Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
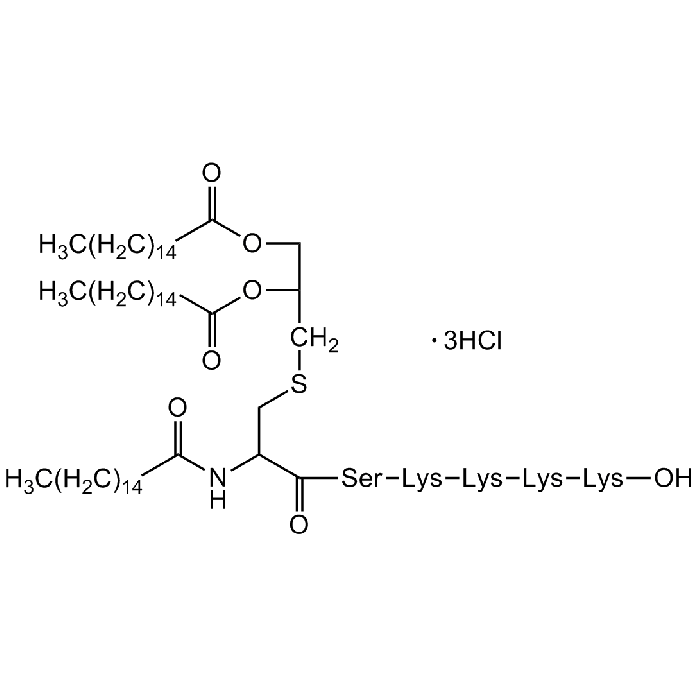
Pam3Cys-Ser-(Lys)4 . 3HCl
As low as
490
CHF
CHF 490.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CP3-0003-M0022 mgCHF 490.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Pam3Cys-Ser-(Lys)4 trihydrochloride; Pam3CSK4; Pam3Cys-SKKKK; (S)-[2,3-Bis(palmitoyloxy)-(2- RS)-propyl]-N-palmitoyl-(R)-Cys-(S)-Ser-(S)-Lys4-OH |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C81H156N10O13S . 3HCl |
| MW | 1510.3 . 109.4 |
| CAS | 112208-04-5 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | Absence of detectable protein or DNA contaminants with agonistic TLR activity. |
| Appearance | Colorless powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, saline or aqueous buffers at pH <7.5. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute in 2ml endotoxin-free water to get a 1mg/ml stock solution. Use a homogeniser or sonicator to prepare a homogenous solution. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. |
| Concentration | 1mg/ml after reconstitution. |
| InChi Key | ZRKOETJPZDQIFB-OQOFFOABSA-N |
| Smiles | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)NC(CSCC(COC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)C(=O)N[C@@H](CO)C(=O)C(=O)[C@H](CCCCN)NN[C@@H](CCCCN)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCCN)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCCN)C(O)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Selective agonist of TLR1/TLR2 complex.
- Cell permeable, water soluble synthetic cationic lipohexapeptide analog of the immunologically active N-terminal portion of bacterial lipoprotein that potently activates monocytes and macrophages.
- Potent and effective immune adjuvant. Exerts strong local response, enhances IgG2a and IgG1 titers and upregulates proinflammatory and Th1 cytokine genes.
- Potent activator of the proinflammatory transcription factor NF-κB.
Product References
- Lipopeptide derivatives of bacterial lipoprotein constitute potent immune adjuvants combined with or covalently coupled to antigen or hapten: A. Reitermann, et al.; Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 370, 343 (1989)
- Induction of tumor cytotoxicity in murine bone marrow-derived macrophages by two synthetic lipopeptide analogues: P. Hoffmann, et al.; Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 370, 575 (1989)
- Activation of superoxide formation and lysozyme release in human neutrophils by the synthetic lipopeptide Pam3Cys-Ser-(Lys)4. Involvement of guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins and synergism with chemotactic peptides: R. Seifert, et al.; Biochem. J. 267, 795 (1990)
- Synthesis of novel immunologically active tripalmitoyl-S-glycerylcysteinyl lipopeptides as useful intermediates for immunogen preparations: J. Metzger, et al.; Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 37, 46 (1991)
- The influence of various adjuvants on antibody synthesis following immunization with an hapten: J. Kellner, et al.; Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 373, 51 (1992)
- Lipopeptides are effective stimulators of tyrosine phosphorylation in human myeloid cells: S. Offermanns, et al.; Biochem. J. 282, 551 (1992)
- Comparison of adjuvant formulations for cytotoxic T cell induction using synthetic peptides: C.E. Hioe, et al.; Vaccine 14, 412 (1996)
- Cell Activation and Apoptosis by Bacterial Lipoproteins Through Toll-like Receptor-2: A.O. Aliprantis, et al.; Science 285, 736 (1999)
- Adjuvant effects of various lipopeptides and interferon-gamma on the humoral immune response of chickens: M.H. Erhard, et al.; Poult. Sci. 79, 1264 (2000)
- Immunostimulation by the synthetic lipopeptide P3CSK4: TLR4-independent activation of the ERK1/2 signal transduction pathway in macrophages: M.R. Muller, et al.; Immunology 103, 49 (2001)
- Lipopeptide structure determines TLR2 dependent cell activation level: U. Buwitt-Beckmann, et al.; FEBS J. 272, 6354 (2005)
- TLR1- and TLR6-independent recognition of bacterial lipopeptides: U. Buwitt-Beckmann, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 281, 9049 (2006)
- Human Langerhans cells selectively activated via Toll-like receptor 2 agonists acquire migratory and CD4+T cell stimulatory capacity: M. Peiser, et al.; J. Leukoc. Biol. 83, 1118 (2008)
- Post-injury immunosuppression and secondary infections are caused by an AIM2 inflammasome-driven signaling cascade: S. Roth, et al.; Immunity 54, 648 (2021)





