Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
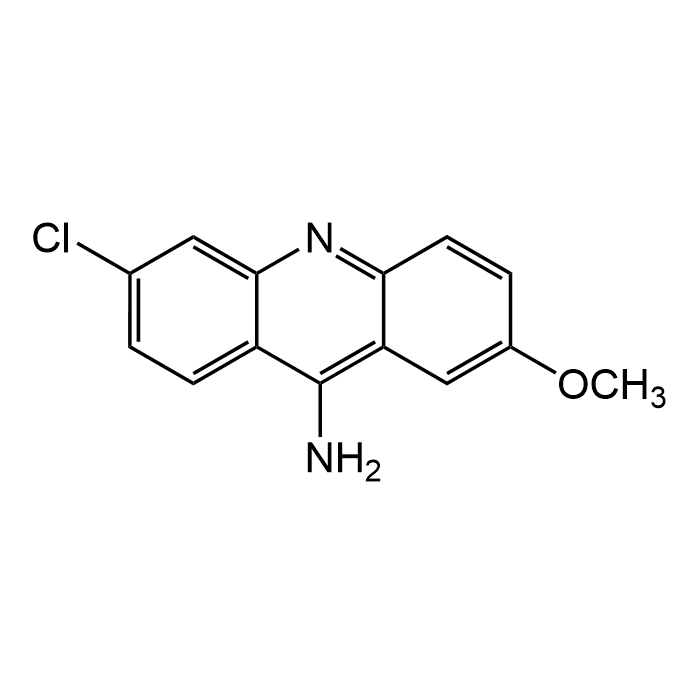
9-Amino-6-chloro-2-methoxyacridine
As low as
258
CHF
CHF 258.00
In stock
Only %1 left
CDX-A0099-M02525 mgCHF 258.00
CDX-A0099-M05050 mgCHF 451.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | ACMA; 2-Methoxy-6-chloro-9-aminoacridine; 9-Amino-3-chloro-7-methoxyacridine; G 185; NSC 15300 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C14H11ClN2O |
| MW | 258.7 |
| CAS | 3548-09-2 |
| RTECS | AR7330000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Yellow to orange powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, DMF or methanol (1mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | IHHSSHCBRVYGJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | ClC1=CC=C(C(N)=C(C=C(OC)C=C2)C2=N3)C3=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
9-Amino-6-chloro-2-methoxyacridine (ACMA) is a cell-permeable ph-sensitive fluorescent probe that intercalates into DNA. It selectively binds to poly(dA-dT) sequences with the fluorescence lifetime decreasing with incorporation of guanosine. It is used for nucleic acid staining/labeling. ACMA fluorescence is pH-dependent and is quenched when a pH gradient is established. Spectral Data: λex 411nm; λem 475nm (in methanol). Excitation of the ACMA-DNA complex (excitation/emission maxima λ419/483 nm) is possible with most UV-light sources, making it compatible for use with both shorter- and longer-wavelength dyes. ACMA also apparently binds to membranes in the energized state and becomes quenched if a pH gradient forms. It has been extensively employed to follow cation and anion movement across membranes and to study the proton-pumping activity of various membrane-bound ATPases. ACMA also inhibits acetylcholinesterase.
Product References
(1) C. Helene, et al.; Biochem. Soc. Trans. 14, 201 (1986) | (2) T. Hard, et al.; J. Phys. Chem. 93, 4338 (1989) | (3) H. Rottenberg & R. Moreno-Sanchez; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1183, 161 (1993) | (4) S.D. Watts & R.A. Capaldi; J. Biol. Chem. 272, 15065 (1997) | (5) K. Fukui, et al.; J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 50, 18 (1999) | (6) S. Bencharit, et al.; Chem. Biol. 10, 341 (2003) | (7) I. Carqueijeiro, et al.; Methods Mol. Biol. 1405, 121 (2016) | (8) P. Uzdavinys, et al.; PNAS 114, E1101 (2017)





