Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
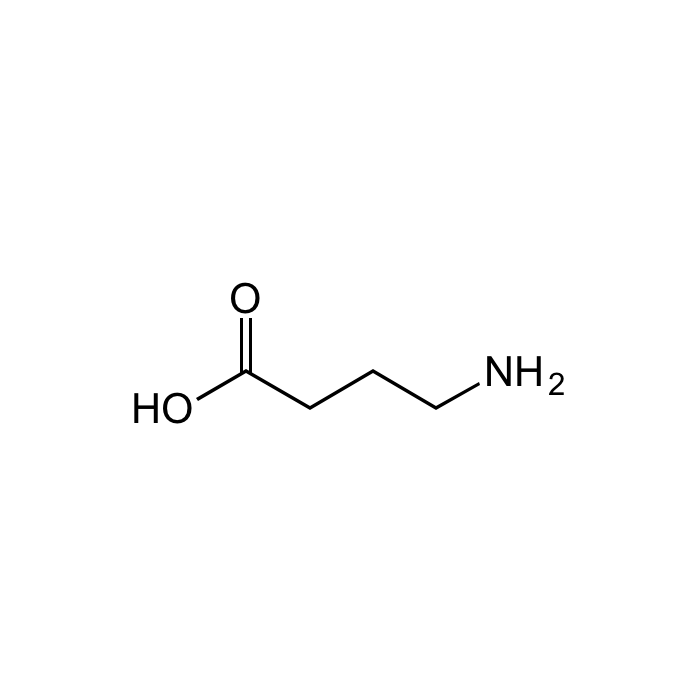
GABA [γ-Aminobutyric acid]
As low as
25
CHF
CHF 25.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3664-G0011 gCHF 25.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 4-Aminobutanoic acid; Piperidic acid; Piperidinic acid |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C4H9NO2 |
| MW | 103.12 |
| CAS | 56-12-2 |
| RTECS | ES6300000 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% |
| Appearance | White crystals or crystalline powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | BTCSSZJGUNDROE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | OC(CCCN)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Amino acid that functions as the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system and also functions as a neuromodulator in some peripheral tissues.
- GABAA and GABAB receptor agonist that increases Cl- conductance.
- GABA acts at inhibitory synapses in the brain by binding to specific transmembrane receptors in the plasma membrane of both pre- and postsynaptic neuronal processes. This binding causes the opening of ion channels to allow the flow of either negatively charged chloride ions into the cell or positively charged potassium ions out of the cell. This action results in a negative change in the transmembrane potential, usually causing hyperpolarization. GABAergic neurons are involved in myorelaxation, anxiolytic treatment, sedation and anaesthetics.
- GABA can also influence heart rate and blood pressure and function as a immunomodulator.
- GABA signaling stimulates α-cell-mediated β-like cell neogenesis. GABA induced insulin-producing β-like cell neogenesis.
Product References
- GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid), a non-protein amino acid counters the β-adrenergic cascade-activated oncogenic signaling in pancreatic cancer: a review of experimental evidence: H.A. Al-Wadei, et al.; Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 55, 1745 (2011)
- GABA is an effective immunomodulatory molecule: Z. Jin, et al.; Amino Acids 45, 87 (2013)
- Anion transport and GABA signaling: C.A. Huebner & K. Holthoff; Front. Cell Neurosci. 7, 177 (2013) (Review)
- Inhibiting neuroinflammation: The role and therapeutic potential of GABA in neuro-immune interactions: T. Crowley, et al.; Brain Behav. Immun. 54, 260 (2016)
- Mechanisms and functions of GABA co-release: N.X. Tritsch, et al.; Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 17, 139 (2016) (Review)
- The Neuro-endocrinological Role of Microbial Glutamate and GABA Signaling: R. Mazzoli & E. Pessione; Front. Microbiol. 7, 1934 (2016) (Review)
- Long-Term GABA Administration Induces Alpha Cell-Mediated Beta-like Cell Neogenesis: N. Ben-Othman, et al.; Cell 168, 73 (2017)
- GABA Signaling Stimulates β Cell Regeneration in Diabetic Mice: G.C. Weir & S. Bonner-Weir; Cell 168, 7 (2017)