Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
Biocytine
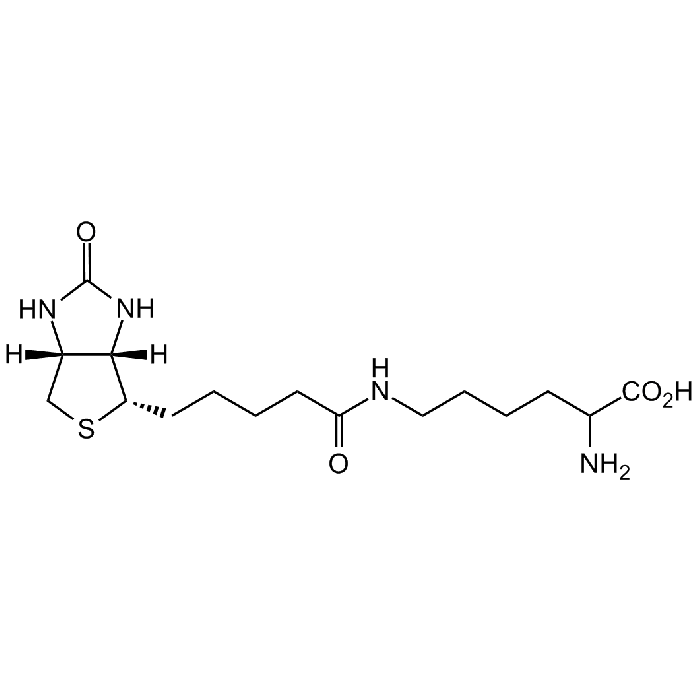
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Bct; Nε-(+)-Biotinyl-L-lysine; ε-N-(d-Biotinyl)-L-lysine; |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C16H28N4O4S |
| MW | 372.48 |
| CAS | 576-19-2 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (NMR) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in PBS or water (20 mg/ml). We do not recommend to store aqueous solutions for more than one day. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | BAQMYDQNMFBZNA-WBGPXRNDSA-N |
| Smiles | [H][C@]12CS[C@@H](CCCCC(NCCCCC(N)C(O)=O)=O)[C@@]1([H])NC(N2)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | -20°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Biocytin is a conjugate of biotin and lysine known formally as ε-N-(d-biotinyl)-L-lysine. The addition of lysine to biotin increases the chain length extending from biotin, allowing the synthesis of medium-chain reagents. It also provides terminal carboxyl and amino groups for derivatization or conjugation to proteins and other molecules. Covalent linking reactions typically involve carbodiimide or NHS-ester crosslinking chemistries. Biocytin is also used as an anterograde, retrograde, or intracellular neuroanatomical tracer that is fixable with aldehyde-based fixatives. It is also used in biotinidase assays. Biocytin may be injected into brain by iontophoresis or by pressure injection methods, and localized in tissue sections using avidin-conjugated labels.
(1) M. Bodanszky & D.T. Fagan; JACS 99, 235 (1977) | (2) E. Friauf, et al.; J. Neurosci. 10, 2601 (1990) | (3) X.J. Sun, et al.; J. Histochem. Cytochem. 46, 263 (1998) | (4) A. Erisir & C. Aoki; J. Neurosci. Methods 81, 189 (1998) | (5) C. Koebbert, et al; Prog. Neurobiol. 62, 327 (2000) | (6) S.L. Chang, et al.; J. Neurosci. Methods 97, 1 (2000) | (7) K. Kumasaka, et al.; Clin. Chim. Acta 306, 71 (2001) | (8) Y. Morozov, et al.; J. Neurosci. Methods 117, 81 (2002) | (9) G. Roth, et al.; J. Comp. Neurol. 478, 35 (2004) | (10) H.G. Xue, et al.; Brain Res. Brain Res. Protoc. 13, 106 (2004) | (11) M.A. MacNeil & P.A. Gaul; J. Comp. Neurol. 506, 6 (2008) | (12) R. Bopp, et al.; PLoS Biol. 12, 1 (2014)





