Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
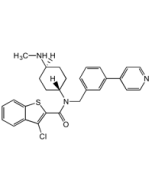
SAG . dihydrochloride (water soluble)
As low as
40
CHF
CHF 40.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3585-M0011 mgCHF 40.00
AG-CR1-3585-M0055 mgCHF 120.00
AG-CR1-3585-M02525 mgCHF 270.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 3-Chloro-N-[trans-4-(methylamino)cyclohexyl]-N-[3-(4-pyridinyl)benzyl]-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxamide . 2HCl |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C28H28ClN3OS . 2HCl . 3H2O |
| MW | 490.1 . 72.9 . 54.0 |
| CAS | 912545-86-9 and 364590-63-6 (both free base) |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Light yellow solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water or DMSO. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | IYXUQUYRWPGIQL-KOONDFAVSA-N |
| Smiles | O.CNC1CCC(CC1)N(CC1=CC(=CC=C1)C1=CC=NC=C1)C(=O)C1=C(Cl)C2=CC=CC=C2S1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. Store solutions at -20°C in the dark. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Cell permeable Sonic hedgehog (Shh) agonist.
- Cell permeable G-Protein-Coupled Receptor (GPCR) smoothened (Smo) agonist.
- Induces Sonic hedgehog (Shh) pathway activation and counteracts cyclopamine inhibition of Smo.
- Acts as an activator of Smo at low concentrations and as an inhibitor of Smo at very high concentrations.
- Potent activator of VEGF expression in vitro.
Product References
- Small-molecule modulators of Hedgehog signaling: identification and characterization of Smoothened agonists and antagonists: M. Frank-Kamenetsky, et al.; J. Biol. 1, 10 (2002)
- Small molecule modulation of Smoothened activity: J.K. Chen, et al.; PNAS 99, 14071 (2002)
- Activity-dependent internalization of smoothened mediated by beta-arrestin 2 and GRK2: W. Chen, et al.; Science 306, 2257 (2004)
- Smoothened Signal Transduction is Promoted by G-Protein Coupled Receptor Kinase 2: A.R. Meloni et al.; Mol. Cell Biol. 26, 7550 (2006)
- Oxysterols stimulate Sonic hedgehog signal transduction and proliferation of medulloblastoma cells: R.B. Corcoran & M.P. Scott; PNAS 103, 8408 (2006)
- Identification and characterization of Hedgehog modulator properties after functional coupling of Smoothened to G15: C. Masdeu, et al.; BBRC 349, 471 (2006)
- Wnt signaling stimulates transcriptional outcome of the Hedgehog pathway by stabilizing GLI1 mRNA: F.K. Noubissi, et al.; Cancer Res. 69, 8572 (2009)
- Evidence for allosteric interactions of antagonist binding to the smoothened receptor: C.M. Rominger, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 329, 995 (2009)
- Converse conformational control of smoothened activity by structurally related small molecules: H. Yang, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 284, 20876 (2009)
- Identification of a suppressive mechanism for Hedgehog signaling through a novel interaction of Gli with 14-3-3: Y. Asoaka, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 285, 4185 (2010)
- Smoothened agonist augments proliferation and survival of neural cells: O. Bragina, et al.; Neurosci. Lett. 482, 81 (2010)
- Subregional specification of embryonic stem cell-derived ventral telencephalic tissues by timed and combinatory treatment with extrinsic signals: T. Danjo, et al.; J. Neurosci. 31, 1919 (2011)
- Potent small molecule Hedgehog agonists induce VEGF expression in vitro: K. Seifert, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 20, 6465 (2012)
- Mitogen-activated kinase kinase kinase 1 inhibits hedgehog signaling and medulloblastoma growth through GLI1 phosphorylation: L. Antonucci, et al. Int. J. Oncol. 54, 505 (2018)
- Induction of the CD24 Surface Antigen in Primary Undifferentiated Human Adipose Progenitor Cells by the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway: F. Muoio, et al.; Biologics 1, 129 (2021)
- MAPK15 Controls Hedgehog Signaling in Medulloblastoma Cells by Regulating Primary Ciliogenesis: S. Pietrobono, et al.; Cancers 13, 4903 (2021)