Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
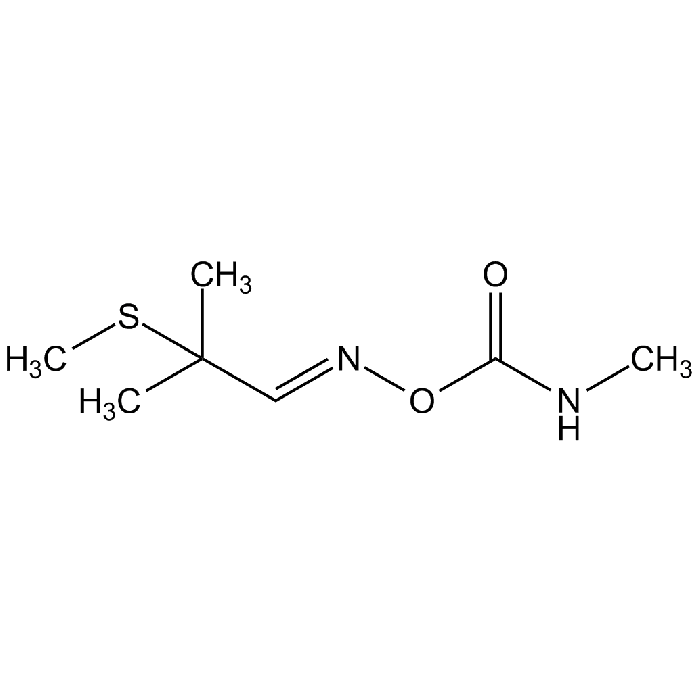
Aldicarb
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | O-(Methylcarbamoyl)-2-methyl-2-(methylthio)propionaldehyd-oxime; NSC 379586; UC-21149; Temik |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C7H14N2O2S |
| MW | 190.26 |
| CAS | 116-06-3 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥99% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Off-white to yellow solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water (6mg/ml) or most organic solvents. |
| Identity | Determined by NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | QGLZXHRNAYXIBU-WEVVVXLNSA-N |
| Smiles | CNC(=O)O\N=C\C(C)(C)SC |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Carbamate pesticide that reversibly inhibits acetylcholinesterase, causing rapid accumulation of acetylcholine at the synaptic cleft. Used as a pesticide and as fast-acting acetylcholinesterase inhibitor for research purposes to study cholinergic neurotransmission in simple systems such as the nematode C. elegans. It is the active ingredient in mixtures used to control insect, mite, and nematode pests in agriculture. Aldicarb has a high acute mammalian toxicity (LD50 = 0.3-0.5 mg/kg) following oral or parenteral administration. Compound can be used as analytical reference material.
(1) J.F. Risher, et al.; Environ. Health Perspect. 72, 267 (1987) | (2) M.G. Cid & E. Matos; Mutat. Res. 191, 99 (1987) | (3) P. Thomas, et al.; Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 15, 221 (1990) | (4) R.L. Baron; Environ. Health Perspect. 102, 23 (1994) | (5) E. Maran, et al.; Food Chem. Toxicol. 48, 1592 (2010) | (6) S. Suo, & S. Ishiura; PLoS One 8, e72578 (2013) | (7) R.V. Shamagsumova, et al.; Talanta 144, 559 (2015) | (8) R.N. Plagens, et al.; BMC Biol. 19, 75 (2021)