Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
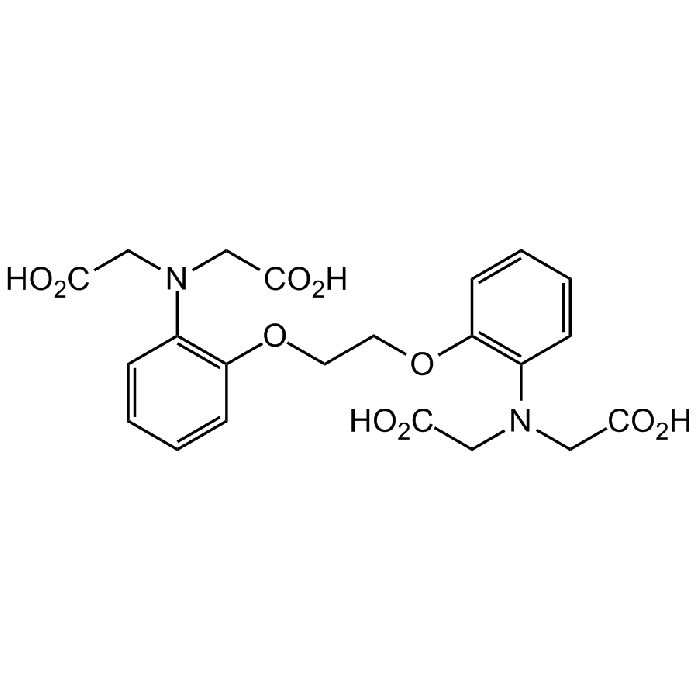
BAPTA (free acid)
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 1,2-Bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C22H24N2O10 |
| MW | 476.4 |
| CAS | 85233-19-8 |
| RTECS | MC0423000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml) or DMF (20mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | FTEDXVNDVHYDQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C(O)CN(CC(O)=O)C1=C(OCCOC2=C(N(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O)C=CC=C2)C=CC=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
BAPTA is a membrane-impermeable highly selective calcium chelator and is useful for manipulating extracellular Ca2+ levels, with 105-fold greater affinity for Ca2+ than for Mg2+. The presence of four carboxylic acid functional groups allows for the binding of two calcium ions. BAPTA and its derivatives can be used as calcium indicators, since the absorption maximum for BAPTA changes when it is complexed with calcium (absorption maxima free/complexed = 254/274 nm, emission maxima free/complexed = 363/363 nm). Key advantages of BAPTA include relative insensitivity toward intracellular pH change and fast release of calcium. This product is a high quality and sensitive compound for calcium signaling studies, investigation of signal transduction, apoptotic cascades and neuroscience research.
(1) R.Y. Tsien, et al.; Biochemistry. 19, 2396 (1980) | (2) R.Y. Tsien, et al.; Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 12, 91 (1983) | (3) G. Grynkiewicz, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 260, 3440 (1985) | (4) H. Kijima, et al.; J. Physiol. 403, 135 (1988) | (5) N. Tanabe, et al.; Neurosci. Lett. 92, 52 (1988) | (6) R.C. Hardie; Cell Calcium. 38, 547 (2005) | (7) R.W. Sabnis; Handbook of biological dyes and stains (2010)





