P. Choudhary & L.S. Tran; Curr. Med. Chem. 18, 4557 (2011) (Review)
- Stigmasterol: A comprehensive review: N. Kaur, et al.; IJPSR 2, 2259 (2011) (Review)
- Rhinacanthus nasutus Extracts Prevent Glutamate and Amyloid-β Neurotoxicity in HT-22 Mouse Hippocampal Cells: Possible Active Compounds Include Lupeol, Stigmasterol and β-Sitosterol: J.M. Brimson, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 13, 5074 (2012)