Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
BioViotica
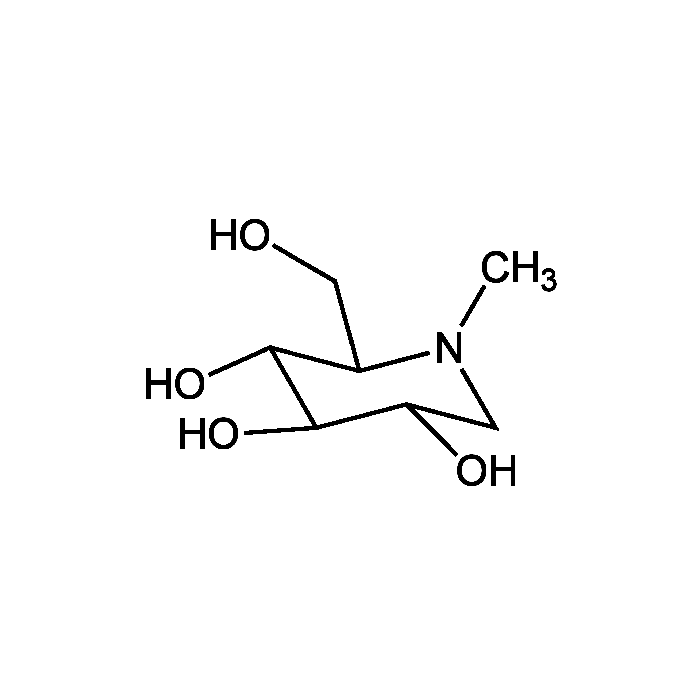
N-Methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin
As low as
115
CHF
CHF 115.00
In stock
Only %1 left
BVT-0130-M0011 mgCHF 115.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | N-Methyl-dNM; N-Methylmoranoline; MOR-14; 1,5-Dideoxy-1,5-(methylimino)-D-glucitol |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C7H15NO4 |
| MW | 177.2 |
| CAS | 69567-10-8 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Streptomyces sp. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC, 1H-NMR) |
| Appearance | White solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by BioViotica. |
| InChi Key | AAKDPDFZMNYDLR-XZBKPIIZSA-N |
| Smiles | CN1C[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1CO |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light when in solution. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- α-Glucosidase inhibitor.
- Glucosidase I inhibitor (IC50=0.3μM), 10-fold more potent over 1-Deoxynojirimycin (dNM).
- Inhibitor of glycoprotein processing.
- Strong glycosyltransferase (GTF) inhibitor.
- Angiogenesis inhibitor.
- Reduces the size of myocardial infarcts.
Product References
- N-methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin, a novel inhibitor of glycoprotein processing, and its effect on fowl plague virus maturation: P.A. Romero, et al.; Virology 130, 238 (1983)
- Effect of N-methyl-1-deoxy-nojirimycin on the degradation of cellobiose by Cellulomonas cartalyticum: H. Sahm, et al.; Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 20, 54 (1984)
- Purification by affinity chromatography of glucosidase 1, an endoplasmic reticulum hydrolase involved in the processing of asparagine-linked oligasaccharides: H. Hettkamp, et al.; Eur. J. Biochem. 142, 85 (1984)
- Comparison between 1-deoxynojirimycin and N-methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin as inhibitors of oligosaccharide processing in intestinal epithelial cells: P.A. Romero, et al.; Biochem. J. 226, 733 (1985)
- Different effects of glucosidase inhibitors 1-deoxynojirimycin, N-methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin and castanospermine on the glycosylation of rat alpha1-proteinase inhibitor and α1-acid glycoprotein: V. Gross, et al.; Biochem. J. 236, 853 (1986)
- Inhibition of myoblast fusion by the glucosidase inhibitor N-methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin, but not by the mannosidase inhibitor 1-deoxymannojirimycin: P.C. Holland, et al.; Biochem. J. 238, 335 (1986)
- The glycoprotein-processing inhibitors bromoconduritol and N-methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin alter the adhesion phenotype of skeletal myoblasts: G.C. Trudel, et al.; Biochem. Cell Biol. 68, 1411 (1990)
- Glucosidase I, a transmembrane endoplasmic reticular glycoprotein with a luminal catalytic domain: K. Shailubhai, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 266, 16587 (1991)
- Subsite specificity of the active site of glucosyltransferases from Streptococcus sobrinus: K.S. Devulapalle & G. Mooser; J. Biol. Chem. 269, 11967 (1994)
- N-methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin (MOR-14), an α-glucosidase inhibitor, markedly reduced infarct size in rabbit hearts: M. Arai, et al.; Circ. Res. 97, 1290 (1998)
- N-methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin (MOR-14), an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, markedly improves postischemic left ventricular dysfunction: Y. Nishida, et al.; Heart Vessels 15, 268 (2000)
- Combination of N-methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin and ischemic preconditioning markedly reduces the size of myocardial infarcts in rabbits: D.-J. Wu, et al.; Circ. J. 65, 673 (2001)
- Role of protein kinase C in the reduction of infarct size by N-methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin, an α-1,6-glucosidase inhibitor: M. Arai, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol. 135, 635 (2001)
- Biological study of the angiogenesis inhibitor N-(8-(3-ethynylphenoxy)octyl-1-deoxynojirimycin: Y. Zhao, et al.; Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 75, 570 (2010)





