Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
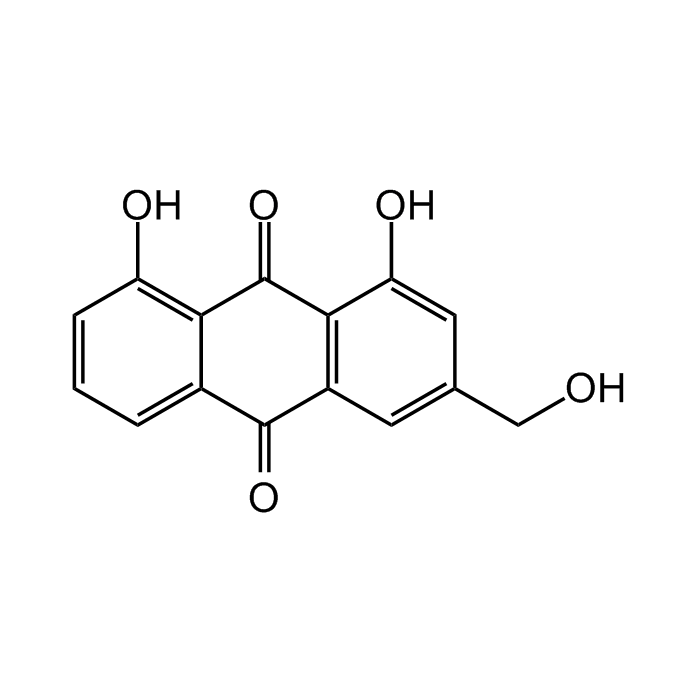
Aloe-Emodine
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 1,8-Dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)anthraquinone; 3-Hydroxymethylchrysazine; Rhabarberone; Diacerein Impurity B; NSC 38628 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C15H10O5 |
| MW | 270.24 |
| CAS | 481-72-1 |
| RTECS | CB6712200 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Plant |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Yellow to orange powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (2mg/ml) or DMF (5mg/ml). Insoluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | YDQWDHRMZQUTBA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | OC1=C2C(C(C(C=C(CO)C=C3O)=C3C2=O)=O)=CC=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Aloe-emodin is a naturally anthraquinone derivative and an active ingredient of Aloe vera leaves and other plants. Aloe-emodin has been shown to exhibit many pharmacological effects, including anticancer, antivirus, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiparasitic, neuroprotective, and hepatoprotective activities. It has potent laxative action by activating CFTR Cl- channels and inducing chloride secretion in colonic mucosa and releasing acetylcholine, which stimulates contraction of intestinal smooth muscle. It also demonstrates anti-tumor activity, inducing apoptosis in various cancer cells by increasing the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and induces apoptosis in glioma models through disruption of the mitochondria membrane potential. Aloe-emodin is reported to have estrogenic activity as a phytoestrogen, has been shown to inhibit breast cancer cell proliferation by downregulating ERα protein levels, and neuroprotective effects in vivo.
(1) T. Pecere, et al.; Cancer Res. 60, 2800 (2000) | (2) H. Matsuda, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 11, 1839 (2001) | (3) G. Srinivas, et al.; Med. Res. Rev. 27, 591 (2007) (Review) | (4) H. Yang, et al.; Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 32, 834 (2011) | (5) K. Liu, et al.; Carcinogenesis 33, 1406 (2012) | (6) J. Xu, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol. 165, 197 (2012) | (7) P.H. Huang, et al.; Evid. Based Compl. Alternat. Med. 2013, 1 (2013) | (8) S. Ismail, et al.; J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 15, 1003 (2013) | (9) M.J. Xie, et al.; Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 15, 5201 (2014) | (10) L. Tao, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 24, 5385 (2014) | (11) R. Chen, et al.; Am. J. Chin. Med. 42, 275 (2014) (Review) | (12) X. Dong, et al.; Phytother. Res. [Epub ahead of print] (2019) (Review)





