Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
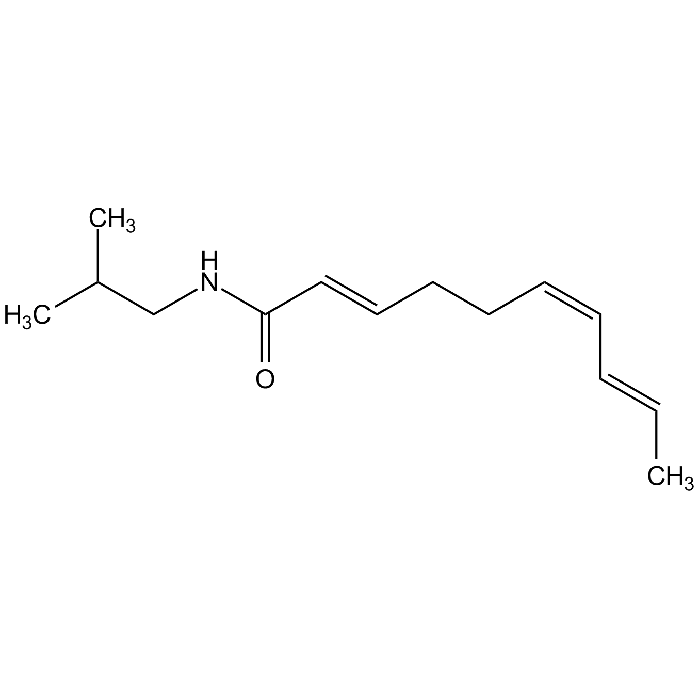
Spilanthol
As low as
290
CHF
CHF 290.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0543-M0055 mgCHF 290.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Affinin; (2E,6Z,8E)-N-Isobutyldeca-2,6,8-trienamide |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C14H23NO |
| MW | 221.3 |
| CAS | 25394-57-4 |
| RTECS | HE1800000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from aerial parts of Acmella oleracea. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Yellowish oil. |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, methanol, chloroform, DMSO, ethyl ether, ethyl acetate or acetone. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | BXOCHUWSGYYSFW-HVWOQQCMSA-N |
| Smiles | CC(C)CNC(/C=C/CC/C=C\C=C\C)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and oxygen. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Spilanthol is a natural, non-toxic compound that has been traditionally used in folk medicine. It has sensory properties (pungency, tingling, numbing, mouth-watering) and is an excellent stable model compound for sensory/chemoreception studies like pellitorine and a biological analog of alpha-sanshool.
- Spilanthol shows various biological properties, including analgesic, antinociceptive, antioxidant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimutagenic, anti-wrinkle, bacteriostatic, insecticidal, anti-malarial, anti-larvicidal and anti-molluscicidal activities. There have also been reports on its activities as an anticonvulsant, aphrodisiac, pancreatic lipase inhibitor, anti-obesity agent, antimicrobial agent, diuretic, pronangiogenic compound, vasorelaxant, anti-HIV and toothache relief agent.
- The exact mechanism of action of spilanthol is still not fully understood. Molecular docking studies showed that the vasodilator effect induced by spilanthol involves activation of TRPA1 and TRPV1 channels and the CB1 and eCB receptors and inhibitory potential for JAK1 and JAK2 proteins, targets for its cytotoxicity against cancer cells.
- Spilanthol has also been used as a pro-drug, which is converted to Spilanthol Endoperoxide (SPLE) in the cellular milieu leading to inhibition of Prx3, increased mitochondrial oxidation and disruption of F-actin network, and inhibition of the bacterial pathogen Chlamydia trachomatis, responsible for a plethora of diseases ranging from blindness to pelvic inflammatory diseases and cervical cancer.
- Spilanthol is considered to be a natural, safe and nontoxic botox alternative (Bio-Botox). Spilanthol perfectly overcomes the epidermal barrier and migrates deep into the skin. Spilanthol has been used in cosmetics for the temporary relief of wrinkles (a sort of Cinderella effect lasting only a few hours).
Product References
- Spilanthol: occurrence, extraction, chemistry and biological activities: A.F. Barbosa, et al.; Rev. Brasileira de Farma. 26, 128 (2016)
- Spilanthol from Traditionally Used Spilanthes acmella Enhances AMPK and Ameliorates Obesity in Mice Fed High-Fat Diet: W. Huang, et al.; Nutrients 11, 991 (2019)
- Spilanthol Inhibits Inflammatory Transcription Factors and iNOS Expression in Macrophages and Exerts Anti-inflammatory Effects in Dermatitis and Pancreatitis: E. Bakondi, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 4308 (2019)
- Discovery of Spilanthol Endoperoxide as a Redox Natural Compound Active against Mammalian Prx3 and Chlamydia trachomatis Infection: R. Dushime, et al.; Antioxidants 9, 1220 (2020)
- Selected Alkaloids Used in the Cosmetics Industry: A. Stępniowska, et al.; J. Cosmet. Sci. 72, 229 (2021)
- Chymase inhibition: A key factor in the anti-inflammatory activity of ethanolic extracts and spilanthol isolated from Acmella oleracea: R. Stein, et al.; J. Ethnopharmacol. 270, 113610 (2021)
- Endothelial TRP channels and cannabinoid receptors are involved in affinin-induced vasodilation: C.J. Valencia-Guzman, et al.; Fitoterapia 153, 104985 (2021)
- Spilanthol-rich essential oil obtained by microwave-assisted extraction from Acmella oleracea (L.) R.K. Jansen and its nanoemulsion: Insecticidal, cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory activities: E. Spinozzi, et al.; Industr. Crops Prod. 172, 114027 (2021)
- Proangiogenic Effect of Affinin and an Ethanolic Extract from Heliopsis longipes Roots: Ex Vivo and In Vivo Evidence: P.E. Garcia-Badillo, et al.; Molecules 26, 7670 (2021)
- A Review of the Chemistry and Biological Activities of Acmella oleracea ("jambù", Asteraceae), with a View to the Development of Bioinsecticides and Acaricides: E. Spinozzi, et al.; Plants 11, 2721 (2022)
- Cytotoxic and molecular evaluation of spilanthol obtained from Acmella oleracea (L.) R. K. Jansen (jambu) in human gastric cancer cells: M.S.D.S. Pinheiro, et al.; Nat. Prod. Res. (epub ahead of print) (2023)
- Alkylamides from Acmella oleracea: antinociceptive effect and molecular docking with cannabinoid and TRPV1 receptors: R.M.K. Yien, et al.; Nat. Prod. Res. 37, 3136 (2023)
- Acmella oleracea extracts as green pesticides against eight arthropods attacking stored products: N.G. Kavallieratos, et al.; Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 30, 94904 (2023)






