Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
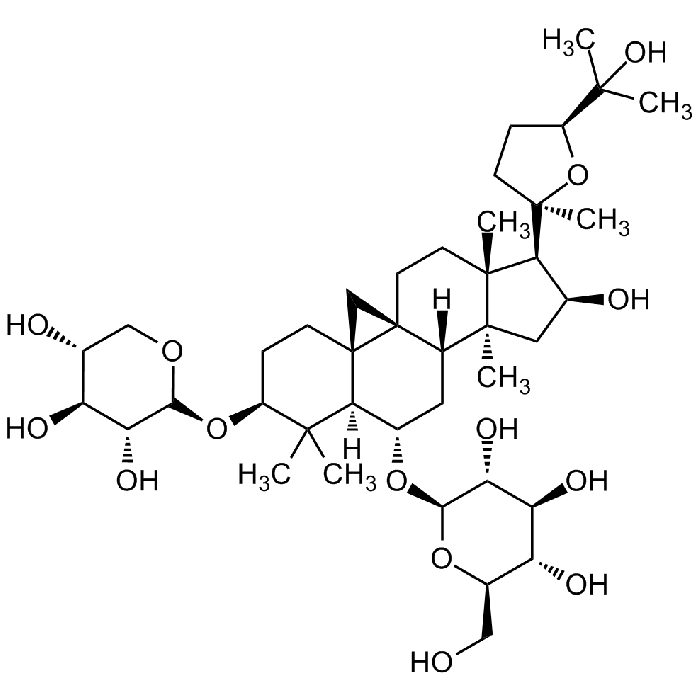
Astragaloside IV
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | AS-IV; AST-IV; Astrasieversianin XIV; Cyclosieversioside F; Cyclosiversioside F; Astramembrannin I; Astragaloside A |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C41H68O14 |
| MW | 784.98 |
| CAS | 84687-43-4 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Plant |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (30mg/ml) or DMF (20mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | QMNWISYXSJWHRY-RXMVGYINSA-N |
| Smiles | O[C@H]1C[C@@]2(C)[C@]3([H])C[C@H](O[C@@H]4O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]4O)[C@@]5([H])C(C)(C)[C@@H](O[C@H]6OC[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]6O)CC[C@]57[C@]3(C7)CC[C@]2(C)[C@H]1[C@]8(C)O[C@H](C(C)(O)C)CC8 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) is a bioactive saponin and constituent of the traditional chinese medicine plant Astragali radix. AS-IV has multiple pharmacologic effects, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, anti-asthma, antidiabetes, anticancer, immunoregulation, neuroprotective and cardioprotective properties via numerous signaling pathways. This includes inhibition of NF-κB, inducing hypoxia-inducible factor-1α accumulation via PI3K/Akt pathway, reducing Aβ production in Alzheimer's disease through inhibition of BACE1, working as a natural PPARγ agonist, improving lipid metabolism in obese mice, enhancing chemosensitivity through CD276 (B7-H3)-pathway inhibition, and suppressing glucose-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
(1) Y.P. Wang, et al.; Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 23, 263 (2002) | (2) W.J. Zhang, et al.; Thromb. Haemost. 90, 904 (2003) | (3) M.E. Xu, et al.; Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 27, 229 (2006) | (4) W.S. Chan, et al.; Neurochem. Int. 55, 414 (2009) | (5) L. Zhang, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 338, 485 (2011) | (6) X. Chen, et al.; J. Ethnopharmacol. 139, 721 (2012) | (7) D. Gui, et al.; PLoS One 7, e39824 (2012) | (8) S. Ren, et al.; J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 33, 413 (2013) (Review) | (9) H. Wu, et al.; Sci. Rep. 6, 30190 (2016) | (10) C.S. He, et al.; Cell Physiol. Biochem. 40, 1221 (2016) | (11) X. Wang, et al.; Mol. Neurobiol. 54, 2939 (2017) | (12) L. Li, et al.; Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 31, 17 (2017) (Review) | (13) L. Xia, et al.; Exp. Ther. Med. 14, 5569 (2017) | (14) P. Sun, et al.; Front. Biosci. 24, 597 (2019) | (15) B. Leng, et al.; Mediators Inflamm. 2019, 1082497 (2019) | (16) Z. Zhang, et al.; Mol. Med. Rep. 20, 4612 (2019)





