Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
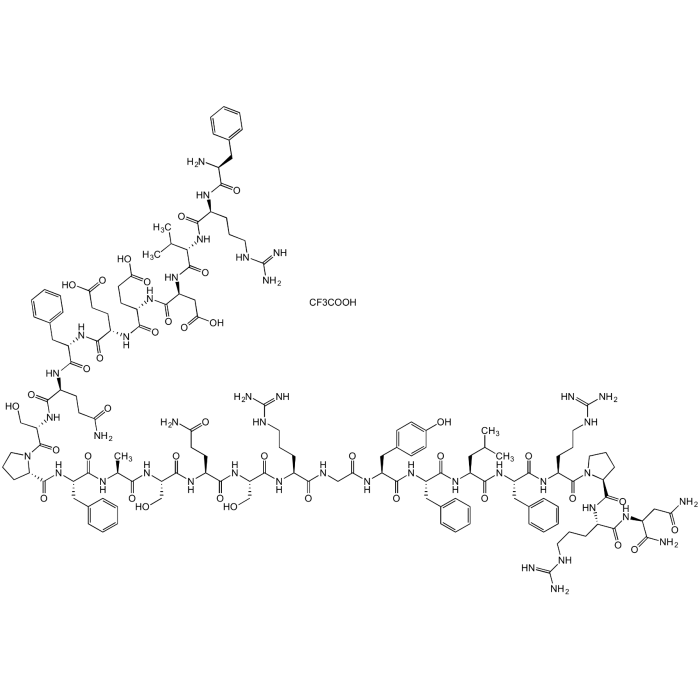
Neuromedin U-25 (human)
As low as
150
CHF
CHF 150.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CP3-0031-M0011 mgCHF 150.00
AG-CP3-0031-M0055 mgCHF 600.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | NMU-25; FRVDEEFQSPFASQSRGYFLFRPRN-NH2 . TFA |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C141H203N41O38 . C2HF3O2 |
| MW | 3080.4 . 114.0 |
| Sequence |
H-Phe-Arg-Val-Asp-Glu-Glu-Phe-Gln-Ser-Pro-Phe-Ala-Ser-Gln-Ser-Arg-Gly-Tyr-Phe-Leu-Phe-Arg-Pro-Arg-Asn-amide |
| CAS | 312306-89-1 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Lyophilized powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Identity | Determined by MS. |
| InChi Key | SJLXOEXLOIEAIN-PJDLJQKUSA-N |
| Smiles | C[C@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H]1CCCN1C([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](N)CC2=CC=CC=C2)=O)CCCNC(N)=N)=O)C(C)C)=O)CC(O)=O)=O)CCC(O)=O)=O)CCC(O)=O)=O)CC3=CC=CC=C3)=O)CCC(N)=O)=O)CO)=O)=O)CC4=CC=CC=C4)=O)C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(NCC(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N5CCC[C@H]5C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N)=O)CC(N)=O)=O)CCCNC(N)=N)=O)=O)CCCNC(N)=N)=O)CC6=CC=CC=C6)=O)CC(C)C)=O)CC7=CC=CC=C7)=O)CC8=CC=C(O)C=C8)=O)=O)CCCNC(N)=N)=O)CO)=O)CCC(N)=O)=O)CO)=O.FC(F)(C(O)=O)F |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Active human form of NMU.
- Binds to two high affinity G-protein coupled receptors, NMUR1 and NMUR2, with NMUR1 predominantly expressed in the peripheral tissues and NMUR2 mainly expressed in the CNS.
- The activation of NMURs leads to intracellular signal transduction via calcium mobilization, phosphoinositide (or PI) signaling and the inhibition of cAMP production and therefore has diverse functions including contraction of smooth muscle, vasoconstriction, nociception, appetite and bone remodeling.
- Implicated in a number of physiological processes including the regulation of feeding, energy homeostasis and glycemic control and therefore used to target obesity and diabetes.
- Activator of innate lymphoid cells 2 (ILC2) during inflammation, as shown in studies in mice [6-8].
Product References
- Expression and vasoconstrictor function of anorexigenic peptides neuromedin U-25 and S in the human cardiovascular system: J.D. Mitchell, et al.; Cardiovasc. Res. 81, 353 (2009)
- Emerging pharmacology and physiology of neuromedin U and the structurally related peptide neuromedin S: J.D. Mitchell, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol. 158, 87 (2009) (Review)
- Peptides and their potential role in the treatment of diabetes and obesity: H.C. Greenwood, et al.; Rev. Diabet. Stud. 8, 355 (2011) (Review)
- Suppression of insulin production and secretion by a decretin hormone: R. W. Alfa, et al.; Cell Metab. 21, 323 (2015)
- Neuromedin U: a multifunctional neuropeptide with pleiotropic roles: V.G. Martinez & L. O'Driscoll; Clin. Chem. 61, 471 (2015) (Review)
- The neuropeptide neuromedin U stimulates innate lymphoid cells and type 2 inflammation: C.S.N. Klose, et al.; Nature 549, 282 (2017)
- The neuropeptide NMU amplifies ILC2-driven allergic lung inflammation: A. Wallrapp, et al.; Nature 549, 351 (2017)
- Neuronal regulation of type 2 innate lymphoid cells via neuromedin U: V. Cardoso, et al.; Nature 549, 277 (2017)





