Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
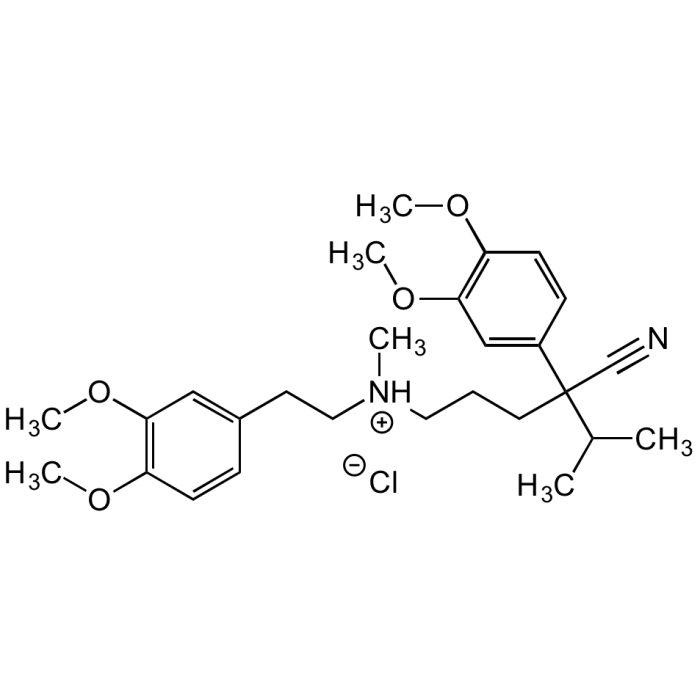
(±)-Verapamil . hydrochloride (USP Grade)
As low as
35
CHF
CHF 35.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3627-M100100 mgCHF 35.00
AG-CR1-3627-G0011 gCHF 45.00
AG-CR1-3627-G0055 gCHF 120.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | NSC135784; NSC272366; NSC657799 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C27H38N2O4 . HCl |
| MW | 454.6 . 36.5 |
| CAS | 152-11-4 |
| RTECS | YV8320000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥99% (NMR) |
| Appearance | White powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol (50 mg/ml), ethanol or water. |
| InChi Key | DOQPXTMNIUCOSY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | [Cl-].COC1=C(OC)C=C(CC[NH+](C)CCCC(C#N)(C(C)C)C2=CC(OC)=C(OC)C=C2)C=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- α1-Adrenergic receptor (α-AR) antagonist.
- Prototypical calcium channel protein inhibitor that blocks the L-type Ca2+ channels in smooth and cardiac muscle cells.
- Vasodilator known to reduce the renal clearance of digoxin and used to control hypertension, angina, cardiac arrhythmia and vascular headaches.
- Apoptosis inducer in primary and metastatic colon adenocarcinoma human cell lines in vitro.
- Inhibitor of drug efflux pump proteins such as Mdr (P-glycoprotein) which are often over-expressed in certain tumor cell lines.
- Substrate of CYP3A4 and CYP2C6.
- Used in fluorescent cell sorting for DNA content, as it blocks efflux of a variety of DNA-binding fluorophores such as Hoechst 33342.
- Anti-diabetic in animal models by limiting TXNIP expression.
Product References
- New antiarrhythmic agents: amiodarone, aprindine, disopyramide, ethmozin, mexiletine, tocainide, verapamil: D.P. Zipes & P.J. Troup; Am. J. Cardiol. 41, 1005 (1978) (Review)
- alpha-adrenergic antagonists as possible calcium channel inhibitors: D. Atlas & M. Adler; PNAS 78, 1237 (1981)
- Verapamil hydrochloride: pharmacological properties and role in cardiovascular therapeutics: S.H. Baky & B.N. Singh; Pharmacotherapy 2, 328 (1982) (Review)
- Verapamil: full spectrum calcium channel blocking agent: an overview: J.R. Guerrero & S.S. Martin; Med. Res. Rev. 4, 87 (1984) (Review)
- The calcium channel blocker verapamil and cancer chemotherapy: W.G. Simpson; Cell Calcium 6, 449 (1985) (Review)
- The mechanism of action of calcium antagonists relative to their clinical applications: B.N. Singh; Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 21, 109S (1986)
- Enhancement of the mutagenicity of anticancer drugs by the calcium antagonists verapamil and fendiline: W. Scheid, et al.; Arzneimittelforschung 41, 901 (1991) (Review)
- Apoptosis of human primary and metastatic colon adenocarcinoma cell lines in vitro induced by 5-fluorouracil, verapamil, and hyperthermia: I.B. Shchepotin, et al.; Anticancer Res. 14, 1027 (1994)
- Reversal of a novel multidrug resistance mechanism in human colon carcinoma cells by fumitremorgin C: S.K. Rabindran, et al.; Cancer Res. 58, 5850 (1998)
- Erythromycin and verapamil considerably increase serum simvastatin and simvastatin acid concentrations: T. Kantola, et al.; Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 64, 177 (1998)
- P-glycoprotein system as a determinant of drug interactions: the case of digoxin-verapamil: M. Verschraagen, et al.; Pharmacol. Res. 40, 301 (1999)
- Preventing β-cell loss and diabetes with calcium channel blockers: G. Xu, et al.; Diabetes 61, 848 (2012)






